Abstract
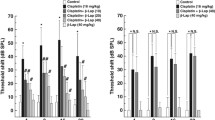
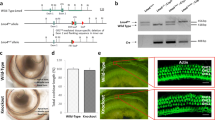
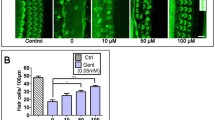
Cisplatin is a widely used chemotherapeutic agent that causes significant hearing loss. Previous studies have shown that cisplatin exposure is associated with increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the cochlea. The inner ear expresses a unique isoform of NADPH oxidase, NOX3. This enzyme may be the primary source of ROS generation in the cochlea. The knockdown of NOX3 by pretreatment with siRNA prevented cisplatin ototoxicity, as demonstrated by preservation of hearing thresholds and inner ear sensory cells. Trans-tympanic NOX3 siRNA reduced the expression of NOX3 and biomarkers of cochlear damage, including transient receptor vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channel and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) in cochlear tissues. In addition, siRNA against NOX3 reduced apoptosis as demonstrated by TUNEL staining, and prevented the increased expression of Bax and abrogated the decrease in Bcl2 expression following cisplatin administration. Trans-tympanic administration of siRNA directed against NOX3 may provide a useful method of attenuating cisplatin ototoxicity. In this paper, we review recent publications dealing with the role of NOX3 in ototoxicity and the effects of siRNA against cisplatin-induced hearing loss.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKeage MJ (1995) Comparative adverse effect profiles of platinum drugs. Drug Saf 13:228–244
Li Y, Womer RB, Silber JH (2004) Predicting cisplatin ototoxicity in children: influence of age and the cumulative dose. Eur J Cancer 40:2445–2451
Kushner BH, Budnick A, Kramer K, Modak S, Cheung N-KV (2006) Ototoxicity from high-dose use of platinum compounds in patients with neuroblastoma. Cancer 107:417–422
Kopelman J, Budnick AS, Sessions RB, Kramer MB, Wong GY (1988) Ototoxicity of high dose cisplatin by bolus administration in patients with advanced cancer and normal hearing. Laryngoscope 98:858–864
Bokemeyer C, Berger CC, Hartmann JT, Kollmansberger C, Schmoll HJ, Kuczyk MA, Kanz L (1998) Analysis of risk factors for cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in patients with testicular cancer. Br J Cancer 77:1355–1362
Chen WC, Jackson A, Budnick AS, Pfister DG, Kraus DH, Hunt MA, Stambuk H, Levegrun S, Wolden SL (2006) Sensorineural hearing loss in combined modality treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 106:820–829
Fleischman KW, Stadnicki SW, Ethier MF, Schaeppi U (1975) Ototoxicity of cis-dichlorodiammine platinum (II) in the guinea pig. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 22:320–332
Kamimura T, Whitworth CA, Rybak LP (1999) Effects of 4-methylthiobenzoic acid on cisplatin ototoxicity in the rat. Hear Res 131:117–127
Sluyter S, Klis SF, de Groot JC, Smoorenburg GF (2003) Alterations in the stria vascularis in relation to cisplatin ototoxicity and recovery. Hear Res 185:49–56
Campbell KC, Meech RP, Rybak LP, Hughes LF (1999) d-methionine protects against cisplatin damage to the stria vascularis. Hear Res 138:13–28
Clerici WJ, DiMartino DL, Prasad MR (1995) Direct effects of reactive oxygen species on cochlear outer hair cell shape in vitro. Hear Res 84:30–40
Clerici WJ, Yang L (1996) Direct effects of intraperilymphatic reactive oxygen species on cochlear function. Hear Res 101:14–22
Kopke RD, Liu W, Gabaizadeh R, Jacono A, Feghali J, Spray D, Garcia P, Steinman H, Malgrange B, Ruben RJ, Rybak L, Van de Water TR (1997) Use of organotypic cultures of Corti’s organ to study the protective effects of antioxidant molecules on cisplatin induced damage of auditory hair cells. Am J Otol 18:559–571
Dehne N, Lautermann J, Petrat F, Rauen U, de Groot H (2001) Cisplatin ototoxicity: involvement of iron and enhanced formation of superoxide anion radicals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 174:27–34
Banfi B, Malgrange B, Knisz J, Steger K, Dubois-Dauphin M, Krause K-H (2004) NOX3, a superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase of the inner ear. J Biol Chem 279:46065–46072
Rybak LP, Somani S (1999) Ototoxicity: amelioration by protective agents. Ann NY Acad Sci 884:143–151
Lee JE, Nakagawa T, Kim TS, Endo T, Shiga A, Iguchi F, Lee SH, Ito J (2004) Role of reactive radicals in degeneration of the auditory system of mice following cisplatin treatment. Acta Otolaryngol 124:1131–1135
Lee JE, Nakagawa T, Kita T, Kim TS, Endo T, Shiga A, Iguchi F, Lee SH, Ito J (2004) Mechanisms of apoptosis induced by cisplatin in marginal cells in mouse stria vascularis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 66:111–118
Ikeda K, Sunose H, Takasaka T (1993) Effects of free radicals on the intracellular calcium concentration in the isolated hair cell of the guinea pig cochlea. Acta Otolaryngol 113:137–141
Pigeolet E, Corbisier P, Houbion A, Lambert D, Michiels C, Raes M, Zachary MD, Remacle J (1990) Glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase inactivation by peroxides and oxygen derived free radicals. Mech Aging Dev 51:283–297
Watanabe K, Inai S, Jinnouchi K, Baba S, Yagi T (2003) Expression of caspase activated deoxyribonuclease (CAD) and caspase 3 (CPP32) in the cochlea of cisplatin (CDDP)-treated guinea pigs. Auris Nasis Larynx 30:219–225
Paffenholz R, Bergstrom RA, Pasutto F, Wabnitz P, Munroe RJ, Jagla W, Heinzmann U, Marquardt lA, Bareiss A, Laufs J, Russ A, Stumm G, Schimenti JC, Bergstrom DE (2004) Vestibular defects in head-tilt mice result from mutations in Nox3, encoding an NADPH oxidase. Genes Dev 18:486–491
Flaherty JF, Fairfield HE, Spruce CA, McCarty CM, Bergstrom DE (2011) Molecular characterization of an allelic series of mutations in the mouse Nox3 gene. Mamm Genome 22:156–169
Darrat I, Ahmad N, Seidman K, Seidman MD (2007) Auditory research involving antioxidants. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 15:358–363
Guthrie OW (2008) Aminoglycoside induced ototoxicity. Toxicology 249:91–96
Henderson D, Bielefeld EC, Harris KC, Bu BH (2006) The role of oxidative stress in noise-induced hearing loss. Ear Hear 27:1–19
Rybak LP, Whitworth CA, Mukherjea D, Ramkumar V (2007) Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and prevention. Hear Res 226:157–167
Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Ramkumar V (2009) Cisplatin ototoxicity and protection: clinical and experimental studies. Tohoku J Exp JMed 219:177–186
Videhult P, Laurell G, Wallin I, Ehrsson H (2006) Kinetics of cisplatin and its monohydrated complex with sulfur-containing compounds designed for local otoprotective administration. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 231:1638–1645
Mukherjea D, Whitworth CA, Nandish S, Dunaway G, Rybak LP, Ramkumar V (2006) Expression of the kidney injury molecule 1 in the rat cochlea and induction by cisplatin. Neuroscience 139:733–740
Vaidya VS, Ozer JS, Dieterle F, Collings FB, Ramirez V, Troth S, Muniappa N, Thudium D, Gerhold D, Holder DJ, Bobadilla NA, Marrer E, Perentes E, Cordier A, Vonderscher J, Maurer G, Goering PL, Sistare PL, Bonventre JV (2010) Kidney injury molecule-1 outperforms traditional biomarkers of kidney injury in preclinical biomarker qualification studies. Nat Biotechnol 28:478–485
Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Kaur T, Sheehan KE, Ramkumar V, Rybak LP (2010) Transtympanic administration of short interfering (si)RNA for the NOX3 isoform of NADPH oxidase protects against cisplatin-induced hearing loss in the rat. Antioxid Redox Signal 13:589–598
Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Whitworth C, Bunch JR, Turner JG, Rybak LP, Ramkumar V (2008) Short interfering RNA against transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 attenuates cisplatin-induced hearing loss in the rat. J Neurosci 28:13056–13065
Bus JS, Gibson JE (1984) Paraquat: model for oxidant-initiated toxicity. Environ Health Perspect 55:37–46
Cristóvão AC, Choi DH, Baltazar G, Beal MF, Kim YS (2009) The role of NADPH oxidase 1-derived reactive oxygen species in paraquat-mediated dopaminergic cell death. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:2105–2118
Bielefeld EC, Hu BH, Harris KC, Henderson D (2005) Damage and threshold shift resulting from cochlear exposure to paraquat-generated superoxide. Hear Res 207:35–42
Nicotera TM, Ding D, McFadden SL, Salvemini D, Salvi R (2004) Paraquat-induced hair cell damage and protection with the superoxide dismutase mimetic m40403. Audiol Neurootol 9:353–362
Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Sheehan K, Kaur T, Sheth S, Bunch J, Perro C, Rybak LP, Ramkumar V (2011) NOX3 NADPH oxidase couples transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 to signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-mediated inflammation and hearing loss. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:999–1010
Acknowledgments
The authors are supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the National Institute for Deafness and other Communicative Disorders (NIDCD) grant R01-DC 02396 (L.P.R.) and F32 DC 009950 (D.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rybak, L.P., Mukherjea, D., Jajoo, S. et al. siRNA-mediated knock-down of NOX3: therapy for hearing loss?. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 69, 2429–2434 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1016-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1016-3