Abstract
Rationale
Drug addicts constantly relapse to drug seeking after recall of memories linked to the drug experience. It is believed that a successful application of therapies that block memory reconsolidation may end the continuous cycle of drug relapse.
Objectives
The purpose of this study is to investigate whether modulation of the endocannabinoid system would impact the reconsolidation of opioid-related hedonic memories in rats previously paired to morphine context.
Methods
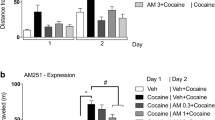
Male Wistar rats were trained to acquire a morphine-conditioned place preference (CPP). One week later, morphine-CPP memory was reactivated by a brief exposure to a drug-paired context. Immediately after the memory reactivation session, independent groups of morphine-trained rats received a single subcutaneous injection of different doses of cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant, CB2-selective antagonist AM630, potent CB1/CB2 agonist WIN 55,212-2, inhibitor of enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase URB597, or vehicle. Morphine-CPP was retested 1 and 2 weeks after reactivation.
Results
Blockade of CB1 (but not CB2) cannabinoid receptors impaired CPP reconsolidation of morphine-CPP at both tests 1 and 2 weeks post-reactivation, whereas direct activation of cannabinoid receptors did not produce significant effects on morphine-induced CPP. However, boosting endocannabinoid signaling by inhibition of anandamide metabolism promoted a transient CB1-dependent enhancement of the CPP.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blednov YA, Cravatt BF, Boehm SL, Walker D, Harris RA (2007) Role of endocannabinoids in alcohol consumption and intoxication: studies of mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1570–1582
Braida D, Pozzi M, Parolaro D, Sala M (2001) Intracerebral self-administration of the cannabinoid receptor agonist CP 55,940 in the rat: interaction with the opioid system. Eur J Pharmacol 413:227–234
Brown TE, Lee BR, Sorg BA (2008) The NMDA antagonist MK-801 disrupts reconsolidation of a cocaine-associated memory for conditioned place preference but not for self-administration in rats. Learn Mem 15(12):857–865
Bucherelli C, Baldi E, Mariottini C, Passani MB, Blandina P (2006) Aversive memory reactivation engages in the amygdala only some neurotransmitters involved in consolidation. Learn Mem 13:426–430
Chaperon F, Soubrie P, Puech AJ, Thiebot MH (1998) Involvement of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors in the establishment of place conditioning in rats. Psychopharmacology 135:324–332
de Oliveira Alvares L, Pasqualini Genro B, Diehl F, Molina VA, Quillfeldt JA (2008) Oposite action of hippocampal CB1 receptors in memory reconsolidation and extinction. Neuroscience 154(4):1648–1655
De Vries TJ, Schoffelmeer ANM (2005) Cannabinoid CB1 receptors control conditioned drug seeking. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26(8):420–426
Epstein DH, Preston KL, Stewart J, Shaham Y (2006) Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 189:1–16
Fang Q, Li FQ, Li YQ, Xue YX, He YY, Liu JF, Lu L, Wang JS (2011) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant disrupts nicotine reward associated memory in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99:738–742
Fattore L, Deiana S, Spano SM, Cossu G, Fadda P, Scherma M, Fratta W (2005) Endocannabinoid system and opioid addiction: behavioural aspects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81(2):343–359
Fegley D, Gaetani S, Duranti A, Tontini A, Mor M, Tarzia G, Piomelli D (2005) Characterization of the fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor cyclohexyl carbamic acid 3′-carbamoyl-biphenyl-3-yl ester (URB597): effects on anandamide oleoylethanolamide deactivation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:352–358
Gamaleddin I, Zvonok A, Makriyannis A, Goldberg SR, Le Foll B (2012) Effects of a selective cannabinoid CB2 agonist and antagonist on intravenous nicotine self administration and reinstatement of nicotine seeking. PLoS One 7(1):e 29900
Gobbi G, Bambico FR, Manqieri R, Bortalato M, Campolongo P, Solinas M, Cassano T et al (2005) Antidepressant like activity and modulation of brain monominergic transmission by blockade of anandaminde hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:18620–18625
Harloe JP, Thorpe AJ, Lichtman AH (2008) Differential endocannabinoid regulation of extinction in appetitive and aversive Barnes maze tasks. Learn Mem 15:806–809
Ishiguro H, Iwasaki S, Teasenfitz L, Higuchi S, Horiuchi Y, Saito T, Arinami T et al (2007) Involvement of cannabinoid CB2 receptor in alcohol preference in mice and alcoholism in humans. Pharmacogenomics J 7:380–385
Justinova Z, Mangieri RA, Bortolato M, Chefer SI, Mukhin AG, Clapper JR, King AR et al (2008) Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition heightens anandamide signaling without producing reinforcing effects in primates. Biol Psychiatry 64:930–937
Kathuria S, Gaetani S, Fegley D, Valino F, Duranti A, Tontini A, Mor M et al (2003) Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Nat Med 9:76–81
Katona I, Rancz EA, Acsady L, Ledent C, Mackie K, Hajos N, Freund TF (2001) Distribution of CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the amygdala and their role in the control of GABAergic transmission. J Neurosci 21:9506–9518
Kobilo T, Hazvi S, Dudai Y (2007) Role of cortical cannabinoid CB1 receptor in conditioned taste aversion memory. Eur J Neurosci 25:3417–3421
Lin HC, Mao SC, Gean PW (2006) Effects of intra-amygdala infusion of CB1 receptor agonists on the reconsolidation of fear potentiated startle. Learn Mem 13:316–321
Lutz B (2007) The endocannabinoid system and extinction learning. Mol Neurobiol 36:92–101
Maldonado R, Valverde O, Berrendero F (2006) Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in drug addiction. Trends Neurosci 29(4):225–232
Manwell LA, Satvat E, Lang ST, Allen CP, Leri F, Parker LA (2009) FAAH inhibitor, URB-597, promotes extinction and CB1 antagonist, SR141716, inhibits extinction of conditioned aversion produced by naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal, but not extinction of conditioned preference produced by morphine in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94:154–162
Marsicano G, Wotjak CT, Azad SC, Bisogno T, Rammes G, Cascio MG, Hermann H et al (2002) The endogenous cannabinoid system controls extinction of aversive memories. Nature 418:530–534
Martin M, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Maldonado R, Valverde O (2000) Cocaine, but not morphine, induces conditioned place preference and sensitization to locomotor responses in CB1 knockout mice. Eur J Neurosci 12:4038–4046
Mazzola C, Medalie J, Scherma M, Panlilio LV, Solinas M, Tanda G, Drago F et al (2009) Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibition enhances memory acquisition through activation of PPAR-alpha nuclear receptors. Learn Mem 16:332–337
Milekic MH, Brown SD, Castellini C, Alberini CM (2006) Persistent disruption of an established morphine conditioned place preference. J Neurosci 26:3010–3020
Milton AL, Everitt BJ (2010) The psychological and neurochemical mechanisms of drug memory reconsolidation: implications for the treatment of addiction. Eur J Neurosci 31:2308–2319
Nader K (2003) Memory traces unbound. Trends Neurosci 26:65–72
Niyuhire F, Varvel SA, Thorpe AJ, Stokes RJ, Wiley JL, Lichtman AH (2007) The disruptive effects of the CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant on extinction learning in mice are task-specific. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 191:223–231
O'Brien CP, Childress AR, McLellan AT, Ehrman R (1992) Classical conditioning in drug-dependent humans. Ann N Y Acad Sci 654:400–415
O'Sullivan SE (2007) Cannabinoids go nuclear: evidence for activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Br J Pharmacol 152:576–582
Pamplona FA, Prediger RD, Pandolfo P, Takahashi RN (2006) The cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2 facilitates the extinction of contextual fear memory and spatial memory in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 188:641–649
Pamplona FA, Bitencourt RM, Takahashi RN (2008) Short- and long-term effects of cannabinoids on the extinction of contextual fear memory in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90(1):290–293
Pandolfo P, Vendruscolo LF, Sordi R, Takahashi RN (2009) Cannabinoid-induced conditioned place preference in the spontaneously hypertensive rat-an animal model of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 205(2):319–326
Pickel VM, Chan J, Kash TL, Rodriguez JJ, MacKie K (2004) Compartment-specific localization of cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and micro-opioid receptors in rat nucleus accumbens. Neuroscience 27:101–112
Robbins TW, Ersche KD, Everitt BJ (2008) Drug addiction and the memory systems of the brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1141:1–21
Scherma M, Panlilio LV, Fadda P, Fattore L, Gamaleddin I, Le Foll B, Justinová Z et al (2008) Inhibition of anandamide hydrolysis by cyclohexyl carbamic acid 3′-carbamoyl-3-ylester (URB597) reverses abuse-related behavioral and neurochemical effects of nicotine in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 327:482–490
Singh ME, Verty AN, McGregor IS, Mallet PE (2004) A cannabinoid receptor antagonist attenuates conditioned place preference but not behavioural sensitization to morphine. Brain Res 1026(2):244–253
Solinas M, Panlilio LV, Tanda G, Makriyannis A, Matthews SA, Goldberg SR (2005) Cannabinoid agonists but not inhibitors of endogenous cannabinoid transport or metabolism enhance the reinforcing efficacy of heroin in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:2046–2057
Starowicz K, Nigam S, Di Marzo V (2007) Biochemistry and pharmacology of endovanilloids. Pharmacol Ther 114(1):13–33
Suzuki A, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW, Masushige S, Silva AJ, Kida S (2004) Memory reconsolidation and extinction have distinct temporal and biochemical signatures. J Neurosci 24(20):4787–4795
Suzuki A, Mukawa T, Tsukagoshi A, Frankland PW, Kida S (2008) Activation of LVGCCs and CB1 receptors required for destabilization of reactivated contextual fear memories. Learn Mem 15:426–433
Torregrossa MM, Taylor JR (2013) Learning to forget: manipulating extinction and reconsolidation processes to treat addiction. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 226(4):659–672
Trigo JM, Martin-García E, Berrendero F, Robledo P, Maldonado R (2010) The endogenous opioid system: a common substrate in drug addiction. Drug Alcohol Depend 108(3):183–194
Varvel SA, Anum EA, Lichtman AH (2005) Disruption of CB (1) receptor signaling impairs extinction of spatial memory in mice. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 179:863–872
Wang X, Cen X, Lu L (2001) Noradrenaline in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis is critical for stress-induced reactivation of morphine-conditioned place preference in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 432:153–161
Wilson RI, Nicoll RA (2002) Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Science 296:678–682
Xi ZX, Peng XQ, Li X, Song R, Zhang HY, Liu QR, Yang HJ et al (2011) Brain cannabinoid CB2 receptors modulate cocaine's actions in mice. Nat Neurosci 14:1160–1166
Yu LL, Wang XY, Zhao M, Liu Y, Li YQ, Wang X, Xue YX, Lu L (2009) Effects of cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant in consolidation and reconsolidation of methamphetamine reard memory in mice. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 204(2):203–211
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC), and Programa de Apoio aos Núcleos de Excelência (PRONEX), all of Brazil. RNT is the holder of a CNPq research fellowship. CR de Carvalho and JS Cruz are supported by scholarships from CNPq.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Carvalho, C.R., Pamplona, F.A., Cruz, J.S. et al. Endocannabinoids underlie reconsolidation of hedonic memories in Wistar rats. Psychopharmacology 231, 1417–1425 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3331-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3331-2