Abstract
Rationale
Obesity is a leading public health problem worldwide. Multiple lines of evidence associate deficits in the brain reward circuit with obesity.
Objective
Whether alterations in brain reward sensitivity precede or are a consequence of obesity is unknown. This study aimed to investigate both innate and obesity-induced differences in the sensitivity to the effects of an indirect dopaminergic agonist.
Methods
Rats genetically prone to diet-induced obesity (DIO) and their counterpart diet-resistant (DR) were fed a chow diet, and their response to d-amphetamine on intracranial self-stimulation and food intake were assessed. The same variables were then evaluated after exposing the rats to a high-fat diet, after DIO rats selectively developed obesity. Finally, gene expression levels of dopamine receptors 1 and 2 as well as tyrosine hydroxylase were measured in reward-related brain regions.
Results
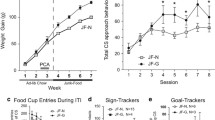
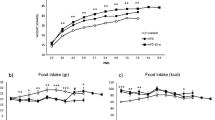
In a pre-obesity state, DIO rats showed innate decreased sensitivity to the reward-enhancing and anorectic effects of d-amphetamine, as compared to DR rats. In a diet-induced obese state, the insensitivity to the potentiating effects of d-amphetamine on intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) threshold persisted and became more marked in DIO rats, while the anorectic effects were comparable between genotypes. Finally, innate and obesity-induced differences in the gene expression of dopamine receptors were observed.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrate that brain reward deficits antedate the development of obesity and worsen after obesity is fully developed, suggesting that these alterations represent vulnerability factors for its development. Moreover, our data suggests that the reward-enhancing and anorectic effects of d-amphetamine are dissociable in the context of obesity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlskog JE (1974) Food intake and amphetamine anorexia after selective forebrain norepinephrine loss. Brain Res 82:211–240
Alsio J, Olszewski PK, Norback AH, Gunnarsson ZE, Levine AS, Pickering C, Schioth HB (2010) Dopamine D1 receptor gene expression decreases in the nucleus accumbens upon long-term exposure to palatable food and differs depending on diet-induced obesity phenotype in rats. Neuroscience 171:779–787
Baiamonte BA, Valenza M, Roltsch EA, Whitaker AM, Baynes BB, Sabino V, Gilpin NW (2014) Nicotine dependence produces hyperalgesia: role of corticotropin-releasing factor-1 receptors (CRF1Rs) in the central amygdala (CeA). Neuropharmacology 77:217–223
Blum K, Braverman ER, Wood RC, Gill J, Li C, Chen TJ, Taub M, Montgomery AR, Sheridan PJ, Cull JG (1996) Increased prevalence of the Taq I A1 allele of the dopamine receptor gene (DRD2) in obesity with comorbid substance use disorder: a preliminary report. Pharmacogenetics 6:297–305
Bray GA (2004) Medical consequences of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2583–2589
Clegg DJ, Benoit SC, Reed JA, Woods SC, Dunn-Meynell A, Levin BE (2005) Reduced anorexic effects of insulin in obesity-prone rats fed a moderate-fat diet. Am J Physiol Regulat, Integrat comparat Physiol 288:R981–R986
Cottone P, Sabino V, Nagy TR, Coscina DV, Zorrilla EP (2007) Feeding microstructure in diet-induced obesity susceptible versus resistant rats: central effects of urocortin 2. J Physiol 583:487–504
Cottone P, Wang X, Park JW, Valenza M, Blasio A, Kwak J, Iyer MR, Steardo L, Rice KC, Hayashi T, Sabino V (2012) Antagonism of sigma-1 receptors blocks compulsive-like eating. Neuropsychopharmacol : Off Public Am College Neuropsychopharmacol
Cottone P, Sabino V, Nagy TR, Coscina DV, Levin BE, Zorrilla EP (2013) Centrally administered urocortin 2 decreases gorging on high-fat diet in both diet-induced obesity-prone and -resistant rats. Int J Obes (Lond) 37:1515–1523
Davis JF, Tracy AL, Schurdak JD, Tschop MH, Lipton JW, Clegg DJ, Benoit SC (2008) Exposure to elevated levels of dietary fat attenuates psychostimulant reward and mesolimbic dopamine turnover in the rat. Behav Neurosci 122:1257–1263
Dore R, Iemolo A, Smith KL, Wang X, Cottone P, Sabino V (2013) CRF mediates the anxiogenic and anti-rewarding, but not the anorectic effects of PACAP. Neuropsychopharmacol : Off Public Am College Neuropsychopharmacol 38:2160–2169
Esposito R, Kornetsky C (1977) Morphine lowering of self-stimulation thresholds: lack of tolerance with long-term administration. Science 195:189–191
Esposito RU, Perry W, Kornetsky C (1980) Effects of d-amphetamine and naloxone on brain stimulation reward. Psychopharmacology 69:187–191
Fleckenstein AE, Volz TJ, Riddle EL, Gibb JW, Hanson GR (2007) New insights into the mechanism of action of amphetamines. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:681–698
Foltin RW (2011) Consumption of palatable food decreases the anorectic effects of serotonergic, but not dopaminergic drugs in baboons. Physiol Behav 103:493–500
Francis LA, Lee Y, Birch LL (2003) Parental weight status and girls’ television viewing, snacking, and body mass indexes. Obes Res 11:143–151
Fulton S, Pissios P, Manchon RP, Stiles L, Frank L, Pothos EN, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS (2006a) Leptin regulation of the mesoaccumbens dopamine pathway. Neuron 51:811–822
Fulton S, Woodside B, Shizgal P (2006b) Potentiation of brain stimulation reward by weight loss: evidence for functional heterogeneity in brain reward circuitry. Behav Brain Res 174:56–63
Geiger BM, Behr GG, Frank LE, Caldera-Siu AD, Beinfeld MC, Kokkotou EG, Pothos EN (2008) Evidence for defective mesolimbic dopamine exocytosis in obesity-prone rats. FASEB J : Off Public Fed Am Soc Experiment Biol 22:2740–2746
Geiger BM, Haburcak M, Avena NM, Moyer MC, Hoebel BG, Pothos EN (2009) Deficits of mesolimbic dopamine neurotransmission in rat dietary obesity. Neuroscience 159:1193–1199
Goodall EB, Carey RJ (1975) Effects of d- versus l-amphetamine, food deprivation, and current intensity on self-stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus, substantia nigra, and medial frontal cortex of the rat. J Comparat Physiol Psychol 89:1029–1045
Grilly DM, Loveland A (2001) What is a “low dose” of d-amphetamine for inducing behavioral effects in laboratory rats? Psychopharmacology 153:155–169
Grinker JA, Drewnowski A, Enns M, Kissileff H (1980) Effects of d-amphetamine and fenfluramine on feeding patterns and activity of obese and lean Zucker rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:265–275
Guo J, Simmons WK, Herscovitch P, Martin A, Hall KD (2014) Striatal dopamine D2-like receptor correlation patterns with human obesity and opportunistic eating behavior. Mol Psychiatry 19:1078–1084
Iemolo A, Valenza M, Tozier L, Knapp CM, Kornetsky C, Steardo L, Sabino V, Cottone P (2012) Withdrawal from chronic, intermittent access to a highly palatable food induces depressive-like behavior in compulsive eating rats. Behav Pharmacol 23:593–602
Ikemoto S, Panksepp J (1999) The role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in motivated behavior: a unifying interpretation with special reference to reward-seeking. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31:6–41
Irani BG, Dunn-Meynell AA, Levin BE (2007) Altered hypothalamic leptin, insulin, and melanocortin binding associated with moderate-fat diet and predisposition to obesity. Endocrinology 148:310–316
Johnson PM, Kenny PJ (2010) Dopamine D2 receptors in addiction-like reward dysfunction and compulsive eating in obese rats. Nat Neurosci 13:635–641
Kelley AE, Berridge KC (2002) The neuroscience of natural rewards: relevance to addictive drugs. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci 22:3306–3311
Kenny PJ, Markou A (2005) Conditioned nicotine withdrawal profoundly decreases the activity of brain reward systems. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci 25:6208–6212
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2010) Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacol : Off Public Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 35:217–238
Kornetsky C, Esposito RU (1979) Euphorigenic drugs: effects on the reward pathways of the brain. Fed Proc 38:2473–2476
Koyama S, Mori M, Kanamaru S, Sazawa T, Miyazaki A, Terai H, Hirose S (2014) Obesity attenuates D2 autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of putative ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons. Physiol Rep 2:e12004
Lehnert T, Sonntag D, Konnopka A, Riedel-Heller S, Konig HH (2013) Economic costs of overweight and obesity. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 27:105–115
Leibowitz SF (1975a) Amphetamine: possible site and mode of action for producing anorexia in the rat. Brain Res 84:160–167
Leibowitz SF (1975b) Catecholaminergic mechanisms of the lateral hypothalamus: their role in the mediation of amphetamine anorexia. Brain Res 98:529–545
Levin BE (1991) Spontaneous motor activity during the development and maintenance of diet-induced obesity in the rat. Physiol Behav 50:573–581
Levin BE (1999) Arcuate NPY neurons and energy homeostasis in diet-induced obese and resistant rats. Am J Physiol 276:R382–R387
Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA (2000) Defense of body weight against chronic caloric restriction in obesity-prone and -resistant rats. Am J Physiol Regulat, Integrat Comparat Physiol 278:R231–R237
Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA (2006) Differential effects of exercise on body weight gain and adiposity in obesity-prone and -resistant rats. Int J Obes (Lond) 30:722–727
Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA, Balkan B, Keesey RE (1997) Selective breeding for diet-induced obesity and resistance in Sprague-Dawley rats. Am J Physiol 273:R725–R730
Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA, Ricci MR, Cummings DE (2003) Abnormalities of leptin and ghrelin regulation in obesity-prone juvenile rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E949–E957
Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA, Banks WA (2004) Obesity-prone rats have normal blood-brain barrier transport but defective central leptin signaling before obesity onset. Am J Physiol Regulat, Integrat Comparat Physiol 286:R143–R150
Madsen AN, Hansen G, Paulsen SJ, Lykkegaard K, Tang-Christensen M, Hansen HS, Levin BE, Larsen PJ, Knudsen LB, Fosgerau K, Vrang N (2010) Long-term characterization of the diet-induced obese and diet-resistant rat model: a polygenetic rat model mimicking the human obesity syndrome. J Endocrinol 206:287–296
Markou A, Koob GF (1991) Postcocaine anhedonia. An animal model of cocaine withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacol : Off Public Am College Neuropsychopharmacol 4:17–26
Markou A, Koob GF (1992) Bromocriptine reverses the elevation in intracranial self-stimulation thresholds observed in a rat model of cocaine withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacol : Off Public Am College Neuropsychopharmacol 7:213–224
Mayer J, Thomas DW (1967) Regulation of food intake and obesity. Science 156:328–337
Melis M, Spiga S, Diana M (2005) The dopamine hypothesis of drug addiction: hypodopaminergic state. Int Rev Neurobiol 63:101–154
O’Brien CP, Gardner EL (2005) Critical assessment of how to study addiction and its treatment: human and non-human animal models. Pharmacol Ther 108:18–58
Pellegrino LJ, Pellegrino AS, Cushman AJ (1979) A stereotaxic atlas of the rat brain, 2dth edn. Plenum Press, New York
Ricci MR, Levin BE (2003) Ontogeny of diet-induced obesity in selectively bred Sprague-Dawley rats. Am J Physiol Regulat, Integrat Comparat Physiol 285:R610–R618
Sabino V, Cottone P, Zhao Y, Steardo L, Koob GF, Zorrilla EP (2009) Selective reduction of alcohol drinking in Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats by a sigma-1 receptor antagonist. Psychopharmacology 205:327–335
Sahakian BJ, Winn P, Robbins TW, Deeley RJ, Everitt BJ, Dunn LT, Wallace M, James WP (1983) Changes in body weight and food-related behaviour induced by destruction of the ventral or dorsal noradrenergic bundle in the rat. Neuroscience 10:1405–1420
Schulteis G, Markou A, Cole M, Koob GF (1995) Decreased brain reward produced by ethanol withdrawal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:5880–5884
Sharma S, Fulton S (2012) Diet-induced obesity promotes depressive-like behaviour that is associated with neural adaptations in brain reward circuitry. Int J Obes (Lond)
Shizgal P, Fulton S, Woodside B (2001) Brain reward circuitry and the regulation of energy balance. Int J Obes Relat Metab Dis : J Int Assoc Stud Obes 25(Suppl 5):S17–S21
South T, Huang XF (2008) High-fat diet exposure increases dopamine D2 receptor and decreases dopamine transporter receptor binding density in the nucleus accumbens and caudate putamen of mice. Neurochem Res 33:598–605
Speakman JR (2004) Obesity: the integrated roles of environment and genetics. J Nutrit 134:2090S–2105S
Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI, Monda KL, Thorleifsson G, Jackson AU, Lango Allen H, Lindgren CM, Luan J, Magi R, Randall JC, Vedantam S, Winkler TW, Qi L, Workalemahu T, Heid IM, Steinthorsdottir V, Stringham HM, Weedon MN, Wheeler E, Wood AR, Ferreira T, Weyant RJ, Segre AV, Estrada K, Liang L, Nemesh J, Park JH, Gustafsson S, Kilpelainen TO, Yang J, Bouatia-Naji N, Esko T, Feitosa MF, Kutalik Z, Mangino M, Raychaudhuri S, Scherag A, Smith AV, Welch R, Zhao JH, Aben KK, Absher DM, Amin N, Dixon AL, Fisher E, Glazer NL, Goddard ME, Heard-Costa NL, Hoesel V, Hottenga JJ, Johansson A, Johnson T, Ketkar S, Lamina C, Li S, Moffatt MF, Myers RH, Narisu N, Perry JR, Peters MJ, Preuss M, Ripatti S, Rivadeneira F, Sandholt C, Scott LJ, Timpson NJ, Tyrer JP, van Wingerden S, Watanabe RM, White CC, Wiklund F, Barlassina C, Chasman DI, Cooper MN, Jansson JO, Lawrence RW, Pellikka N, Prokopenko I, Shi J, Thiering E, Alavere H, Alibrandi MT, Almgren P, Arnold AM, Aspelund T, Atwood LD, Balkau B, Balmforth AJ, Bennett AJ, Ben-Shlomo Y, Bergman RN, Bergmann S, Biebermann H, Blakemore AI, Boes T, Bonnycastle LL, Bornstein SR, Brown MJ, Buchanan TA, Busonero F, Campbell H, Cappuccio FP, Cavalcanti-Proenca C, Chen YD, Chen CM, Chines PS, Clarke R, Coin L, Connell J, Day IN, den Heijer M, Duan J, Ebrahim S, Elliott P, Elosua R, Eiriksdottir G, Erdos MR, Eriksson JG, Facheris MF, Felix SB, Fischer-Posovszky P, Folsom AR, Friedrich N, Freimer NB, Fu M, Gaget S, Gejman PV, Geus EJ, Gieger C, Gjesing AP, Goel A, Goyette P, Grallert H, Grassler J, Greenawalt DM, Groves CJ, Gudnason V, Guiducci C, Hartikainen AL, Hassanali N, Hall AS, Havulinna AS, Hayward C, Heath AC, Hengstenberg C, Hicks AA, Hinney A, Hofman A, Homuth G, Hui J, Igl W, Iribarren C, Isomaa B, Jacobs KB, Jarick I, Jewell E, John U, Jorgensen T, Jousilahti P, Jula A, Kaakinen M, Kajantie E, Kaplan LM, Kathiresan S, Kettunen J, Kinnunen L, Knowles JW, Kolcic I, Konig IR, Koskinen S, Kovacs P, Kuusisto J, Kraft P, Kvaloy K, Laitinen J, Lantieri O, Lanzani C, Launer LJ, Lecoeur C, Lehtimaki T, Lettre G, Liu J, Lokki ML, Lorentzon M, Luben RN, Ludwig B, Manunta P, Marek D, Marre M, Martin NG, McArdle WL, McCarthy A, McKnight B, Meitinger T, Melander O, Meyre D, Midthjell K, Montgomery GW, Morken MA, Morris AP, Mulic R, Ngwa JS, Nelis M, Neville MJ, Nyholt DR, O’Donnell CJ, O’Rahilly S, Ong KK, Oostra B, Pare G, Parker AN, Perola M, Pichler I, Pietilainen KH, Platou CG, Polasek O, Pouta A, Rafelt S, Raitakari O, Rayner NW, Ridderstrale M, Rief W, Ruokonen A, Robertson NR, Rzehak P, Salomaa V, Sanders AR, Sandhu MS, Sanna S, Saramies J, Savolainen MJ, Scherag S, Schipf S, Schreiber S, Schunkert H, Silander K, Sinisalo J, Siscovick DS, Smit JH, Soranzo N, Sovio U, Stephens J, Surakka I, Swift AJ, Tammesoo ML, Tardif JC, Teder-Laving M, Teslovich TM, Thompson JR, Thomson B, Tonjes A, Tuomi T, van Meurs JB, van Ommen GJ, Vatin V, Viikari J, Visvikis-Siest S, Vitart V, Vogel CI, Voight BF, Waite LL, Wallaschofski H, Walters GB, Widen E, Wiegand S, Wild SH, Willemsen G, Witte DR, Witteman JC, Xu J, Zhang Q, Zgaga L, Ziegler A, Zitting P, Beilby JP, Farooqi IS, Hebebrand J, Huikuri HV, James AL, Kahonen M, Levinson DF, Macciardi F, Nieminen MS, Ohlsson C, Palmer LJ, Ridker PM, Stumvoll M, Beckmann JS, Boeing H, Boerwinkle E, Boomsma DI, Caulfield MJ, Chanock SJ, Collins FS, Cupples LA, Smith GD, Erdmann J, Froguel P, Gronberg H, Gyllensten U, Hall P, Hansen T, Harris TB, Hattersley AT, Hayes RB, Heinrich J, Hu FB, Hveem K, Illig T, Jarvelin MR, Kaprio J, Karpe F, Khaw KT, Kiemeney LA, Krude H, Laakso M, Lawlor DA, Metspalu A, Munroe PB, Ouwehand WH, Pedersen O, Penninx BW, Peters A, Pramstaller PP, Quertermous T, Reinehr T, Rissanen A, Rudan I, Samani NJ, Schwarz PE, Shuldiner AR, Spector TD, Tuomilehto J, Uda M, Uitterlinden A, Valle TT, Wabitsch M, Waeber G, Wareham NJ, Watkins H, Wilson JF, Wright AF, Zillikens MC, Chatterjee N, McCarroll SA, Purcell S, Schadt EE, Visscher PM, Assimes TL, Borecki IB, Deloukas P, Fox CS, Groop LC, Haritunians T, Hunter DJ, Kaplan RC, Mohlke KL, O’Connell JR, Peltonen L, Schlessinger D, Strachan DP, van Duijn CM, Wichmann HE, Frayling TM, Thorsteinsdottir U, Abecasis GR, Barroso I, Boehnke M, Stefansson K, North KE, McCarthy MI, Hirschhorn JN, Ingelsson E, Loos RJ (2010) Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat Genet 42:937–948
Steinberg EE, Boivin JR, Saunders BT, Witten IB, Deisseroth K, Janak PH (2014) Positive reinforcement mediated by midbrain dopamine neurons requires D1 and D2 receptor activation in the nucleus accumbens. PLoS One 9:e94771
Sulzer D (2011) How addictive drugs disrupt presynaptic dopamine neurotransmission. Neuron 69:628–649
van de Giessen E, Celik F, Schweitzer DH, van den Brink W, Booij J (2014) Dopamine D2/3 receptor availability and amphetamine-induced dopamine release in obesity. J Psychopharmacol 28:866–873
Velazquez-Sanchez C, Ferragud A, Moore CF, Everitt BJ, Sabino V, Cottone P (2014) High trait impulsivity predicts food addiction-like behavior in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacol : Off Public Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 39:2463–2472
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Telang F (2008) Overlapping neuronal circuits in addiction and obesity: evidence of systems pathology. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 363:3191–3200
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Baler RD (2011) Reward, dopamine and the control of food intake: implications for obesity. Trends Cogn Sci 15:37–46
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Tomasi D, Baler R (2012) Food and drug reward: overlapping circuits in human obesity and addiction. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 11:1–24
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Tomasi D, Baler RD (2013a) The addictive dimensionality of obesity. Biol Psychiatr 73:811–818
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Tomasi D, Baler RD (2013b) Obesity and addiction: neurobiological overlaps. Obes Rev : Off J Int Assoc Stud Obes 14:2–18
Vucetic Z, Reyes TM (2010) Central dopaminergic circuitry controlling food intake and reward: implications for the regulation of obesity. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2:577–593
Vucetic Z, Carlin JL, Totoki K, Reyes TM (2012) Epigenetic dysregulation of the dopamine system in diet-induced obesity. J Neurochem 120:891–898
Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Logan J, Pappas NR, Wong CT, Zhu W, Netusil N, Fowler JS (2001) Brain dopamine and obesity. Lancet 357:354–357
Wellman PJ, Pittenger DJ, Wikler KC (1982) Diet palatability and amphetamine-induced anorexia. Physiol Psychol 10:117–121
Acknowledgments
We thank Aditi R. Narayan, Jina Kwak, and Aditya Khedkar for technical assistance, and Andrew Kim, Jeffrey Santos, and Angela Tung for editorial assistance. This publication was made possible by grant numbers DA030425, MH091945, and MH093650A1 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), and the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), and by the Peter Paul Career Development Professorship (P.C.). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Timothy R. Nagy, Maria S. Johnson, and the UAB Small Animal Phenotyping Core for performing the rat carcass analysis, which was founded by grant numbers P30DK056336 (NORC) and P60DK079626 (DRTC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Pietro Cottone and Valentina Sabino contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 116 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valenza, M., Steardo, L., Cottone, P. et al. Diet-induced obesity and diet-resistant rats: differences in the rewarding and anorectic effects of d-amphetamine. Psychopharmacology 232, 3215–3226 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3981-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3981-3