Abstract.
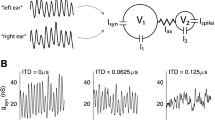
A biologically detailed model of the binaural avian nucleus laminaris is constructed, as a two-dimensional array of multicompartment, conductance-based neurons, along tonotopic and interaural time delay (ITD) axes. The model is based primarily on data from chick nucleus laminaris. Typical chick-like parameters perform ITD discrimination up to 2 kHz, and enhancements for barn owl perform ITD discrimination up to 6 kHz. The dendritic length gradient of NL is explained concisely. The response to binaural out-of-phase input is suppressed well below the response to monaural input (without any spontaneous activity on the opposite side), implicating active potassium channels as crucial to good ITD discrimination.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NL :
-
Nucleus Laminaris
- NM :
-
Nucleus Magnocellularis
- ITD :
-
Interaural Time Difference
- BF :
-
Best Frequency
Acknowledgments.
Thanks to Raul Rodriguez Esteban, Kate MacLeod, Daphne Soares, and Suchitra Parameshwaran. Support was given to JZS by National Institutes of Health Grant No. R03DC04382 and NSF Grant No. 972033 and to CEC by National Institutes of Health Grant No. DCD00426.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grau-Serrat, V., Carr, C. & Simon, J. Modeling coincidence detection in nucleus laminaris. Biol. Cybern. 89, 388–396 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-003-0444-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-003-0444-4