Abstract
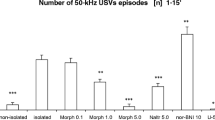
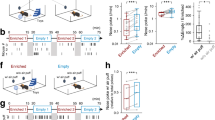
Rationale: Endogenous opioid systems within the mesencephalic periaqueductal gray matter (PAG) appear to be intricately involved in many affective, defensive, submissive, and reflexive responses, and these systems are activated by aversive stimuli. Objectives: The present experiments evaluated the influence of opioid receptors within the PAG on affective vocal and reflexive responses to aversive stimuli in socially inexperienced, as well as defensive and submissive responses in defeated, adult male Long-Evans rats. Methods: Defeat stress consisted of: (1) an aggressive confrontation with a ”resident” stimulus rat in which the experimental ”intruder” rat exhibited escape, defensive and submissive behaviors [i.e. upright, supine postures and ultrasonic vocalizations (USV)], and subsequently, (2) protection from the resident rat with a wire mesh screen for ca. 25 min. Defeat stress was immediately followed by an experimental session with thermal antinociceptive and tactile startle stimuli (20 psi airpuffs). Results: The µ opioid receptor agonist morphine (0.3, 1, 3 µg IC) attenuated startle-induced USV and the tail-flick reflex in socially inexperienced and defeated rats, with both groups of rats demonstrating equal sensitivity to morphine. Morphine decreased defeat-induced USV and increased the display of the crouch posture in defeated rats; these morphine effects in socially inexperienced and defeated rats were re- versed with the opioid receptor antagonist naltrexone (0.1 mg/kg IP). Conclusions: These results reveal that the ventrolateral PAG is an important site in which µ opioid receptor agonists such as morphine mediate affective vocal and submissive responses, yet this structure is not critical in the display of defeat stress-augmented effects of morphine. Endogenous opioid mechanisms appear to participate in the organization of defensive behavior, namely, to facilitate a shift from active to passive forms of coping.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 November 1998 / Final version: 29 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vivian, J., Miczek, K. Interactions between social stress and morphine in the periaqueductal gray: effects on affective vocal and reflexive pain responses in rats. Psychopharmacology 146, 153–161 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130051101
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130051101