Abstract
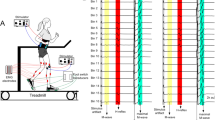
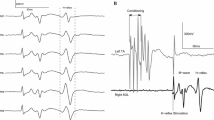
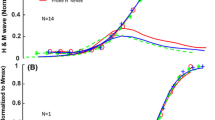
We measured the soleus and the gastrocnemius H-reflex modulation in seven subjects during walking at 4.5 km/h and during running at 8, 12 and 15 km/h. The recordings in the medial gastrocnemius were corrected for cross-talk from the soleus muscle. The gastrocnemius H-reflex was in general lower than the soleus H-reflex. In both muscles the H-reflex increased significantly from walking to running but also with increasing running speed. The peak of EMG activity increased in both muscles with increasing speed. The V-wave of both muscles was absent or rather low during walking, but it increased significantly from walking to running with increasing running speed in the soleus but not in the medial gastrocnemius. In both muscles the V-wave was highest just prior to heel strike. It is suggested that this was due to a high firing frequency of the motoneurones in this phase of the movement. It is concluded that a shift towards the faster gastrocnemius at higher running speeds on behalf of the soleus muscle did not occur. The fact that the physiological cross-sectional area of the soleus is much larger than that of the lumped gastrocnemii is most probably the reason why the soleus is important also at higher running velocities.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMG:
-
Electromyography
- H-reflex:
-
Hoffmann reflex
References
Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Andersen JL, Magnusson P, Dyhre-Poulsen P (2002) Neural adaptation to resistance training: changes in evoked V-wave and H-reflex responses. J Appl Physiol 92:2309–2318
Alway SE, MacDougall JD, Sale DG, Sutton JR, McComas AJ (1988) Functional and structural adaptations in skeletal muscle of trained athletes. J Appl Physiol 64(3):1114–1120
Bigland B, Lippold OC (1954) Motor unit activity in the voluntary contraction of human muscle. J Physiol 125:322–335
Capaday C, Stein RB (1986) Amplitude modulation of the soleus H-reflex in the human during walking and standing. J Neurosci 6:1308–1313
Capaday C, Stein RB (1987) Difference in the amplitude of the human soleus H-reflex during walking and running. J Physiol 392:513–522
Cronin NJ, Carty CP, Barrett RS (2011) Triceps surae short latency stretch reflexes contribute to ankle stiffness regulation during human running. PLoS One 6(8):e23917
Dalgaard P (2008) Introductory statistics with R, 2nd edn. Springer, New Mexico
Duchateau J, Enoka R (2011) Human motor unit recordings: origins and insight into the integrated motor system. Brain Res 1409:42–61
Duchateau J, Semmler J, Enoka RM (2006) Training adaptations in the behaviour of human motor units. J Appl Physiol 101(6):1766–1775
Duysens J, Tax AAM, van der Doelen D, Trippel M, Dietz V (1991) Selective activation of human soleus or gastrocnemius in reflex responses during walking and running. Exp Brain Res 87:193–204
Dyhre-Poulsen P, Simonsen EB (2002) H reflexes recorded during locomotion. Adv Exp Med Biol 508:377–383
Edström L, Nyström B (1969) Histochemical types and sizes of fibres in normal human muscles. Biopsy study Acta Neurol Scand 45:257–269
Ferris DP, Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Farley CT, Dyhre-Poulsen P (2001) Soleus H-reflex gain in humans walking and running under simulated reduced gravity. J Physiol 530:167–180
Friedrich JA, Brand RA (1990) Muscle fiber architecture in the human lower limb. J Biomech 23:91–95
Gerilovsky L, Tsvetinov P, Trenkova G (1989) Peripheral effects on the amplitude of monopolar and bipolar H-reflex potentials from the soleus muscle. Exp Brain Res 76:173–181
Ishikawa M, Komi PV (2007) The role of the stretch reflex in the gastrocnemius muscle during human locomotion at various speeds. J Appl Physiol 103:1030–1036
Joyce GC, Rack PM, Westbury DR (1968) Some mechanical properties of the cat soleus muscle at various stimulus rates. J Physiol 197(1):23P–25P
Koh TJ, Grabiner MD (1992) Cross talk in surface electromyograms of human hamstring muscles. J Orthop Res 10:701–709
Kyrölainen H, Avela J, Komi PV (2005) Changes in muscle activity with increasing running speed. J Sports Sci 23(10):1101–1109
Moritani T, Oddsson L, Thorstensson A (1990a) Observations on the H-reflex and EMG changes of the human soleus and gastrocnemius during locomotion. In: Brandt T, Paulus W, Bles W, Dieterich M, Krafczyk S, Straube A (eds) Disorders of posture and gait. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, NY, pp 103–106
Moritani T, Oddsson L, Thorstensson A (1990b) Differences in modulation of the gastrocnemius and soleus H-reflexes during hopping in man. Acta Physiol Scand 138:575–576
Nardone A, Schieppati M (1988) Shift of activity from slow to fast muscle during voluntary lengthening contractions of the triceps surae muscles in humans. J Physiol 395:363–381
Nardone A, Romanó C, Schieppati M (1989) Selective recruitment of high-threshold human motor units during voluntary isotonic lengthening of active muscles. J Physiol 395:363–381
Nilsson J, Thorstensson A, Halbertsma J (1985) Changes in leg movements and muscle activity with speed of locomotion and mode of progression in humans. Acta Physiol Scand 123:457–475
Sale DG, MacDougal JD, Upton A, McComas AJ (1983) Effect of strength training upon motoneurone excitability in man. Med Sci Sports Exerc 15:57–62
Schieppati M (1987) The Hoffmann reflex: a means of assessing spinal reflex excitability and its descending control in man. Prog Neurobiol 28:345–376
Simonsen EB, Dyhre-Poulsen P (1999) Amplitude of the human soleus H reflex during walking and running. J Physiol 513(3):929–939
Simonsen EB, Dyhre-Poulsen P, Voigt M (1995) Excitability of the soleus H reflex during graded walking in humans. Acta Physiol Scand 153(1):21–32
Van Cutsem M, Duchateau J, Hainaut K (1998) Changes in single motor unit behaviour contribute to the increase in contraction speed after dynamic training in humans. J Physiol 513:295–305
Voigt M, Dyhre-Poulsen P, Simonsen EB (1998) Modulation of short latency stretch reflexes during human hopping. Acta Physiol Scand 163:181–194
Vugt JPP, van Dijk JG (2000) A convenient method to reduce crosstalk in surface EMG. Clin Neurophysiol 112:583–592
Winter DA (2005) Biomechanics and motor control of human movement, 3rd edn. Wiley, New Jersey
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Dr. Poul Dyhre-Poulsen, who participated in the experiments but sadly passed away before the preparation of the present article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonsen, E.B., Alkjær, T. & Raffalt, P.C. Reflex response and control of the human soleus and gastrocnemius muscles during walking and running at increasing velocity. Exp Brain Res 219, 163–174 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3075-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3075-y