Abstract
Rationale
Kappa agonists can attenuate reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior induced by cocaine priming. The mechanisms underlying this effect have not been characterized fully but may have a serotonergic component as kappa agonists also increase the release of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT).
Objectives
This study investigated the role of kappa opioid receptor and 5-HT mechanisms in kappa agonist-induced attenuation of cocaine priming in monkeys.
Methods
Squirrel monkeys were trained to self-administer cocaine (0.18–0.3 mg/kg/injection) under a second-order schedule in which drug seeking was maintained jointly by cocaine injections and a cocaine-paired visual stimulus. In extinction sessions, saline was substituted for cocaine, and the cocaine-paired stimulus was omitted. During test sessions, only saline was available for self-administration, and response-contingent presentations of the cocaine-paired stimulus were restored.
Results
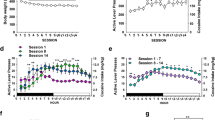
Priming injections of cocaine (0.1–1.0 mg/kg) induced reinstatement of drug seeking. Maximal levels of responding were similar to those maintained by active cocaine self-administration. Pretreatment with the kappa agonists enadoline (0.01 mg/kg) and spiradoline (0.3 mg/kg) or the 5-HT transport inhibitors fluoxetine (5.6 mg/kg) and citalopram (10.0 mg/kg) attenuated the priming effects of cocaine, shifting the cocaine dose–response function rightward and downward. Inhibition of cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug seeking by spiradoline and fluoxetine was reversed by R(+)8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (0.03 mg/kg), a 5HT1A agonist that inhibits 5-HT release. The effects of spiradoline also were reversed by the kappa antagonist nor-binaltorphimine (10.0 mg/kg).
Conclusions
Results suggest that the capacity of kappa opioid agonists to increase extracellular 5-HT levels may at least partially underlie kappa agonist-induced modulation of cocaine seeking.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker EL, Kimmel HL, Blakely RD (1994) Chimeric human and rat serotonin transporters reveal domains involved in recognition of transporter ligands. Mol Pharmacol 46:799–807
Berger B, Rothmaier AK, Wedekind F, Zentner J, Feuerstein TJ, Jackisch R (2006) Presynaptic opioid receptors on noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons in the human as compared to the rat neocortex. Br J Pharmacol 148:795–806
Bronson ME, Lin YP, Burchett K, Picker MJ, Dykstra LA (1993) Serotonin involvement in the discriminative stimulus effects of kappa opioids in pigeons. Psychopharmacology 111:69–77
Burmeister JJ, Lungren EM, Neisewander JL (2003) Effects of fluoxetine and d-fenfluramine on cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 168:146–154
Carey GJ, Bergman J (2001) Enadoline discrimination in squirrel monkeys: effects of opioid agonists and antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:215–223
Carey AN, Borozny K, Aldrich JV, McLaughlin JP (2007) Reinstatement of cocaine place-conditioning prevented by the peptide kappa-opioid receptor antagonist arodyn. Eur J Pharmacol 569:84–89
Cunningham KA, Callahan PM (1991) Monoamine reuptake inhibitors enhance the discriminative state induced by cocaine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 104:177–180
Czoty PW, Ginsburg BC, Howell LL (2002) Serotonergic attenuation of the reinforcing and neurochemical effects of cocaine in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300:831–837
Czoty PW, McCabe C, Nader MA (2005) Effects of the 5-HT1A agonist (±)-8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) on cocaine choice in cynomolgus monkeys. Behav Pharmacol 16:187–191
Devine DP, Leone P, Pocock D, Wise RA (1993) Differential involvement of ventral tegmental mu, delta and kappa opioid receptors in modulation of basal mesolimbic dopamine release: in vivo microdialysis studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:1236–1246
Di Chiara G, Imperato A (1988) Opposite effects of mu and kappa opiate agonists on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and in the dorsal caudate of freely moving rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:1067–1080
Glick SD, Maisonneuve IM, Raucci J, Archer S (1995) Kappa opioid inhibition of morphine and cocaine self-administration in rats. Brain Res 681:147–152
Hjorth S, Magnusson T (1988) The 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT, preferentially activates cell body 5-HT autoreceptors in rat brain in vivo. Naunyn-Schmeideberg’s Arch Pharmacol 338:463–471
Ho BY, Takemori AE (1989) Serotonergic involvement in the antinociceptive action of and the development of tolerance to the kappa-opioid receptor agonist, U-50, 488H. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250:508–514
Ho BY, Takemori AE (1990) Release by U-50, 488H of [3H]serotonin from brain slices and spinal cord synaptosomes of U-50, 488H-tolerant and nontolerant mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254:8–12
Howell LL, Byrd LD (1995) Serotonergic modulation of the behavioural effects of cocaine in the squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:1551–1559
Kalyuzhny AE, Wessendorf MW (1999) Serotonergic and GABAergic neurons in the medial rostral ventral medulla express kappa-opioid receptor immunoreactivity. Neuroscience 90:229–234
Khroyan TV, Barrett-Larimore RL, Rowlett JK, Spealman RD (2000) Dopamine D1- and D2-like receptor mechanisms in relapse to cocaine-seeking behaviour: effects of selective antagonists and agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:680–687
Limebeer CL, Litt DE, Parker LA (2009) Effect of 5-HT3 antagonists and a 5-HT1A agonist on fluoxetine-induced conditioned gaping reactions in rats. Psychopharmacology 203:763–770
McLaughlin JP, Marton-Popovici M, Chavkin C (2003) Kappa opioid receptor antagonism and prodynorphin gene disruption block stress-induced behavioural responses. J Neurosci 23:5674–5683
McLaughlin JP, Land BB, Li S, Pintar JE, Chavkin C (2006) Prior activation of kappa opioid receptors by U50, 488 mimics repeated forced swim stress to potentiate cocaine place preference conditioning. Neuropharmacology 31:787–794
Mello NK, Negus SS (1998) Effects of kappa opioid agonists on cocaine- and food-maintained responding by rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:812–824
Miller GM, Yatin SM, De La Garza R II, Goulet M, Madras BK (2001) Cloning of dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin transporters from monkey brain: relevance to cocaine sensitivity. Mol Brain Res 87:124–143
Müller CP, Carey RJ, Salloum JB, Huston JP (2003) Serotonin1A-receptor agonism attenuates the cocaine-induced increase in serotonin levels in the hippocampus and nucleus accumbens but potentiates hyperlocomotion: an in vivo microdialysis study. Neuropharmacology 44:592–603
Negus SS, Mello NK, Portoghese PS, Lin CE (1997) Effects of kappa opioids on cocaine self-administration by rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282:44–55
Pinnock RD (1992) Activation of kappa-opioid receptors depresses electrically evoked excitatory postsynaptic potentials on 5-HT-sensitive neurones in the rat dorsal raphé nucleus in vitro. Brain Res 583:237–246
Pitts RC, Dykstra LA (1994) Antinociceptive and response rate-altering effects of kappa opioid agonists, spiradoline, enadoline and U69, 593, alone and in combination with opioid antagonists in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:1501–1508
Platt DM, Carey GJ, Spealman RD (2005) Intravenous self-administration techniques in monkeys. In: Enna S, Williams M, Ferkany J, Kenakin T, Porsolt R, Sullivam J (eds) Current protocols in neuroscience. Wiley, New York, pp 9.21.1–9.21.15
Platt DM, Rowlett JK, Spealman RD (2007) Noradrenergic mechanisms in cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug seeking in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322:894–902
Portas CM, Thakkar M, Rainnie D, McCarley RW (1996) Microdialysis perfusion of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) in the dorsal raphe nucleus decreases serotonin release and increases rapid eye movement sleep in the freely moving cat. J Neurosci 16:2820–2828
Powell KR, Dykstra LA (1995) The role of serotonin in the effects of opioids in squirrel monkeys responding under a titration procedure: I. Kappa opioids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:1305–1316
Powell KR, Holtzman SG (1999) Differential antagonism of the rate-decreasing effects of κ-opioid receptor agonists by naltrexone and norbinaltorphimine. Eur J Pharmacol 377:21–28
Powell KR, Picker MJ, Dykstra LA (1994) Serotonin involvement in the discriminative stimulus effects of mu and kappa opioids in rats. Behav Pharmacol 5:255–264
Redila VA, Chavkin C (2008) Stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking is mediated by the kappa opioid system. Psychopharmacology 200:59–70
Schama KF, Howell LL, Byrd LD (1997) Serotonergic modulation of the discriminative-stimulus effects of cocaine in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacology 132:27–34
Schenk S, Partridge B, Shippenberg TS (1999) U69593, a kappa-opioid agonist, decreases cocaine self-administration and decreases cocaine-produced drug-seeking. Psychopharmacology 144:339–346
Schenk S, Partridge B, Shippenberg TS (2000) Reinstatement of extinguished drug-taking behavior in rats: effect of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist, U69593. Psychopharmacology 151:85–90
Spanagel R, Herz A, Shippenberg TS (1990) The effects of opioid peptides on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem 55:1734–1740
Spealman RD (1993) Modification of the behavioral effects of cocaine by selective serotonin and dopamine uptake inhibitors in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacology 112:93–99
Spealman RD, Bergman J (1992) Modulation of the discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine by mu and kappa opioids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:607–615
Spealman RD, Bergman J (1994) Opioid modulation of the discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine: comparison of μ, κ and δ agonists in squirrel monkeys discriminating low doses of cocaine. Behav Pharmacol 5:21–31
Spealman RD, Lee B, Tiefenbacher S, Platt DM, Rowlett JK, Khroyan TV (2004) Triggers of relapse: nonhuman primate models of reinstated cocaine seeking. In: Bevins RA, Bardo MT (eds) Motivational factors in the etiology of drug abuse. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, pp 57–84
Szumlinski KK, Frys KA, Kalivas PW (2004) Dissociable roles for the dorsal and median raphé in the facilitatory effect of 5-HT1A receptor stimulation upon cocaine-induced locomotion and sensitization. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1675–1687
Tella SR (1995) Effects of monoamine reuptake inhibitors on cocaine self-administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 51:687–692
Thompson AC, Zapata A, Justice JB Jr, Vaughan RA, Sharpe LG, Shippenberg TS (2000) Kappa-opioid receptor activation modified dopamine uptake in the nucleus accumbens and opposes the effects of cocaine. J Neurosci 20:9333–9340
Tran-Nguyen LTL, Bellew JG, Grote KA, Neisewander JL (2001) Serotonin depletion attenuates cocaine seeking but enhances sucrose seeking and the effects of cocaine priming on reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 157:340–348
Valdez GR, Platt DM, Rowlett JK, Rüedi-Bettschen D, Spealman RD (2007) κ agonist-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in squirrel monkeys: a role for opioid and stress-related mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:525–533
Von Voigtlander PF, Lewis RA, Neff GL (1984) Kappa opioid analgesia is dependent on serotonergic mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 231:270–274
Walker JM, Thompson LA, Frascella J, Friederich MW (1987) Opposite effects of mu and kappa opiates on the firing-rate of dopamine cells in the substantia nigra of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 134:53–59
Walsh SL, Cunningham KA (1997) Serotonergic mechanisms involved in the discriminative stimulus, reinforcing and subjective effects of cocaine. Psychopharmacology 130:41–58
Acknowledgments
We thank Kristen Bano, Annemarie Duggan, and Donna Reed for expert technical assistance. This research was supported by DA11928, DA11054, and RR00168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rüedi-Bettschen, D., Rowlett, J.K., Spealman, R.D. et al. Attenuation of cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug seeking in squirrel monkeys: kappa opioid and serotonergic mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 210, 169–177 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1705-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1705-2