Abstract
Purpose
Emerging evidence suggests that primary and metastatic brain tumors may be sensitive to hormonal manipulations. However, the pharmacokinetics of compounds against such targets in the brain and, more importantly, in the brain tumor are not well characterized. Here, we investigated the pharmacokinetics of letrozole, a third-generation aromatase inhibitor, in the normal brain and in orthotopically implanted C6 glioma in Sprague–Dawley rats.
Methods
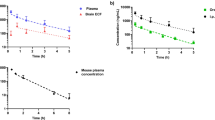
Intracerebral microdialysis was employed to determine the concentrations of unbound letrozole in the brain extracellular fluid (ECF) while simultaneously collecting blood samples (via jugular vein) to assess plasma levels of letrozole. Letrozole was administered intravenously at doses of 4, 6, 8 and 12 mg/kg, and ECF and blood samples were collected over 8 h. For assessing normal versus tumoral brain pharmacokinetics, letrozole (4 or 8 mg/Kg; i.v.) was administered 10 days after implantation of C6 glioma in the brain. Dual-probe intracerebral microdialysis was employed for assessing ECF samples from tumor-free and tumor-bearing regions of the brain.
Results
Normal brain ECF and plasma C max and AUC0–8h increased linearly with letrozole doses up to 8 mg/kg dose, but at 12 mg/kg, the pharmacokinetics were nonlinear. The relative brain distribution coefficients, AUCECF/AUCplasma (ub), were 0.3–0.98. The tumoral uptake of letrozole was 1.5- to 2-fold higher relative to tumor-free region.
Conclusions
Thus, letrozole permeability across the blood brain barrier is high, and the exposure to the brain is dose dependent. Furthermore, the brain tumoral letrozole levels are markedly higher than those in the tumor-free regions, which underscore potential selectivity of its activity against tumor cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M (2004) The blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis 16:1–13
Wagner LE 2nd, Eaton M, Sabnis SS, Gingrich KJ (1999) Meperidine and lidocaine block of recombinant voltage-dependent Na + channels: evidence that meperidine is a local anesthetic. Anesthesiology 91(5):1481–1490
Leibenr S, Fischmann A, Rascher G, Duffner F, Kalbacher H, Wolburg H (2000) Claudin-1 and claudin-5 expression and tight junction morphology are altered in blood vessels of human glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol 100(3):323–331
Shibata S (1989) Ultrastructure of capillary walls in human brain tumors. Acta Neutopathol 78(8):561–571
Blasberg R, Horowitz M, Molnar P, Strong J, Kornblith P, Pleasants R, Fenstermacher J (1983) Regional [14C]misonidazole distribution in experimental RT-9 brain tumors. Cancer Res 43(8):3800–3807
Ostrowitzki S, Fick J, Roberts TP, Wendland MF, Aldape KD, Mann JS, Israel MA, Brasch RC (1998) Comparison of gadopentetate dimeglumine and albumin(Gd-DTPA)30 for microvessel characterization in an intracranial glioma model. J Magn Reson Imaging 8(4):799–806
Nakagawa H, Groothuis DR, Owens ES, Fenstermacher JD, Patlak CS, Blasberg RG (1987) Dexamethasone effects on [125I]albumin distribution in experimental RG-2 gliomas and adjacent brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 7(6):687–701
Schlageter KE, Molnar P, Lapin GD, Groothuis DR (1999) Microvessel organization and structure in experimental brain tumors: microvessel populations with distinctive structural and functional properties. Microvasc Res 58(3):312–328
Regina A, Demeule M, Laplante A, Jodoin J, Dagenais C, Berthelet F, Moghrabi A, Bellveau R (2001) Multidrug resistance in brain tumors: roles of the blood-brain barrier. Cancer Metastasis Rev 20(1–2):13–25
Toth K, Vaughan MM, Peress NS, Slocum HK, Rustum YM (1996) MDR-1 P-glycoprotein is expressed by endothelial cells of newly formed capillaries in human gliomas but is not expressed in the neovasculature of other primary tumors. Am J Pathol 149(3):853–858
Patel S, DiBiase S, Meisenberg B, Flannery T, Patel A, Dhople A, Cheston S, Amin P (2012) Phase I clinical trial assessing temozolomide and tamoxifen with concomitant radiotherapy for treatment of high-grade glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:739–742
Vertosick FT Jr, Selker RG, Randall MS, Kristofik MP, Rehn T (1994) A comparison of the relative chemosensitivity of human gliomas to tamoxifen and n-desmethyltamoxifen in vitro. J Neurooncol 19:97–103
Madhup R, Kirti S, Bhatt ML, Srivastava PK, Srivastava M, Kumar S (2006) Letrozole for brain and scalp metastases from breast cancer–a case report. Breast 15:440–442
Ito K et al (2009) A case of brain metastases from breast cancer that responded to anastrozole monotherapy. Breast J 15:435–437
Dellapasqua S, Colleoni M (2010) Letrozole. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 6:251–259
Lonning P (2003) Clinical pharmacokinetics of aromatase inhibitors and inactivators. Clin Pharmacokinet 42:619–631
Lonning P, Pfister C, Martoni A, Zamagni C (2003) Pharmacokinetics of third-generation aromatase inhibitors. Semin Oncol 30:23–32
Kil KE, Biegon A, Ding YS, Fischer A, Ferrieri RA, Kim SW, Pareto D, Schueller MJ, Fowler JS (2009) Synthesis and PET studies of [(11)C-cyano]letrozole (Femara), an aromatase inhibitor drug. Nucl Med Biol 36:215–223
Benveniste H, Huttemeier PC (1990) Microdialysis–theory and application. Prog Neurobiol 35:195–215
Yamamoto BK, Pehek EA (1990) A neurochemical heterogeneity of the rat striatum as measured by in vivo electrochemistry and microdialysis. Brain Res 506:236–242
Workman P, Balmain A, Hickman JA, McNally NJ, Rohas AM, Mitchison NA, Pierrepoint CG, Raymond R, Rowlatt C, Stephens TC et al (1988) UKCCCR guidelines for the welfare of animals in experimental neoplasia. Lab Anim 22:195–201
Paxinos G, Watson CR, Emson PC (1980) Ache-stained horizontal sections of the rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. J Neurosci Methods 3(2):129–149
Lee KJ, Mower R, Hollenbeck T, Castelo J, Johnson N, Gordon P, Sinko PJ, Holme K, Lee YH (2003) Modulation of nonspecific binding in ultrafiltration protein binding studies. Pharm Res 20:1015–1021
Apparaju SK, Gudelsky GA, Desai PB (2008) Pharmacokinetics of gemcitabine in tumor and non-tumor extracellular fluid of brain: an in vivo assessment in rats employing intracerebral microdialysis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61(2):223–229
Silvera SA, Miller AB, Rohan TE (2006) Hormonal and reproductive factors and risk of glioma: a prospective cohort study. Int J Cancer 118:1321–1324
Kabat GC, Etgen AM, Rohan TE (2010) Do steroid hormones play a role in the etiology of glioma? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 19:2421–2427
Kabat GC, Park Y, Hollenbeck AR, Schatzkin A, Rohan TE (2011) Reproductive factors and exogenous hormone use and risk of adult glioma in women in the NIH-AARP diet and health study. Int J Cancer 128:944–950
Huang K, Whelan EA, Ruder AM, Ward EM, Deddens JA, Davis-King KE, Carreon T, Waters MA, Butler MA, Calvert GM et al (2004) Reproductive factors and risk of glioma in women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13:1583–1588
Cicuttini FM, Hurley SF, Forbes A, Donnan GA, Salzberg M, Giles GG, McNeil JJ (1997) Association of adult glioma with medical conditions, family and reproductive history. Int J Cancer 71:203–207
Berny W, Weiser A, Jarmundowicz W, Markowska-Woyciechowska A, Zaluski R, Zub W (2004) Analysis of expression of estrogen (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR) in brain glial tumors and its correlation with expression of p53 protein and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)]. Neurol Neurochir Pol 38:367–371
Fujimoto M, Yoshino E, Hirakawa K, Fujimoto J, Tamaya T (1984) Estrogen receptors in brain tumors. Clin Neuropharmacol 7:357–362
Sun KH (1989) Estrogen receptors in patients with brain tumors. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 27(299–300):318
Walker MC, Tong X, Perry T, Alavijeh MS, Patsalos PN (2000) Comparison of serum, cerebrospinal fluid and brain extracellular fluid pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine. Brit J Pharmcol 130:242–248
de Lange ECM, Danhof M (2002) Considerations in the use of cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics to predict brain target concentrations in the clinical setting. Clin Pharmacokinet 41(10):691–703
Elmquist WF, Sawchuk RJ (1997) Application of microdialysis in pharmacokinetic studies. Pharm Res 14:267–288
Chaurasia CS, Muller M, Bashaw ED, Benfeldt E, Bolinder J, Bullock R, Bungay PM, DeLange EC, Derendorf H, Elmquist WF et al (2007) AAPS-FDA workshop white paper: microdialysis principles, application and regulatory perspectives. Pharm Res 24:1014–1025
Blakeley J, Portnow J (2010) Microdialysis for assessing intratumoral drug disposition in brain cancers: a tool for rational drug development. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 6:1477–1491
Liu XD, Xie L, Zhong Y, Li CX (2000) Gender differences in letrozole pharmacokinetics in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 21(8):680–684
Pfister CU, Martoni A, Zamagni C, Lelli G, De Braud F, Souppart C, Duval M, Hornberger U (2001) Effect of age and single versus multiple dose pharmacokinetics of letrozole (Femara) in breast cancer patients. Biopharm Drug Dispos 22:191–197
Grobben B, De Deyn PP, Slegers H (2002) Rat C6 glioma as experimental model system for the study of glioblastoma growth and invasion. Cell Tissue Res 310:257–270
Devineni D, Klein-Szanto A, Gallo JM (1996) In vivo microdialysis to characterize drug transport in brain tumors: analysis of methotrexate uptake in rat glioma-2 (RG-2)-bearing rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 38(6):499–507
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dave, N., Gudelsky, G.A. & Desai, P.B. The pharmacokinetics of letrozole in brain and brain tumor in rats with orthotopically implanted C6 glioma, assessed using intracerebral microdialysis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72, 349–357 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2205-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2205-y