Abstract
Oxygen free radicals have been implicated as a causal factor in posttraumatic neuronal cell loss following cerebral ischemia and head injury. The conversion of salicylate to dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHBA) in vivo was employed to study the formation of hydroxyl radical (·OH) following central nervous system (CNS) injury. Bilateral carotid occlusion (BCO) in gerbils and concussive head trauma in mice were selected as models of brain injury. The lipid peroxidation inhibitor, tirilazad mesylate (U-74006F), was tested for its ability to attenuate hydroxyl radical formation in these models. In addition, U-74006F was studied as a scavenger of hydroxyl radical in an in vitro assay based on the Fenton reaction.
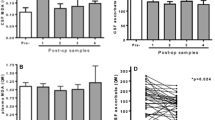
For in vivo experimentation, hydroxyl radical formation was expressed as the ratio of DHBA to salicylate (DHBA/SAL) measured in brain. In the BCO model, hydroxyl radical formation increased in whole brain with 10 min of occlusion followed by 1 min of reperfusion. DHBA/SAL was also found to increase in the mouse head injury model at 1 h postinjury. In both models, U-74006F (1 or 10 mg/kg) blocked the increase in DHBA/SAL following injury. In vitro, reaction of U-74006F with hydroxyl radical gave a product with a mol wt that was 16 greater than U-74006F, indicative of hydroxyl radical scavenging. We speculate that U-74006F may function by blocking oxyradical-dependent cell damage, and thereby maintaining free iron (which catalyzes hydroxyl radical formation) concentrations at normal levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck T. and Bielenberg G. H. (1990) Failure of the lipid peroxidation inhibitor U-74006F to improve neurological outcome after transient forebrain ischemia in the rat.Brain Res. 532, 336–338.
Beck T. and Bielenberg G. W. (1991) The effects of two 21-aminosteroids on overt infarct size 48 hours after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat.Brain Res. 560, 159–162.
Braughler J. M. and Pregenzer J. F. (1989) The 21-aminosteroid inhibitors of lipid peroxidation: reactions with lipid peroxyl and phenoxyl radicals.J. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 7, 125–130.
Braughler J. M., Duncan L. A., and Chase R. L. (1986) The involvement of iron in lipid peroxidation.J. Biol. Chem. 261, 10,282–10,289.
Cao W., Carney J. M., Duchon A., Floyd R. A., and Chevion A. (1988) Oxygen free radical involvement in ischemia and reperfusion injury to brain.Neurosci. Lett. 88, 233–238.
Chiueh C. C., Huang S. J., and Murphy D. L. (1992) Enhanced hydroxyl radical generation by 2′-methyl analog of MPTP: suppression by clorgyline and deprenyl.Synapse 1116, 183–191.
Floyd R. A. and Carney J. M. (1991) Age influence on oxidative events during brain ischemia/reperfusion.Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 12, 155–177.
Floyd R. A., Henderson R., Watson J. J., and Wong P. K. (1986) Use of salicylate with high pressure liquid chromatography and electrochemical detection (LCED) as a sensitive measure of hydroxyl free radicals in adriamycin treated rats.J. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2, 13–18.
Fujii T., Hiramoto Y., Terao J., and Fukuzawa K. (1991) Site-specific mechanism of initiation by a-tocopherol of lipid peroxide-dependent lipid peroxidation in charged micelles.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 284, 120–126.
Gelvan D. and Saltman P. (1991) Small chelators and the nature of the metal ion in site-specificity of ·OH damage, inOxidative Damage & Repair: Chemical, Biological and Medical Aspects (Davies K. J. A., ed.), pp. 825–830, Pergamon, New York.
Giovanni A., Hastings T. G., Liang L. P., and Zigmond M. J. (1992) Methamphetamine increases hydroxyl radicals in rat striatum: role of dopamine.Soc. Neurosc. Abstr. 18, 1444.
Grootveld M. and Halliwell B. (1986) Aromatic hydroxylation as a potential measure of hydroxyl-radical formationin vivo.Biochem. J. 237, 499–504.
Hall E. D. (1985) High-dose glucocorticoid treatment improves neurological recovery in head-injured mice.J. Neurosurg. 62, 882–887.
Hall E. D. and Pazara K. E. (1989) Effects of novel 21-aminosteroid antioxidants on post-ischemic neuronal degeneration, inCerebrovascular Diseases (Ginsberg M. D. and Dietrich W. D., eds.), pp. 387–391, Raven, New York.
Hall E. D., Yonkers P. A., McCall J. M., and Braughler J. M. (1988) Effects of the 21-aminosteroid U-74006F on experimental head injury in mice.J. Neurosurg. 68, 456–461.
Hall E. D., Braughler J. M., and McCall J. M. (1990) Role of oxygen radicals in stroke: effect of the 21-aminosteroids (lazaroids), a novel class of antioxidants, inCurrent and Future Trends in Anticonvulsant, Anxiety, and Stroke Therapy (Meldrum B. S. and Williams M., eds.), pp. 351–362, Wiley-Liss, New York.
Hall E. D., Andrus P. K., Althaus J. S., and VonVoigtlander P. F. (1993a) Hydroxyl radical production and lipid peroxidation parallels selective post-ischemic vulnerability in gerbil brain.J. Neurosc. Res. 34, 107–112.
Hall E. D., Andrus P. K., and Yonkers P. A. (1993b) Brain hydroxyl radical generation in acute experimental head injury.J. Neurochem. 60, 588–594.
Halliwell B. (1992) Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system.J. Neurochem. 59, 1609–1623.
Haraldseth O., GrØnas T., and Unsgard G. (1991) Quicker metabolic recovery after forebrain ischemia in rats treated with the antioxidant U-74006F.Stroke 22, 1188–1192.
Haseloff R. F., Blasig I. E., Meffert H., and Ebert B. (1990) Hydroxyl radical scavenging and antipsoriatic activity of benzoic acid derivatives.Free Rad. Biol. Med. 9, 111–115.
Ingold K. U., Bowry V. W., Stocker R., and Walling C. (1993) Autoxidation of lipids and antioxidation by α-tocopherol and ubiquinol in homogeneous solution and in aqueous dispersions of lipids: Unrecognized consequences of lipid particle size as exemplified by oxidation of human low density lipoprotein.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 45–49.
Janero D. R. and Burghardt B. (1989) Prevention of oxidative injury to cardiac phospholipid by membrane-active “stabilizing agents.” Res.Comm. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 63, 163–173.
Kobayashi A., Watanabe H., Ozawa K., Hayashi H., and Yamazaki N. (1989) Oxygen-derived free radicals related injury in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion.Jpn. Circ. J. 53, 1122–1131.
Kontos H.A. and Povlishock J. T. (1986) Oxygen radicals in brain injury.CNS Trauma 3, 257–263.
Lesiuk H., Sutherland G., Peeling J., Butler K., and Saunders J. (1991) Effect of U-74006F on forebrain ischemia in rats.Stroke 22, 896–901.
McIntosh T. K., Thomas M., Smith D., and Banbury M. (1992) The novel 21-aminosteroid U-74006F attenuates cerebral edema and improves survival after brain injury in the rat.J. Neurotrauma 9, 33–46.
Moorhouse C. P., Halliwell B., Grootveld M., and Gutteridge J. M. C. (1985) Cobalt (II) ion as a promoter of hydroxyl radical and possible ‘cryptohydroxyl’ radical formation under physiological conditions. Differential effects of hydroxyl radical scavengers.Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 843, 261–268.
Pahlmark K., Smith M. L., and Siesjö B. K. (1991) Failure of U-74006F to ameliorate neuronal damage due to transient ischemia or hypoglycemia.J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metab. 2, S138.
Perkins W.J., Lessor N., Downes H., and Riker W. K. (1992) Effect of a 21-aminosteroid on histopathologic outcome after forebrain ischemia in the rat.FASEB J. 5, A1279.
Piantadosi C. A. and Tatro L. G. (1990) Regional H2O2 concentration in rat brain after hyperoxic convulsions.J. Appl. Physiol. 69, 1761–1766.
Powell S. R. and Hall R. (1990) Use of salicylate as a probe for ·OH formation in isolated ischemic rat hearts.Free Rad. Biol. Med. 9, 133–141.
Sakamoto A., Ohnishi S. T., Ohnishi T., and Ogawa R. (1991) Relationship between free radical production and lipid peroxidation during ischemiareperfusion injury in rat brain.Brain Res. 554, 186–192.
Simpson J. A., Cheeseman K. H., Smith S. E., and Dean R. T. (1988) Free-radical generation by copper ions and hydrogen peroxide.Biochem. J. 254, 519–523.
Snedecor G. W. and Cochran W. G. (1967)Statistical Methods, 6th ed., The Iowa State University Press, Ames, LA.
Spina M. B. and Cohen G. (1989) Dopamine turnover and glutathione oxidation: Implications for parkinson disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 1398–1400.
Sutton H. C. (1985) Efficiency of chelated iron compounds as catalysts for the Haber-Weiss reaction.J. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 1, 195–202.
Tosaki A., Blasig I. E., Pali T., and Ebert B. (1990) Heart protection and radical trapping by DMPO during reperfusion in isolated working rat hearts.Free Rad. Biol. Med. 8, 363–372.
Yoshida K., Terao J., Suzuki T., and Takama K. (1991) Inhibitory effect of phosphatidylserine on iron-dependent lipid peroxidation.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 179, 1077–1081.
Young W., Wojak J. C., and DeCrescito V. (1988) 21-aminosteroid reduces ion shifts and edema in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model of regional ischemia.Stroke 19, 1013–1019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Althaus, J.S., Andrus, P.K., Williams, C.M. et al. The use of salicylate hydroxylation to detect hydroxyl radical generation in ischemic and traumatic brain injury. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 20, 147–162 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815368
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815368