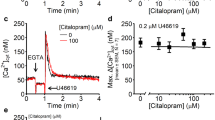
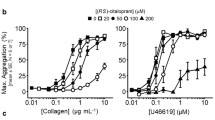
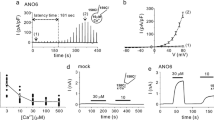
Abstract
Recent literature and our previous observations indicated the presence of both NMDA and serotonin type 3 receptors in human platelets with very similar ionic currents to that of cultured mammalian neuronal receptors. Baseline electrophysiological data shows similar profile for platelets from both normal and schizophrenic subjects, whereas serotonin receptor studies exhibited the presence of 5-hydroxytryptamine type-3 (5-HT3) currents in both normal and schizophrenic platelets significantly different from each other. The two major differences observed were: first, 5-HT3 receptors present in the platelets of schizophrenic patients were four times more sensitive to serotonin than those present in the platelets of normal subjects and, second, that d-serine in micro molar concentrations dampens this effect in platelets from schizophrenic patients but increases the sensitivity of serotonin for platelet 5-HT3 receptors of normal subjects. Patch clamp technique was used to measure the whole cell currents passing through serotonin receptors in these two types of human platelets. The currents were found to be 5-HT3 receptor currents as they were abolished by 10 μM d-tubocurarine. Similarly, micromolar concentrations of d-serine increased the sensitivity of 5HT3 receptor currents in the normal human platelets but decreased it in the platelets of the schizophrenic patients. This effect was reversed when d-amino acid oxidase (0.3 μM) was co applied with 100 μM of d-serine, raising the possibility that d-serine by itself may act as a modulator for platelet 5-HT3 receptor channel currents. These observations raised exciting new questions about the role of platelet serotonin receptors and their regulation by d-serine.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ (1999) Serotonin model of schizophrenia: emerging role of glutamate mechanisms. Brain Res Rev 31(2):302–312
Aspey BS, Alp MS, Patel Y, Harrison MJG (1997) Effects of combined glutamate and platelet-activating factor inhibition on the outcome of focal cerebral ischaemia—an initial screening study. Metab Brain Dis 12(3):237–249
Biegon A, Essar N, Israeli M, Elizur A, Bruch S, Bar-Nathan AA (1990) Serotonin 5-HT2 receptor binding on blood platelets as a state dependent marker in major affective disorder. Psychopharmacology 102(1):73–75
Borges VC, Nogueira GZ, Zeni G, Rocha JBT (2004) Organochalcogens affect the glutamatergic neurotransmission in human platelets. Neurochem Res 29(8):1505–1509
Christopher R, Daiga H, Katz M, Ryan V, Lawrence A, Siu Wa T (1995) Serotonin stimulated intracellular calcium mobilization in platelets from alcoholic men. Psychiatry Res 57(3):275–278
Hamil OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth F (1981) Improved patch clamp techniques for high-resolution current recordings from cells and cell free membrane patches. Pfluger Arch 391:85–100
Harsing Jr, Prauda I, Barkoczy J, Matyus P, Juranyi Z (2004) A 5-HT7 heteroreceptor-mediated inhibition of [3H]serotonin release in raphe nuclei slices of the rat: evidence for a serotonergic–glutamatergic interaction. Neurochem Res 29(8):1487–1497
Julius D (1991) Molecular biology of serotonin receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 14:335–360
Kahn RS, Davidson M (1993) Serotonin, dopamine and their interactions in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 112(1):S1–S4
Kostic VS, Mojsilovic LJ, Stojanovic M (2003) Degenerative neurological disorders associated with deficiency of glutamate dehydrogenase. J Neurol 236(2):111–114
Michal F (1969) d-receptors for serotonin in blood platelets. Nature (Lond) 221:1253
de Miranda J, Panizzutti R, Foltyn VN, Wolosker H (2002) Cofactors of serine racemase that physiologically stimulate the synthesis of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor coagonist D-serine. PNAS 99(22):14542–14547
Mothet JP, Parent AP, Wolosker H, Brady RO Jr, Linden DJ, Ferris CD, Rogawski MA, Snyder SH (2000a) D-Serine is an endogenous ligand for the glycine site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Neurobiology 97(9):4926–4931
Mothet JP, Parent AT, Wolosker H, Brady RO, Linden DJ, Ferris C, D Rogawski M A, Snyder SH (2000b) D-serine is an endogenous ligand for glycine site of the NMDA receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4926–4932
Waziri R, Wilson R, Sherman AD (1983) Plasma serine to cysteine ratio as a biological marker for psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 143:69–73
Wirz-Justice A (1988) Platelet research in psychiatry. Cell Mol Life Sci 44(2):145–152
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by HMR grant Australia and an individual grant from the UAEU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatima Shad, K. Effect of d-serine on the serotonin receptors of human platelets. Exp Brain Res 173, 353–356 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0496-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0496-5