Abstract
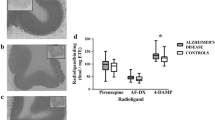
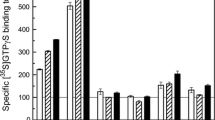
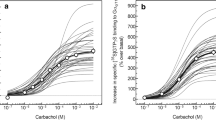
Cortical M1 muscarinic receptor-G-protein coupling, high-affinity, guanine nucleotide-sensitive agonist binding (Flynn et al., 1991; Warpman et al., 1993) and muscarinic receptor-stimulated [3H]PIP2 hydrolysis (Ferrari-DiLeo and Flynn, 1993) are known to be defective in Alzheimer disease. Whether this defect reflects an alteration in the M1 muscarinic receptor, its respective guanine nucleotide binding (G) protein or both is not known. This study compares the number and both basal and muscarinic receptor-mediated function of G-proteins in synaptosomal membranes from cerebral cortical samples of age-matched control subjects and Alzheimer disease patients. Immuno-blotting with anti-Gαq/11 and anti-Gβ antibodies demonstrated no alteration in the number of these G-protein subunits in Alzheimer disease. Basal [35S]GTPγS binding and hydrolysis of [γ-32P]GTP by high-affinity GTPase also were not significantly altered in Alzheimer disease compared to control membrane samples. However, muscarinic agonist-stimulated GTPγS binding and GTP hydrolysis were significantly reduced (80–100%) in Alzheimer disease cortical samples. Diminished agonist-stimulated GTPγS binding and GTP hydrolysis corre-related with the loss of guanine nucleotide-sensitive, high-affinity agonist binding (K L/K H) ratio) to the M1 receptor subtype. These data provide further evidence for the loss of muscarinic receptor-G protein coupling in Alzheimer disease and support the hypothesis that muscarinic receptor-mediated cortical activation may be compromised in Alzheimer disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai H., Ichimiya Y., Kosaka K., Moroji T., and Iizuka R. (1992) Neurotransmitter changes in early- and late-onset Alzheimer-type dementia.Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiat. 16, 883–890.
Araujo D. M., Lapchak P. A., Robitaille Y., Gauthier S., and Quirion R. (1988) Differential alteration of various cholinergic markers in cortical and subcortical regions of human brain in Alzheimer’s disease.J. Neurochem. 50, 1914–1923.
Bartus R. T., Dean R. L., Pontecorvo M. J., and Flicker C. (1985) The cholinergic hypothesis: A historical overview, current perspective, and future directions.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 444, 332–358.
Becker R. E. and Giacobini E. (1988) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of acetylcholinesterase inhibition: can acetylcholine levels in the brain be improved in Alzheimer’s disease?Drug Dev. Res. 14, 235–246.
Bergstrom L., Garlind A., Nilsson L., Alafuzoff I., Fowler C. J., Winblad B., and Cowburn R. F. (1991) Regional distribution of somatostatin receptor binding and modulation of adenylyl cyclase activity in Alzheimer’s disease brain.J. Neurol. Sci. 105, 225–233.
Bernstein G., Blank J. L., Smrcka A. V., Higashijima T., Sternweis P. C., Exton J. H., and Ross E. M. (1992) Reconstitution of agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis using, purified m1 muscarinic receptor, Gq/11, and phospholipase C-β1.J. Biol. Chem. 267, 8081–8088.
Blake M. S., Johnson K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., and Gotshlick E. C. (1984) A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots.Anal. Biochem. 136, 175–179.
Blank J. L., Ross A. H., and Exton J. H. (1991) Purification and characterization of two G-proteins that activate the β1 isozyme of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C.J. Biol. Chem. 266, 18206–18216.
Brodde O-E. and Michel M. C. (1989) Disease states can modify both receptor number and signal transduction pathways.Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 10, 383–384.
Buxbaum J. D., Oishi M., Chen H. I., Pinkas-Kramarski R., Jaffe E. A., Gandy S. E. and Greengard P. (1992) Cholinergic agonists and interleukin 1 regulate processing and secretion of the Alzheimer β/A4 amyloid protein precursor.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10,075–10,078.
Buxbaum J. D., Gandy S. E., Cicchetti P., Ehrlich M. E., Czernik A. J., Fracasso R. P., Ramabhadran T. V., Unterbeck A. J., and Greengard P. (1990) Processing of Alzheimer β/A4 amyloid precursor protein: modulation by agents that regulate protein phosphorylation.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 6003–6006.
Cassel D. and Selinger Z. (1976) Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 452, 538–551.
Cheng Y. and Prusoff W. H. (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (K i ) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 percent inhibition.Biochem. Pharmacol. 22, 3099–3108.
Cowburn R. F., Vestling M., Fowler C. J., Ravid R., Winblad B., and O’Neill C. (1993) Disruptedβ 1-adrenoreceptor-G protein coupling in the temporal cortex of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.Neurosci. Lett. 155, 163–166.
Cutler R., Joseph J. A., Yamagami K., Villalobos-Molina R., and Roth G. S. (1992) Alterations in muscarinic stimulated lowK m GTPase activity in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: implications for altered signal transduction.Soc. Neurosci. Abst. 18, 1484.
DeKosky S. T., Harbaugh R. E., Schmitt F. A., Bakay R. A. E., Chang Chiu H. K., Knopman D. S., Reeder T. M., Shetter A. G., Senter H. J., Markesbery W. R., and the Intraventricular Bethanechol Study Group (1992) Cortical biopsy in Alzheimer’s disease: Diagnostic accuracy and neurochemical, neuropathological, and cognitive correlations.Ann. Neurol. 32, 625–632.
Evans T., Hepler J. R., Masters S. B., Brown J. H., and Harden T. K. (1985) Guanine nucleotide regulation of agonist binding to muscarinic receptors. Relation to efficacy of agonists for stimulation of phosphoinositide breakdown and Ca2+ mobilization.Biochem. J. 232, 751–757.
Ferrari-DiLeo G. and Flynn D. D. (1993) Diminished muscarinic receptor-stimulated [3H]-PIP2 hydrolysis in Alzheimer’s disease.Life Sci. 53, PL 439–444.
Fisher S. K., Heacock A. M., and Agranoff B. W. (1992) Inositol lipids and signal transduction in the nervous system: an update.J. Neurochem. 58, 18–38.
Flynn D. D. and Mash D.C. (1993) Distinct kinetic properties of N-[3H]-methyl-scopolamine afford differential labeling and localization of M1, M2, and M3 muscarinic receptor subtypes in primate brain.Synapse 14, 283–296.
Flynn D. D., Palermo N., and Suarez A. (1989) Agonist binding to M1 muscarinic receptors is sensitive to guanine nucleotides.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 172, 363–372.
Flynn D. D., Weinstein D. A., and Mash D. C. (1991) Loss of high affinity agonist binding to M1 muscarinic receptors in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for the failure of cholinergic replacement therapies.Ann. Neurol. 29, 256–262.
Flynn D. D., Levey A. I., Ferrari-DiLeo G., and Mash D. C. (1993) Probing the status of muscarinic receptor subtypes in Alzheimer’s disease with subtypeselective antisera.Soc. Neurosci. Abst. 19, 1039.
Fonnum F. (1969) Radiochemical microassays for the determination of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities.Biochem. J. 115, 465–472.
Forray C. and El-Fakahany E. E. (1990) On the involvement of multiple muscarinic receptor subtypes in the activation of phosphoinositide metabolism in rat cerebral cortex.Mol. Pharmacol. 37, 893–902.
Fowler C. J., Cowburn R. F., and O’Neill C. (1992) Brain signal transduction disturbances in neurodegenerative disorders.Cell. Signalling 4, 1–9.
Francis P. T., Palmer A. M., Sims N. R., Bowen D. M., Davison A. N., Esiri M. M., Neary D., Snowden J. S., and Wilcock G. K. (1985) Neurochemical studies of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Possible influence on treatment.N. Engl. J. Med. 313, 7–11.
Gabuzda D., Busciglio J., and Yankner B. A. (1993) Inhibition of β-amyloid production by activation of protein kinase C.J. Neurochem. 61, 2326–2329.
Ghodsi-Hovsepian S., Messer W. S., Jr., and Hoss W. (1990) Differential coupling between muscarinic receptors and G-proteins in regions of the rat brain.Biochem. Pharmacol. 39, 1385–1391.
Giacobini E. (1990) Cholinergic receptors in human brain: effects of aging and Alzheimer’s disease.J. Neurosci. Res. 27, 548–560.
Greenamyre J. T., and Young A. B. (1989) Excitatory amino acids and Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 10, 593–602.
Haga T., Haga K., Kameyama K., and Nakata H. (1993) Phosphorylation of muscarinic receptors: regulation by G proteins.Life Sci. 52, 421–428.
Hilf G. and Jakobs K. H. (1989) Activation of cardiac G-proteins by muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: regulation by Mg2+ and Na+ ions.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 172, 155–163.
Hilf G., Gierschik P., and Jakobs K. H. (1989) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-stimulated binding of guanosine 5′-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) to guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins in cardiac membranes.Eur. J. Biochem. 186, 725–731.
Honer W. G., Dickson D. W., Gleeson J., and Davies P. (1992) Regional synaptic pathology in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 13, 375–382.
Hu J., Wang S-Z., and El-Fakahany E. E. (1991) Effects of agonist efficacy on desensitization of phosphoinositide hydrolysis mediated by m1 and m3 muscarinic receptors expressed in Chinese Hamster Ovary cells.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 257, 938–945.
Huang H.-M. and Gibson G. E. (1993) Altered β-adrenergic receptor-stimulated cAMP formation in cultured skin fibroblasts from Alzheimer’s donors.J. Biol. Chem. 268, 14,616–14,621.
Hung A. Y., Haass C., Nitsch R. M., Qui W. Q., Citron M., Wurtman R. J., Growdon J. H., and Selkoe D. J. (1993) Activation of protein kinase C inhibits cellular production of the amyloid β-protein.J. Biol. Chem. 268, 22,959–22,962.
Joachim C. L. and Selkoe D. J. (1992) The seminal role of β-amyloid in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease.Alzheimer Disease Assoc. Disorders 6, 7–34.
Jope R. S., Song L., Li X., and Powers R. (1994) Impaired phosphoinositide hydrolysis in Alzheimer’s disease brain.Neurobiol. Aging 15, 221–226.
Kachaturian Z. S. (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease.Arch. Neurol. 42, 1097–1105.
Kalaria R. N., Andorn A. C., Tabaton M., Whitehouse P. J., Harik S. I., and Unnerstall J. R. (1989) Adrenergic receptors in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: Increasedβ 2-receptors in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus.J. Neurochem. 53, 1772–1781.
Kang J., Lemaire H-G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., and Grzeschik K-H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., and Muller-Hill B. (1987) The precursor of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor.Nature 325, 733–736.
Katzman R. and Saitoh T. (1991) Advances in Alzheimer’s disease.FASEB J. 5, 278–286.
Kent R. S., De Lean A., and Lefkowitz R. J. (1980) A quantitative analysis of beta-adrenergic receptor interactions: resolution of high and low affinity states of the receptor by computer modeling of ligand binding data.Mol. Pharmacol. 17, 14–23.
Knapp M. J., Knopman D. S., Solomon P. R., Pendlebury W. W., Davis C. S., and Gracon S. I. (1994) A 30-week randomized controlled trial of high-dose tacrine in patients with Alzheimer’s disase.J. Am. Med. Assoc. 271, 985–991.
Kosik K. S. (1989) the molecular and cellular pathology of Alzheimer neurofibrillary lesions.J. Gerontol. 44, B55–58.
Laemmli U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature (Lond.) 227, 680–685.
Levey A. I., Kitt C. A., Simonds W. F., Price D. L., and Brann M. R. (1991) Identification and localization of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor proteins in brain with subtype-specific antibodies.J. Neurosci. 11, 3218–3226.
Mash D. C., and Flynn D. D. (1992) Reply to loss of high-affinity agonist receptor binding in Alzheimer’s disease.Ann. Neurol. 31, 231–232.
Mash D. C., Flynn D. D., and Potter L. T. (1985) Loss of M2 muscarine receptors in the cerebral cortex in Alzheimer’s disease and experimental cholinergic denervation.Science 228, 1115–1117.
Masliah E., Cole G. M., Hansen L. A., Mallory M., Albright T., Terry R. D., and Saitoh T. (1991) Protein kinase C alteration is an early biochemical marker in Alzheimer’s disease.J. Neurosci. 11, 2759–2767.
McLaughlin M., Ross B. M., Milligan G., McCulloch J., and Knowler J. T. (1991) Robustness of G proteins in Alzheimer’s disease: an immunoblot study.J. Neurochem. 57, 9–14.
Mouradian M. M., Mohr E., Williams J. A., and Chase T. N. (1988) no response to high-dose muscarinic agonist therapy in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurology 38, 606–608.
Nathanson N. M. (1987) Molecular properties of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 195–236.
Nishimoto I., Okamoto T., Matsuura Y., Takahashi S., Okamoto T., Murayama Y., and Ogata E. (1993) Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor complexes with brain GTP-binding protein Go.Nature 362, 75–79.
Nitsch R. M., Slack B. E., Wurtman R. J., Growdon J. H. (1992) Release of Alzheimer amyloid precursor derivatives stimulated by activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.Science 258, 304–307.
O’Neill C., Cowburn R. F., Wiehager B., Alafuzoff I., Winblad B., and Fowler C. J. (1991a) Preservation of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor-G protein interactions in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.Neurosci. Lett. 133, 15–19.
O’Neill C., Fowler C. J., Wiehager B., Cowburn R. F., Alafuzoff I., and Winblad B. (1991b) Coupling of human brain cerebral corticalα 2-adrenoreceptors to GTP-binding proteins in Alzheimer’s disease.Brain Res. 563, 39–43.
Perry E. K., Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Bergmann K., Gibson P. H., and Perry R. H. (1978) Correlation of cholinergic abnormalities with senile plaques and mental test scores in senile dementia.Br. J. Med. J. 2, 1457–1459.
Rebeck G. W., and Hyman B. T. (1993) Neuroanatomical connections and specific regional vulnerability in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 14, 45–47.
Ross B. M., McLaughlin M., Roberts M., Milligan G., McCulloch J., and Knowler J. T. (1993) Alterations in the activity of adenylate cyclase and high affinity GTPase in Alzheimer’s disease.Brain Res. 622, 35–42.
Shimohama S., Taniguchi T., Fujuwara M., and Kameyama M. (1987) Changes in β-adrenergic receptor subtypes in Alzheimer-type dementia.J. Neurochem. 48, 1215–1221.
Smith C. J., Perry E. K., Perry R. H., Fairbairn A. F., and Birdsall N. J. M. (1987) Guanine nucleotide modulation of muscarinic cholinergic receptor binding in postmortem human brain—a preliminary study in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurosci. Lett. 82, 227–232.
Stern Y., Sano M., and Mayeux R. (1987) Effect of oral physostigmine in Alzheimer’s disease.Ann. Neurol. 22, 306–310.
Towbin H., Staehelin T., and Gordon J. (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 4350–4354.
Trojanowski J. Q., Schmidt M. L., Shin R-W., Bramblett G. T., Rao D., and Lee V. M.-Y. (1993) Altered tau and neurofilament proteins in neurodegenerative diseases: diagnostic implications for Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body dementias.Brain Pathol. 3, 45–54.
Ukas J., Brunner L. C., Nguyen L., and Cotman C. W. (1993) Reduced density of adenosine A1 receptors and preserved coupling of adenosine A1 receptors to G proteins in Alzheimer hippocampus: a quantitative autoradiographic study.Neuroscience 52, 843–854.
Warpman U., Alafuzoff I., and Nordberg A. (1993) Coupling of muscarinic receptors to GTP proteins in postmortem human brain—alterations in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurosci. Lett. 150, 39–43.
Watkins P. B., Zimmerman H. J., Knapp M. J., Gracon S. I., and Lewis K. W. (1994) Hepatotoxic effects of tacrine administration in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.J. Am. Med. Assoc. 271, 992–998.
Wess J. (1993) Mutational analysis of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: structural basis of ligand/receptor/G protein interactions.Life Sci. 53, 1447–1463.
Yankner B. A. and Mesulam M.-M. (1991) β-Amyloid and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.New Engl. J. Med. 325, 1849–1856.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrari-DiLeo, G., Mash, D.C. & Flynn, D.D. Attenuation of muscarinic receptor-G-protein interaction in Alzheimer disease. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 24, 69–91 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160113
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160113