Abstract
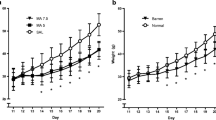
Methamphetamine induces neurotransmitter reductions and neurotoxicity at high doses in adult animals, but its effects on early brain development and behavior have received little attention. In this experiment the effects of methamphetamine exposure during a period equivalent to the human third trimester were examined. Rats (Sprague-Dawley CD) were injected subcutaneously withd-methamphetamine (d-MA) (30 mg/kg b.i.d.) early in postnatal development (days 1–10), later (postnatal days 11–20), or with water during both of these periods. Both early and later MA-exposed offspring exhibited reduced locomotor activity. The effect was most evident at 30 days of age and was smaller at 45 and 60 days and only present at these latter ages in males. Only the early MA exposure group showed prolonged suppression of activity in response to a challenge dose of fluoxetine and a persistant deficit in weight while only the later MA exposure group showed attenuated suppression of activity in response to a challenge dose of fluoxetine. Based both on the present data and those in the preceding article, it was concluded that the effects of MA are both long lasting and stage dependent and involve arousal as well as cognitive functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuff-Smith KD, George M, Lorens SA, Vorhees CV (1992) Preliminary evidence for methamphetamine-induced behavioral and ocular effects in rat offspring following exposure during early organogenesis. Psychopharmacology 109:255–263
Adams J, Buelke-Sam J, Kimmel CA, LaBorde JB (1982) Behavioral alterations in rats prenatally exposed to low doses ofd-amphetamine. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 4:63–70
Bell RW, Drucker RR, Woodruff AB (1965) The effects of prenatal injections of adrenalin chloride andd-amphetamine sulfate on subsequent emotionality and ulcer proneness of offspring. Psychon Sci 2:269–270
Buelke-Sam J, Kimmel CA, Adams J, Miller DR, Nelson CJ (1982) Behavioral assessment of rats treated prenatally with low doses ofd-amphetamine: II. Activity and pharmacological challenge testing. Teratology 25:30A-31A
Cho AK (1990) Ice: a new dosage form of an old drug. Science 249:631–634
Cho D, Lyu H, Lee H, Kim P, Chin K (1991) Behavioral teratogenicity of methamphetamine. J Toxicol Sci 16 [Suppl]:37–49
Clark CV, Gorman D, Vernadakis A (1970) Effects of prenatal administration of psychotropic drugs on behavior of developing rats. Dev Psychobiol 3 [4]:225–235
Derlet RW, Heischober B (1990) Methamphetamine: stimulant of the 1990s? West J Med 153 [6]:625–628
Dixon SD (1989) Effects of transplacental exposure to cocaine and methamphetamine on the neonate. West J Med 150:436–442
Dixon SD, Bejar R (1989) Echoencephalographic findings in neonates associated with maternal cocaine and methamphetamine use: incidence and clinical correlates. J Pediatr 115 [5]:770–778
Dow-Edwards DL, Freed LA, Milhorat TH (1988) Stimulation of brain metabolism by perinatal cocaine exposure. Dev Brain Res 42:137–141
Dow-Edwards DL, Freed-Malen LA, Hughes HE (1993) Longterm alterations in brain function following cocaine administration during the preweanling period. Dev Brain Res 72:309–313
Hitzemann BA, Hitzemann RJ, Brase DA, Loh HH (1976) Influence of prenatald-amphetamine administration on development and behavior of rats. Life Sci 18:605–612
Holson R, Adams J, Buelke-Sam J, Gough B, Kimmel CA (1985)d-Amphetamine as a behavioral teratogen: effects depend on dose, sex, age and task. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 7:753–758
Hughes HE, Dow-Edwards DL (1993) Postnatal cocaine exposure affects the adult acoustic startle response in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 15 (in press)
Hughes HE, Pringle GF, Scribani LA, Dow-Edwards DL (1991) Cocaine treatment in neonatal rats affects the adult behavioral response to amphetamine. Neurotoxicol Teratol 13:335–339
Little BB, Snell LM, Gilstrap LC (1988) Methamphetamine abuse during pregnancy: outcome and fetal effects. Obstet Gynecol 72[4]:541–544
Lucot JB, Wagner GC, Schuster CR, Seiden LS (1982) Decreased sensitivity of rat pups to long-lasting dopamine and serotonin depletions produced by methylamphetamine. Brain Res 247:181–183
Martin JC (1975) Effects on offspring of chronic maternal methamphetamine exposure. Dev Psychobiol 8:397–404
Martin JC, Martin DC (1981) Voluntary activity in the aging rat as a function of maternal drug exposure. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 3:261–264
Martin JC, Martin DC, Radow B, Sigman G (1976) Growth, development and activity in rat offspring following maternal drug exposure. Exp Aging Res 2:235–251
Middaugh LD (1989) Prenatal amphetamine effects on behavior: possible mediation by brain monoamines. Ann NY Acad Sci 562:308–318
Middaugh LD, Blackwell LA, Santos CA, Zemp JW (1974) Effects ofd-amphetamine sulfate given to pregnant mice on activity and on catecholamines in the brains of offspring. Dev Psychobiol 7[5]:429–438
Monder H (1981) Effects of prenatal amphetamine exposure on the development of behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 75:75–78
Nasello AG, Ramirez OA (1978) Open field and Lashley III maze behaviour of the offspring of amphetamine-treated rats. Psychopharmacology 58:171–173
Nasello AG, Astrada CA, Ramirez OA (1974) Effects on the acquisition of conditioned avoidance responses and seizure threshold in the offspring of amphetamine treated gravid rats. Psychopharmacologia 40:25–31
Satinder KP, Sterling JW (1983) Differential effects of pre- and/or postnatald-amphetamine on avoidance response in genetically selected lines of rats. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 5:315–320
Sato M, Fujiwara Y (1986) Behavioral and neurochemical changes in pups prenatally exposed to methamphetamine. Brain Dev 8:390–396
Seliger DL (1973) Effects of prenatal administration ofd-amphetamine on rat offspring activity and passive avoidance learning. Physiol Psychol 1:273–280
Vorhees CV (1985) Behavioral effects of prenatald-amphetamine in rats: a parallel trial to the Collaborative Behavioral Teratology study. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 7:709–716
Vorhees CV, Acuff-Smith KD, Minck DR, Butcher RE (1992) A method for measuring locomotor behavior in rodents: contrastsensitive computer-controlled video tracking activity assessment in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 14:43–49
Vorhees CV, Ahrens KG, Acuff-Smith KD, Schilling MA, Fisher JE (1994) Methamphetamine exposure during early postnatal development in rats: I. Acoustic startle augmentation and spatial learning deficits. Psychopharmacology 114:392–401
Wagner GC, Schuster CR, Seiden LS (1981) Neurochemical consequences following administration of CNS stimulants to the neonatal rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 14:117–119
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Horng JS, Molloy BB (1975) A new selective inhibitor for uptake of serotonin into synaptosomes of rat brain: 3-(p-trifluoromethylphenoxy)-N-methyl-3-phenyl-propylamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 193:804–811
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vorhees, C.V., Ahrens, K.G., Acuff-Smith, K.D. et al. Methamphetamine exposure during early postnatal development in rats: II. Hypoactivity and altered responses to pharmacological challenge. Psychopharmacology 114, 402–408 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02249329
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02249329