Summary
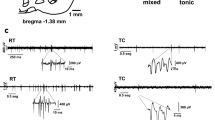
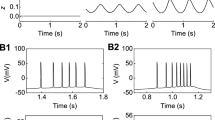
Electrical stimulation of the prefrontal cortex produces an inhibition-excitation (IE) activity pattern in the majority of responsive midbrain dopaminergic neurons. The excitatory phase often contains events, time-locked to the stimulation, which resemble natural bursts. The present study investigated the relationship between the inhibition and time-locked bursts by reducing the impact of the inhibition through membrane hyperpolarisation with the dopamine agonist apomorphine (i.v.) or antagonism with the GABAA antagonist picrotoxin (i.v. and iontophoretic). Apomorphine abolished or reduced time-locked bursting in all IE cells. Picrotoxin reduced the initial inhibition in the majority of IE cells, and abolished or reduced time-locked bursting at the highest intravenous dose. However, reductions in the initial inhibition were not systematically related to reductions in time-locked bursting. Hence, the phenomena do not appear to be causally related. Instead, time-locked bursts appear to be based on a straightforward excitation, which makes them closely analogous to natural bursts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckstead RM (1979) An autoradiographic examination of corticocortical and subcortical projections of the rat mediodorsal-prejection (prefrontal) cortex in the rat. J Comp Neurol 184: 43–62
Bolam JP, Smith Y (1990) The GABA and substance P input to dopaminergic neurones in the substantia nigra of the rat. Brain Res 529: 57–78
Chergui K, Charlety PJ, Akaola H, Saunier CF, Brunet JL, Buda M, Svensson TH, Chouvet G (1993) Tonic activation of NMDA receptors causes spontaneous burst discharge of rat midbrain dopamine neuronsin vivo. Eur J Neurosci 5: 137–144
Clark D, Chiodo LA (1988) Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterisation of identified nigrostriatal and mesoaccumbens dopamine neurons in the rat. Synapse 2: 474–485
Coombs JS, Eccles JC, Fatt P (1955) Excitatory synaptic action in motoneurons. J Physiol 130: 374–395
Deschênes M, Roy JP, Steriade M (1982) Thalamic bursting mechanism: an inward slow current revealed by membrane hyperpolarisation. Brain Res 239: 289–293
Freeman AS, Meltzer LT, Bunney BS (1985) Firing properties of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons in freely moving rats. Life Sci 36: 1983–1994
Futami T, Takakusaki K, Kitai ST (1995) Glutamatergic and cholinergic inputs from the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus to dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. Neurosci Res 21: 331–342
Gariano RF, Groves PM (1988) Burst firing in midbrain dopamine neurons by stimulation of the medial prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortices. Brain Res 462: 194–198
Gonon FG (1988) Nonlinear relationship between impulse flow and dopamine released by rat midbrain neurons as studied byin vivo electrochemistry. Neuroscience 24: 19–28
Grace AA, Bunney BS (1983) Intracellular and extracellular electrophysiology of nigral dopaminergic neurons. 1. Identification and characterisation. Neuroscience 10: 301–315
Grace AA, Bunney BS (1984a) The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: Single spike firing. J Neurosci 4: 2866–2876
Grace AA, Bunney BS (1984b) The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: burst firing. J Neurosci 4: 2877–2890
Grace AA, Bunney BS (1985) Opposing effects of striatonigral feedback pathways on midbrain dopamine cell activity. Brain Res 333: 271–284
Grace AA, Onn S-P (1989) Morphology and electrophysiological properties of immunocytochemically identified rat dopamine neurons recordedin vitro. J Neurosci 9: 3463–3481
Grenhoff J, Ugedo L, Svensson TH (1988) Firing patterns of midbrain dopamine neurons: differences between A9 and A10. Acta Physiol Scand 134: 127–132
Hajós M, Greenfield SA (1993) Topographic heterogeneity of substantia nigra neurons: diversity in intrinsic membrane properties and synaptic inputs. Neuroscience 55: 919–934
Hajós M, Greenfield SA (1994) Synaptic connections between pars compacta and pars reticulata neurones: electrophysiological evidence for functional modules within the substantia nigra. Brain Res 660: 216–224
Häusser MA, Yung WH (1994) Inhibitory synaptic potentials in guinea-pig substantia nigra dopamine neuronesin vitro. J Physiol 479: 401–422
Heimer L, Zahm DS, Churchill L, Kalivas PW, Wohltmann C (1991) Specificity in the projection patterns of accumbal core and shell in rat. Neuroscience 41: 89–125
Ip NY, Zigmond RE (1984) Pattern of presynaptic nerve activity can determine the type of neurotransmitter regulating a postsynaptic event. Nature 311: 472–474
Johnson SW, North RA (1992) Two types of neurone the rat ventral tegmental area and their synaptic inputs. J Physiol 450: 455–468
Jones DL, Mogenson GJ (1980) Nucleus accumbens to globus pallidus GABA projection: electrophysiological and iontophoretic investigations. Brain Res 188: 93–105
Kang Y, Kitai ST (1993a) Calcium spike underlying rhythmic firing in dopaminergic neurons of the rat substantia nigra. Neurosci Res 18: 195–207
Kang Y, Kitai ST (1993b) A whole cell patch-clamp study on the pacemaker potential in dopaminergic neurons of rat substantia nigra compacta. Neurosci Res 18: 209–221
Llinas R, Yarom Y (1981a) Electrophysiology of mammalian inferior olivary neuronesin vitro. Different types of voltage dependent ionic conductances. J Physiol 315: 549–567
Llinas R, Yarom Y (1981b) Properties and distribution of ionic conductances generating electroresponsiveness of mammalian inferior olivary neuronsin vitro. J Physiol 315: 569–584
Murase S, Grenhoff J, Chouvet G, Gonon FG, Svensson TH (1993) Prefrontal cortex regulates burst firing and transmitter release in rat mesolimbic dopamine neurons studied in vivo. Neurosci Lett 157: 53–56
Nakamura S, Iwatsubo K, Tsai C-T, Iwama K (1979) Cortically induced inhibition of neurons in the rat substantia nigra (pars compacta). Jpn J Physiol 29: 353–357
Overton P, Clark D (1992) Iontophoretically administered drugs acting at theN-methyl-D-aspartate receptor modulate burst firing in A9 dopamine neurons in the rat. Synapse 10: 131–140
Overton PG, Greenfield SA (1995) Determinants of neuronal firing pattern in the guineapig subthalamic nucleus: an in vivo andin vitro comparison. J Neural Transm [P-D Sect] 10: 41–54
Pinnock RD (1983) Sensitivity of compacta neurones in the rat substantia nigra slice to dopamine agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 96: 269–276
Sesack SR, Pickel VM (1992) Prefrontal cortical efferents in the rat synapse on unlabelled neuronal targets of catecholamine terminals in the nucleus accumbens septi and on dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area. J Comp Neurol 320: 145–160
Seutin V, Verbanck P, Massotte L, Dresse A (1990) Evidence for the presence ofN-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the ventral tegmental area of the rat: an electrophysiologicalin vitro study. Brain Res 514: 147–150
Silva NL, Bunney BS (1988) Intracellular studies of dopamine neurons in vitro: pacemakers modulated by dopamine. Eur J Pharmacol 149: 307–315
Somogyi P, Smith AD (1979) Projection of neostriatal spiny neurons to the substantia nigra. Application of a combined Golgi-staining and horseradish peroxidase transport procedure at both light and electron microscopic levels. Brain Res 178: 3–15
Somogyi P, Bolam JP, Totterdell S, Smith AD (1981) Monosynaptic input from nucleus accumbens-ventral striatal region to retrogradely labelled nigrostriatal neurons. Brain Res 217: 245–263
Sugita S, Johnson SW, North RA (1992) Synaptic inputs to GABAA and GABAB receptors originate from discrete afferent neurons. Neurosci Lett 134: 207–211
Svensson TH, Tung C-S (1989) Local cooling of the prefrontal cortex induces pacemakerlike firing of dopamine neurons in rat ventral tegmental areain vivo. Acta Physiol Scand 136: 135–136
Tepper JM, Martin LP, Anderson DR (1995) GABAA receptor mediated inhibition of rat substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons by pars reticulata projection neurons. J Neurosci 15: 3092–3103
Tong Z-Y, Overton PG, Clark D (1995a) Chronic administration of (+)-amphetamine alters the reactivity of midbrain dopaminergic neurons to prefrontal cortex stimulation in the rat. Brain Res 674: 63–74
Tong Z-Y, Overton PG, Clark D (1995b) Stimulation of the prefrontal cortex in the rat induces patterns of activity in midbrain dopaminergic neurons which resemble natural burst events. Synapse (in press)
Waszczak BL, Eng N, Walters JR (1980) Effects of muscimol and picrotoxin on single unit activity of substantia nigra neurons. Brain Res 188: 185–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Overton, P.G., Tong, Z.Y. & Clark, D. A pharmacological analysis of the burst events induced in midbrain dopaminergic neurons by electrical stimulation of the prefrontal cortex in the rat. J. Neural Transmission 103, 523–540 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01273151
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01273151