Abstract
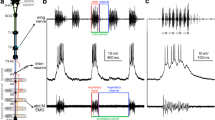
Membrane potential changes and/or discharges from 36 inspiratory neurons were recorded intracellularly in the dorsal respiratory group (DRG; i.e., the ventrolateral subdivision of the nucleus tractus solitarii) in decerebrate, paralyzed, and ventilated cats. Electrical activities were recorded from both somata (n=10) and axons (n=26). Activities during quiet breathing were compared with those observed during fictive coughing and swallowing evoked by repetitive electrical stimulation of afferent fibers of the superior laryngeal nerve (SLN). These nonrespiratory behaviors were evident in paralyzed animals as characteristic discharge patterns of the phrenic, abdominal, and hypoglossal nerves. Twenty-six neurons exhibiting antidromic action potentials in response to electrical stimuli applied to the cervical (C3–5) spinal cord were classified as inspiratory bulbospinal neurons (IBSNs). These neurons were considered as premotoneurons. The remaining 10 inspiratory neurons (INAA) were not antidromically activated by electrical stimuli applied to either cervical spinal cord or ipsilateral cervical vagus. These neurons are thought to be propriobulbar neurons. We recorded the activity of 31 DRG inspiratory neurons (24 IBSNs and 7 I-NAA) during coughing. All but one (a late-recruited IBSN) discharged a burst of action potentials during the coughing-related phrenic nerve activity. Typically, ramp-like membrane depolarization trajectories and discharge frequencies during coughing were similar to those observed during inspiration. We recorded the activity of 33 DRG inspiratory neurons (23 IBSNs and 10 I-NAA) during swallowing. Most (28/33) neurons were briefly activated, i.e., discharged a burst of action potentials during swallowing, but peak discharge frequency decreased compared with that measured during inspiration. The membrane potentials of nine somata exhibited a brief bell-shaped depolarization during swallowing, the amplitude of which was similar to that observed during inspiration. These results suggest that some inspiratory premotoneurons and propriobulbar neurons of the DRG might be involved in nonrespiratory motor activities, even if clearly antagonistic to breathing (e.g., swallowing). We postulate the existence in the medulla oblongata of adult mammals of neurons exhibiting a “functional flexibility”.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianchi AL (1971) Localisation et étude des neurones respiratoires bulbaires. Mise en jeu antidromique par stimulation spinale ou vagale. J Physiol (Paris) 63:5–40
Bianchi AL (1974) Modalités de décharge et propriétés anatamofonctionelles des neurones respiratoires bulbaires. J Physiol (Paris) 68:555–587
Bianchi AL, Grélot L (1989) Converse motor output of inspiratory bulbospinal premotoneurons during vomiting. Neurosci Lett 104:298–302
Bianchi AL, Grélot L, Iscoe S, Remmers JE (1988) Electrophysiological properties of rostral medullary respiratory neurons in the cat: an intracellular study. J Physiol (Lond) 407:29–310
Bianchi AL, Denavit-Saubié M, Champagnat J (1995) Central control of breathing in mammals: neuronal circuitry, membrane properties, and neurotransmitters. Physiol Rev 75:1–46
Bolser D (1991) Fictive cough in the cat. J Appl Physiol 71:2325–2331
Contreras RJ, Beckstead RM, Norgren R (1982) The central projections of the trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves: an autoradiographic study in the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst 6:303–322
Coombs JS, Curtis DR, Eccles JC (1957) The interpretation of spike potentials of motoneurons. J Physiol (Lond) 139:198–231
Dick TE, Oku Y, Romaniuk JR, Cherniack NS (1993) Interaction between central pattern generators for breathing and swallowing in the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 465:715–730
Doty RW (1951) Influence of stimulus pattern on reflex deglutition. Am J Physiol 76:142–158
Doty RW, Bosma JF (1956) An electromyographic analysis of deglutition. J Neurophysiol 19:44–60
Ezure K (1990) Synaptic connexions between medullary respiratory neurons and considerations on the genesis of respiratory rhythm. Prog Neurobiol 35:429–450
Fontana GA, Pantaleo T, Bongianni F, Cresci F, Viroli L, Sarago G (1992) Changes in respiratory activity induced by mastication in humans. J Appl Physiol 72:779–786
Fortin G, Champagnat J (1993) Spontaneous synaptic activities in rat nucleus tractus solitarius neurons in vitro: evidence for reexcitatory processing. Brain Res 630:125–135
Gestreau C, Portillo F, Yousfi-Malki M, Puizillout JJ, Grélot L (1994) Brainstem distribution of c-fos immunoreactivity following repetitive coughing in decerebrate cats. Eur J Neurosci [Suppl] 7:95.01
Grélot L (1990) Reconfiguration of the respiratory neuronal network during expulsion and upper airway protective reflexes. In: Neural nets and rhythms in vertebrates and invertebrates, proceedings of an International Symposium. Arcachon, France
Grélot L, Milano S (1991) Diaphragmatic and abdominal muscle activities during coughing in the decerebrate cat: a model for fictive coughing. Neuroreport 2:165–168
Grélot L, Barillot JC, Bianchi AL (1989) Pharyngeal motoneurons: respiratory-related activity and responses to laryngeal afferents in the decerebrate cat. Exp Brain Res 78:336–344
Grélot L, Milano S, Portillo F, Miller AD, Bianchi AL (1992) Membrane potential changes of phrenic motoneurons during fictive vomiting, coughing and swallowing in the decerebrate cat. J Neurophysiol 68:2110–2119
Grélot L, Milano S, Portillo F, Miller AD (1993) Respiratory interneurons of the lower cervical (C4–C5) spinal cord: membrane potential changes during coughing, vomiting and swal lowing in the decerebrate cat. Pflugers Arch 425:313–320
Hooper SL, Moulins M (1989) Switching of a neuron from one network to another by sensory-induced changes in membrane properties. Science 244:1587–1589
Issa FG, Porostocky S (1994) Effect of continuous swallowing on respiration. Resp Physiol 95:181–193
Jakus J, Tomori Z, Stransky A (1985) Activity of bulbar respiratory neurons during cough and other respiratory tract reflexes in cats. Physiol Bohemoslov 34:127–136
Jean A (1972) Localisation et activité des neurones déglutiteurs bulbaires. J Physiol (Paris) 64:227–268
Jean A, Kessler JP, Tell F (1994) Nucleus tractus solitarii and deglutition: monoamines, excitatory amino acids and cellular properties. In: Barraco IRA (ed) Nucleus of the solitary tract. CRC, Boca Raton, Fla, pp 361–376
Jiang C, Lipski J (1992) Synaptic inputs to medullary respiratory neurons from superior laryngeal afferents in the cat. Brain Res 584:197–206
Jodkowski JS, Berger AJ (1988) Influences from laryngeal afferents on expiratory bulbospinal neurons and motoneurons. J Appl Physiol 64:1337–1345
Kase Y, Wakita Y, Kito G, Miyama T, Yuizono T, Kataoka M (1970) Centrally-induced coughs in the cat. Life Sci 9:49–59
Kessler JP, Jean A (1985) Identification of the medullary swallowing regions in the rat. Exp Brain Res 57:256–263
Kessler JP, Jean A (1991) Evidence that activation of N-methyl-daspartate (NMDA) and non-NMDA receptors within the nucleus tractus solitarii triggers swallowing. Eur J Pharmacol 201:59–67
Koga T, Fukuda H (1992) Neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract mediating inputs from emetic vagal afferents and the area postrema to the pattern generator for the emetic act in dogs. Neurosci Res 14:166–179
McFarland DH, Lund JP (1993) An investigation of the coupling between respiration, mastication, and swallowing in the awake rabbit. J Neurophysiol 69:95–108
Meyrand P, Simmers J, Moulins M (1991) Construction of a pattern-generating circuit with neurons of different networks. Nature 351:60–63
Milano S, Grélot L, Bianchi AL, Iscoe S (1992) Discharge patterns of phrenic motoneurons during fictive coughing and vomiting in decerebrate cat. J Appl Physiol 73:1626–1632
Mori M, Sakai Y (1972) Re-examination of centrally-induced cough in cats using a micro-stimulation technique. Jpn J Pharmacol 22:635–643
Oku Y, Tanaka I, Ezure K (1994) Activity of bulbar respiratory neurones during fictive coughing and swallowing in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol (Lond) 480(2):309–324
Pearson KG (1993) Common principles of motor control in vertebrates and invertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci 16:265–297
Sasaki K, Otake K, Mannen H, Ezure K, Manabe M (1989) Morphology of augmenting inspiratory neurons of the ventral respiratory group in the cat. J Comp Neurol 282:157–168
Shannon R, Morris KE, Lindsey BG (1992) Medullary ventral respiratory group (VRG) neurons responses during fictive coughing. Soc Neurosci Abstr 58.6
Sumi T (1963) The activity of brain-stem respiratory neurons and spinal respiratory motoneurons during swallowing. J Neurophysiol 26:466–477
Suzuki H, Kondo T, Yamabayashi H, Kobayashi I, Ohta Y (1991) Influence of central respiratory activity on the cough response in anesthetized dogs. Jpn J Physiol 41:879–891
Tell F, Jean A (1991) Activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors induces endogenous rhythmic bursting activities in nucleus tractus solitarii neurons: an intracellular study on adult rat brainstem slices. Eur J Neurosci 3:1353–1365
Tell F, Jean A (1993) Ionic basis for endogenous rhythmic patterns induced by activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in neurons of the rat nucleus tractus solitarii. J Neurophysiol 70:2379–2390
Tomori Z, Widdicombe JG (1969) Muscular, bronchomotor and cardiovascular reflexes elicited by mechanical stimulation of the respiratory tract. J Physiol (Lond) 200:25–49
Von Euler C, Hayward JN, Marttila I, Wyman RJ (1973) Respiratory neurons of the ventrolateral nucleus of the solitary tract in the cat: vagal input, spinal connexions and morphological identification. Brain Res 61:23–33
Weimann J, Meyrand P, Marder E (1991) Neurons that form multiple pattern generators: identification and multiple activity patterns of gastric/pyloric neurons in the crab stomatogastric system. J Neurophysiol 65:111–122
Wu JY, Cohen LB, Falk CX (1994) Neuronal activity during different behaviors in aplysia: a distributed organization? Science 263:820–823
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gestreau, C., Milano, S., Bianchi, A.L. et al. Activity of dorsal respiratory group inspiratory neurons during laryngeal-induced fictive coughing and swallowing in decerebrate cats. Exp Brain Res 108, 247–256 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228098
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228098