Summary
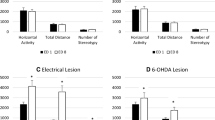
6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA; 200 μg, 150 μg or 110 μg) or vehicle was infused stereotaxically into the lateral ventricles of rats, usually following pretreatment with desmethylimipramine (DMI). Various brain regions were then assayed for dopamine (DA), serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine (NE). As expected, 6-OHDA depleted DA in all brain regions examined. Unexpectedly, however, the two highest doses of 6-OHDA significantly decreased 5-HT levels in the hippocampus and increased 5-HT levels in the striatum. In addition, despite pretreatment with doses of DMI commonly considered adequate to block 6-OHDA-induced depletion of NE, all doses of 6-OHDA tested significantly reduced NE levels in the hippocampus, hypothalamus and septum.
We interpret our data as suggesting that some brain regions are susceptible to nonspecific toxic effects of 6-OHDA at doses commonly employed. Furthermore, these nonspecific effects may or may not occur, depending on seemingly minor variations in experimental technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartholini G, Richards JG, Pletscher A (1970) Dissociation between biochemical and ultrastructural effects of 6-hydroxydopamine in rat brain. Experientia 26: 142–144
Bloom FE, Algeri S, Gropetti A, Revuelta A, Costa E (1969) Lesions of central norepinephrine terminals with 6-OH-dopamine: biochemistry and fine structure. Science 166: 1284–1286
Breese GR, Traylor T (1970) Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on brain norepinephrine and dopamine: evidence for selective degeneration of catecholamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 174: 413–420
Breese GR, Traylor TD (1971) Depletion of brain noradrenaline and dopamine by 6-hydroxydopamine. Br J Pharmacol 42: 88–99
Breese GR, Baumeister AA, McGown TJ, Emerick SG, Frye GD, Crotty K, Mueller RA (1984) Behavioral differences between neonatal and adult 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats to dopamine agonists: relevance to neurological symptoms in clinical syndromes with reduced brain dopamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 231: 343–354
Constantinidis J, Geissbuhler F, Tissot R (1971) Histochemical study on the effect of intraventricular administration of 6-hydroxydopamine on monoamine-containing neurons in the CNS. In: Malforms T. Thoenen H (eds) 6-Hydroxydopamine and catecholamine neurons. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 129–134
Erinoff L, MacPhail RC, Heller A, Seiden LS (1979) Age-dependent effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on locomotor activity in the rat. Brain Res 164: 195–205
Fenn RJ, Siggia S, Curran DJ (1978) Liquid chromatography detector based on single and twin electrode thin-layer electrochemistry: application to the determination of catecholamines in blood plasma. Anal Chem 50: 1067–1072
Fuller RW (1981) Enhancement of monoaminergic neurotransmission by antidepressant drugs. In: Enna SJ, Malick JB, Richelson E (eds) Antidepressants: neurochemical, behavioral and clinical perspectives. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–12
Gershanik OS, Heikkila RE, Duvoisin RC (1979) Asymmetric action of intraventricular monoamine neurotoxins. Brain Res 174: 345–350
Hedreen JC, Chalmers JP (1972) Neuronal degeneration in rat brain induced by 6-hydroxydopamine: a histological and biochemical study. Brain Res 47: 1–26
Heffner TG, Hartman JA, Seiden LS (1980) A rapid method for the regional dissection of the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13: 453–456
Ings R, Pappas B (1981) Neonatal intraspinal 6-hydroxydopamine: depletion of norepinephrine but not dopamine. Eur J Pharmacol 70: 577–583
Jacks BR, de Champlain J, Cordeau JP (1972) Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on putative transmitter substances in the central nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol 18: 353–360
Jonsson, G (1980) Chemical neurotoxins as denervation tools in neurobiology. Ann Rev Neurosci 3: 169–187
Keller R, Oke A, Mefford I, Adams RN (1976) Liquid chromatographic analysis of catecholamines: routine assay for regional brain mapping. Life Sci 19: 995–1004
Kostrzewa RM, Jacobowitz DM (1974) Pharmacological actions of 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmacol Rev 26: 199–288
Kotake C, Heffner T, Vosmer G, Seiden LS (1985) Determination of dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and their major metabolic products in rat brain by reverse-phase ion-pair high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22: 85–89
Lucot JB, Horwitz J, Seiden LS (1981) The effects of p-chloramphetamine administration on locomotor activity and serotonin in neonatal and adult rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 217: 738–744
Lungdahl A, Hokfelt T, Jonsson G, Sachs CH (1971) Autoradiographic demonstration of uptake and accumulation of3H-6-hydroxydopamine in adrenergic nerves. Experentia 27: 297–299
Mason ST (1984) Catecholamines and behaviour. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
de Montigny C, Wang RY, Reader TA, Aghajanian GK (1980) Monoaminergic denervation of the rat hippocampus: microiontophoretic studies on pre-and postsynaptic supersensitivity to norepinephrine and serotonin. Brain Res 200: 363–376
Reader TA, Gauthier P (1984) Catecholamines and serotonin in the rat central nervous system after 6-OHDA, 5,7-DHT and p-CPA. J Neural Transm 59: 207–227
Stachowiak MK, Bruno JP, Snyder AM, Stricker EM, Zigmond MJ (1984) Apparent sprouting of striatal serotonergic terminals after dopamine-depleting brain lesions in neonatal rats. Brain Res 291: 164–167
Tranzer JP, Thoenen H (1967) Ultra-morphologische Veränderungen der sympathischen Nervendigunden der Katze nach Vorbehandlung mit 5-und 6-hydroxy-dopamin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol Exp Pathol 257: 343–344
Tranzer JP, Thoenen H (1968) An electron microscopic study of selective acute degeneration of sympathetic nerve terminals after administration of 6-hydroxydopamine. Experientia 24: 155–156
Ungerstedt U (1971) Histochemical studies on the effect of intracerebral and intraventricular injections of 6-hydroxydopamine on monoamine neurons in the rat brain. In: Malmfors T, Thoenen H (eds) 6-Hydroxydopamine and catecholamine neurons. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 101–128
Uretsky NJ, Iversen LL (1969) Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on noradrenaline-containing neurons in the rat brain. Nature 221: 557–559
Uretsky NJ, Iversen LL (1970) Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on catecholamine containing neurons in the rat brain. J Neurochem 17: 269–278
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Zar JH (1984) Biostatistical analysis, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Commins, D.L., Shaughnessy, R.A., Axt, K.J. et al. Variability among brain regions in the specificity of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced lesions. J. Neural Transmission 77, 197–210 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01248932
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01248932