Abstract
Rationale
Both glutamate and serotonin (5-HT) play a key role in the pathophysiology of emotional biases. Recent studies indicate that the glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist ketamine and the 5-HT receptor agonist psilocybin are implicated in emotion processing. However, as yet, no study has systematically compared their contribution to emotional biases.
Objectives
This study used event-related potentials (ERPs) and signal detection theory to compare the effects of the NMDA (via S-ketamine) and 5-HT (via psilocybin) receptor system on non-conscious or conscious emotional face processing biases.
Methods
S-ketamine or psilocybin was administrated to two groups of healthy subjects in a double-blind within-subject placebo-controlled design. We behaviorally assessed objective thresholds for non-conscious discrimination in all drug conditions. Electrophysiological responses to fearful, happy, and neutral faces were subsequently recorded with the face-specific P100 and N170 ERP.
Results
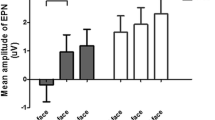
Both S-ketamine and psilocybin impaired the encoding of fearful faces as expressed by a reduced N170 over parieto-occipital brain regions. In contrast, while S-ketamine also impaired the encoding of happy facial expressions, psilocybin had no effect on the N170 in response to happy faces.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the NMDA and 5-HT receptor systems differentially contribute to the structural encoding of emotional face expressions as expressed by the N170. These findings suggest that the assessment of early visual evoked responses might allow detecting pharmacologically induced changes in emotional processing biases and thus provides a framework to study the pathophysiology of dysfunctional emotional biases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel KM, Allin MP, Kucharska-Pietura K, David A, Andrew C, Williams S, Brammer MJ, Phillips ML (2003) Ketamine alters neural processing of facial emotion recognition in healthy men: an fMRI study. Neuroreport 14:387–391
Adolphs R (2003) Cognitive neuroscience of human social behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:165–178
Amaral DG, Behniea H, Kelly JL (2003) Topographic organization of projections from the amygdala to the visual cortex in the macaque monkey. Neuroscience 118:1099–1120
Ashley V, Vuilleumier P, Swick D (2004) Time course and specificity of event-related potentials to emotional expressions. Neuroreport 15:211–216
Balconi M, Lucchiari C (2008) Consciousness and arousal effects on emotional face processing as revealed by brain oscillations. A gamma band analysis. Int J Psychophysiol 67:41–46
Bar M, Tootell RB, Schacter DL, Greve DN, Fischl B, Mendola JD, Rosen BR, Dale AM (2001) Cortical mechanisms specific to explicit visual object recognition. Neuron 29:529–535
Batty M, Taylor MJ (2003) Early processing of the six basic facial emotional expressions. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 17:613–620
Bernat E, Bunce S, Shevrin H (2001) Event-related brain potentials differentiate positive and negative mood adjectives during both supraliminal and subliminal visual processing. Int J Psychophysiol 42:11–34
Bhagwagar Z, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM, Harmer CJ (2004) Normalization of enhanced fear recognition by acute SSRI treatment in subjects with a previous history of depression. Am J Psychiatry 161:166–168
Blau VC, Maurer U, Tottenham N, McCandliss BD (2007) The face-specific N170 component is modulated by emotional facial expression. Behav Brain Funct 3:7
Bressler SL, Tang W, Sylvester CM, Shulman GL, Corbetta M (2008) Top-down control of human visual cortex by frontal and parietal cortex in anticipatory visual spatial attention. J Neurosci 28:10056–10061
Brosch T, Sander D, Pourtois G, Scherer KR (2008) Beyond fear: rapid spatial orienting toward positive emotional stimuli. Psychol Sci 19:362–370
Browning M, Reid C, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM, Harmer CJ (2007) A single dose of citalopram increases fear recognition in healthy subjects. J Psychopharmacol 21:684–690
Carter OL, Burr DC, Pettigrew JD, Wallis GM, Hasler F, Vollenweider FX (2005) Using psilocybin to investigate the relationship between attention, working memory, and the serotonin 1A and 2A receptors. J Cogn Neurosci 17:1497–1508
Deffke I, Sander T, Heidenreich J, Sommer W, Curio G, Trahms L, Lueschow A (2007) MEG/EEG sources of the 170-ms response to faces are co-localized in the fusiform gyrus. NeuroImage 35:1495–1501
Degabriele R, Lagopoulos J, Malhi G (2011) Neural correlates of emotional face processing in bipolar disorder: an event-related potential study. J Affect Disord 133:212–220
Del-Ben CM, Deakin JF, McKie S, Delvai NA, Williams SR, Elliott R, Dolan M, Anderson IM (2005) The effect of citalopram pretreatment on neuronal responses to neuropsychological tasks in normal volunteers: an FMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1724–1734
Derogatis L (1994) SCL-90-R: Symptom Checklist-90-R. Administration, scoring and procedures manual. National Computer Systems, Minneapolis
Diazgranados N, Ibrahim L, Brutsche NE, Newberg A, Kronstein P, Khalife S, Kammerer WA, Quezado Z, Luckenbaugh DA, Salvadore G, Machado-Vieira R, Manji HK, Zarate CA (2010) A randomized add-on trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant bipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67:793–802
Dima D, Stephan KE, Roiser JP, Friston KJ, Frangou S (2011) Effective connectivity during processing of facial affect: evidence for multiple parallel pathways. J Neurosci 31:14378–14385
Dittrich A (1975) Zusammenstellung eines Fragebogens (APZ) zur Erfassung abnormer psychischer Zustände [Construction of a questionnaire (APZ) for assessing abnormal mental states]. Z Klin Psychol Psychiatr Psychother 23:12–20
Dittrich A (1998) The standardized psychometric assessment of altered states of consciousness (ASCs) in humans. Pharmacopsychiatry 31:80–84
Eimer M, Holmes A (2002) An ERP study on the time course of emotional face processing. Neuroreport 13:427–431
Ekman P, Friesen W (1976) Pictures of facial affect. Consulting Psychologists, Palo Alto
Elliott R, Zahn R, Deakin JF, Anderson IM (2011) Affective cognition and its disruption in mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:153–182
Fairhall SL, Ishai A (2007) Effective connectivity within the distributed cortical network for face perception. Cereb Cortex 17:2400–2406
Feng N, Vollenweider FX, Minder EI, Rentsch K, Grampp T, Vonderschmitt DJ (1995) Development of a gas chromatography–mass spectrometry method for determination of ketamine in plasma and its application to human samples. Ther Drug Monit 17:95–100
Fichtenholtz HM, Hopfinger JB, Graham R, Detwiler JM, LaBar KS (2009) Event-related potentials reveal temporal staging of dynamic facial expression and gaze shift effects on attentional orienting. Soc Neurosci 4:317–331
Freese JL, Amaral DG (2005) The organization of projections from the amygdala to visual cortical areas TE and V1 in the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol 486:295–317
Frühholz S, Jellinghaus A, Herrmann M (2011) Time course of implicit processing and explicit processing of emotional faces and emotional words. Biol Psychol 87:265–274
Gazzaley A, Cooney JW, McEvoy K, Knight RT, D’Esposito M (2005) Top-down enhancement and suppression of the magnitude and speed of neural activity. J Cogn Neurosci 17:507–517
Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E, Thelen B, Maier S, Heekeren K, Kovar KA, Sass H, Spitzer M (2002) Effects of the hallucinogen psilocybin on covert orienting of visual attention in humans. Neuropsychobiology 45:205–212
Grob CS, Danforth AL, Chopra GS, Hagerty M, McKay CR, Halberstadt AL, Greer GR (2011) Pilot study of psilocybin treatment for anxiety in patients with advanced-stage cancer. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:71–78
Harmer CJ (2008) Serotonin and emotional processing: does it help explain antidepressant drug action? Neuropharmacology 55:1023–1028
Harmer CJ, Bhagwagar Z, Perrett DI, Völlm BA, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2003) Acute SSRI administration affects the processing of social cues in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:148–152
Harmer CJ, Shelley NC, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2004) Increased positive versus negative affective perception and memory in healthy volunteers following selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition. Am J Psychiatry 161:1256–1263
Hasler F, Bourquin D, Brenneisen R, Vollenweider FX (2002) Renal excretion profiles of psilocin following oral administration of psilocybin: a controlled study in man. J Pharm Biomed Anal 30:331–339
Hasler F, Grimberg U, Benz M, Huber T, Vollenweider F (2004) Acute psychological and physiological effects of psilocybin in healthy humans: a double-blind, placebo-controlled dose–effect study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 172:145–156
Herrington JD, Taylor JM, Grupe DW, Curby KM, Schultz RT (2011) Bidirectional communication between amygdala and fusiform gyrus during facial recognition. NeuroImage 56:2348–2355
Ishai A (2007) Sex, beauty and the orbitofrontal cortex. Int J Psychophysiol 63:181–185
Itier RJ, Taylor MJ (2004) N170 or N1? Spatiotemporal differences between object and face processing using ERPs. Cereb Cortex 14:132–142
Jaworska N, Thompson A, Shah D, Fisher D, Ilivitsky V, Knott V (2010) Electrocortical effects of acute tryptophan depletion on emotive facial processing in depression-prone individuals. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 20:473–486
Kemp AH, Gray MA, Line P, Silberstein RB, Nathan PJ (2003) Preliminary electrophysiological evidence for modulation of the processing of negative effect by serotonin. Brain Cogn 51:198–200
Kemp AH, Gray MA, Silberstein RB, Armstrong SM, Nathan PJ (2004) Augmentation of serotonin enhances pleasant and suppresses unpleasant cortical electrophysiological responses to visual emotional stimuli in humans. NeuroImage 22:1084–1096
Kerestes R, Labuschagne I, Croft RJ, O’Neill BV, Bhagwagar Z, Phan KL, Nathan PJ (2009) Evidence for modulation of facial emotional processing bias during emotional expression decoding by serotonergic and noradrenergic antidepressants: an event-related potential (ERP) study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 202:621–634
Kometer M, Schmidt A, Bachmann R, Studerus E, Seifritz E, Vollenweider FX (2012) Psilocybin Biases Facial Recognition, Goal-Directed Behavior, and Mood State Toward Positive Relative to Negative Emotions Through Different Serotonergic Subreceptors. Biol Psychiatry. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.04.005
Krolak-Salmon P, Fischer C, Vighetto A, Mauguière F (2001) Processing of facial emotional expression: spatio-temporal data as assessed by scalp event-related potentials. Eur J Neurosci 13:987–994
Krombholz A, Schaefer F, Boucsein W (2007) Modification of N170 by different emotional expression of schematic faces. Biol Psychol 76:156–162
Krystal J, Karper L, Seibyl J, Freeman G, Delaney R, Bremner J, Heninger G, Bowers MJ, Charney D (1994) Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, ketamine, in humans. Psychotomimetic, perceptual, cognitive, and neuroendocrine responses. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:199–214
Labuschagne I, Croft RJ, Phan KL, Nathan PJ (2010) Augmenting serotonin neurotransmission with citalopram modulates emotional expression decoding but not structural encoding of moderate intensity sad facial emotional stimuli: an event-related potential (ERP) investigation. J Psychopharmacol 24:1153–1164
Lee TW, Girolami M, Sejnowski TJ (1999) Independent component analysis using an extended infomax algorithm for mixed subgaussian and supergaussian sources. Neural Comput 11:417–441
Macmillan N, Creelman C (1991) Detection theory: a user’s guide. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Marini F, Marzi T, Viggiano MP (2011) “Wanted!” The effects of reward on face recognition: electrophysiological correlates. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 11:627–643
Morgan CJ, Mofeez A, Brandner B, Bromley L, Curran HV (2004) Acute effects of ketamine on memory systems and psychotic symptoms in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:208–218
Nathan PJ, Kemp AH, Harrison BJ (2003) Antidepressants and emotional processing. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1383, author reply 1384–5
Newcomer JW, Farber NB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Selke G, Melson AK, Hershey T, Craft S, Olney JW (1999) Ketamine-induced NMDA receptor hypofunction as a model of memory impairment and psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:106–118
Nichols DE (2004) Hallucinogens. Pharmacol Ther 101:131–181
Noll LK, Mayes LC, Rutherford HJ (2012) Investigating the impact of parental status and depression symptoms on the early perceptual coding of infant faces: an event-related potential study. Soc Neurosci. doi:10.1080/17470919.2012.672457
Nutt DJ, Forshall S, Bell C, Rich A, Sandford J, Nash J, Argyropoulos S (1999) Mechanisms of action of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of psychiatric disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 9(Suppl 3):S81–S86
Passie T, Seifert J, Schneider U, Emrich HM (2002) The pharmacology of psilocybin. Addict Biol 7:357–364
Pegna AJ, Landis T, Khateb A (2008) Electrophysiological evidence for early non-conscious processing of fearful facial expressions. Int J Psychophysiol 70:127–136
Pegna AJ, Darque A, Berrut C, Khateb A (2011) Early ERP modulation for task-irrelevant subliminal faces. Front Psychol 2:88
Pessoa L, Padmala S (2005) Quantitative prediction of perceptual decisions during near-threshold fear detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:5612–5617
Pessoa L, Japee S, Sturman D, Ungerleider LG (2006) Target visibility and visual awareness modulate amygdala responses to fearful faces. Cereb Cortex 16:366–375
Pourtois G, Vuilleumier P (2006) Dynamics of emotional effects on spatial attention in the human visual cortex. Prog Brain Res 156:67–91
Pourtois G, Grandjean D, Sander D, Vuilleumier P (2004) Electrophysiological correlates of rapid spatial orienting towards fearful faces. Cereb Cortex 14:619–633
Quednow BB, Kometer M, Geyer MA, Vollenweider FX (2011) Psilocybin-induced deficits in automatic and controlled inhibition are attenuated by ketanserin in healthy human volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:630–640
Rose M, Schmid C, Winzen A, Sommer T, Büchel C (2005) The functional and temporal characteristics of top-down modulation in visual selection. Cereb Cortex 15:1290–1298
Rossion B, Jacques C (2008) Does physical interstimulus variance account for early electrophysiological face sensitive responses in the human brain? Ten lessons on the N170. NeuroImage 39:1959–1979
Rossion B, Joyce CA, Cottrell GW, Tarr MJ (2003) Early lateralization and orientation tuning for face, word, and object processing in the visual cortex. NeuroImage 20:1609–1624
Sadeh B, Podlipsky I, Zhdanov A, Yovel G (2010) Event-related potential and functional MRI measures of face-selectivity are highly correlated: a simultaneous ERP-fMRI investigation. Hum Brain Mapp 31:1490–1501
Santesso DL, Meuret AE, Hofmann SG, Mueller EM, Ratner KG, Roesch EB, Pizzagalli DA (2008) Electrophysiological correlates of spatial orienting towards angry faces: a source localization study. Neuropsychologia 46:1338–1348
Schmidt A, Bachmann R, Kometer M, Csomor PA, Stephan KE, Seifritz E, Vollenweider FX (2011) Mismatch negativity encoding of prediction errors predicts S-ketamine-induced cognitive impairments. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:865–875
Schneider W, Eschman A, Zuccolotto A (2002) E-prime reference guide. Psychology Software Tools, Pittsburgh
Schultz RT, Grelotti DJ, Klin A, Kleinman J, Van der Gaag C, Marois R, Skudlarski P (2003) The role of the fusiform face area in social cognition: implications for the pathobiology of autism. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 358:415–427
Schyns PG, Petro LS, Smith ML (2007) Dynamics of visual information integration in the brain for categorizing facial expressions. Curr Biol 17:1580–1585
Sheehan D, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan K, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E, Hergueta T, Baker R, Dunbar G (1998) The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychiatry 59:22–33
Singer T, Kiebel SJ, Winston JS, Dolan RJ, Frith CD (2004) Brain responses to the acquired moral status of faces. Neuron 41:653–662
Smith ML (2011) Rapid processing of emotional expressions without conscious awareness. Cereb Cortex 22:1748–1760
Sokhadze EM, Tasman A, Tamas R, El-Mallakh RS (2011) Event-related potential study of the effects of emotional facial expressions on task performance in euthymic bipolar patients. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 36:1–13
Sprengelmeyer R, Jentzsch I (2006) Event related potentials and the perception of intensity in facial expressions. Neuropsychologia 44:2899–2906
Stekelenburg JJ, de Gelder B (2004) The neural correlates of perceiving human bodies: an ERP study on the body-inversion effect. Neuroreport 15:777–780
Studerus E, Gamma A, Vollenweider F (2010) Psychometric evaluation of the altered states of consciousness rating scale (OAV). PLoS One 5:e12412
Studerus E, Kometer M, Hasler F, Vollenweider FX (2011) Acute, subacute and long-term subjective effects of psilocybin in healthy humans: a pooled analysis of experimental studies. J Psychopharmacol 25:1434–1452
Tamietto M, de Gelder B (2010) Neural bases of the non-conscious perception of emotional signals. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:697–709
Vollenweider F, Kometer M (2010) The neurobiology of psychedelic drugs: implications for the treatment of mood disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:642–651
Vollenweider FX, Leenders KL, Scharfetter C, Antonini A, Maguire P, Missimer J, Angst J (1997) Metabolic hyperfrontality and psychopathology in the ketamine model of psychosis using positron emission tomography (PET) and [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 7:9–24
Vuilleumier P, Pourtois G (2007) Distributed and interactive brain mechanisms during emotion face perception: evidence from functional neuroimaging. Neuropsychologia 45:174–194
Williams LM, Liddell BJ, Rathjen J, Brown KJ, Gray J, Phillips M, Young A, Gordon E (2004) Mapping the time course of nonconscious and conscious perception of fear: an integration of central and peripheral measures. Hum Brain Mapp 21:64–74
Wittchen HU, Pfister H (1997) DIA-X-Interviews: Manual für Screening-Verfahren und Interview. Swets & Zeitlinger, Frankfurt
Wronka E, Walentowska W (2011) Attention modulates emotional expression processing. Psychophysiology 48:1047–1056
Zarate CA, Singh JB, Carlson PJ, Brutsche NE, Ameli R, Luckenbaugh DA, Charney DS, Manji HK (2006) A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:856–864
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the Swiss Neuromatrix Foundation (AS, MK, RB, FXV) and the Heffter Research Center Zurich (FXV).
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any financial, personal, or organizational conflicts of interest to report in relation to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, A., Kometer, M., Bachmann, R. et al. The NMDA antagonist ketamine and the 5-HT agonist psilocybin produce dissociable effects on structural encoding of emotional face expressions. Psychopharmacology 225, 227–239 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2811-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2811-0