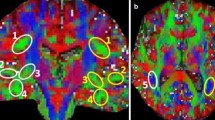
Abstract
Experimental and imaging studies in monkeys have outlined various long association fiber pathways within the fronto-temporo-parietal region. In the present study, the trajectory of the extreme capsule (EmC) fibers has been delineated in five human subjects using DT-MRI tractography. The EmC seems to be a long association fiber pathway, which courses between the inferior frontal region and the superior temporal gyrus extending into the inferior parietal lobule. Comparison of EmC fibers with the adjacent association fiber pathway, the middle longitudinal fascicle (MdLF), in the same subjects reveals that EmC is located in a medial and rostral position relative to MdLF flanking in part the medial wall of the insula. The EmC can also be differentiated from other neighboring fiber pathways such as the external capsule, uncinate fascicle, arcuate fascicle, superior longitudinal fascicles II and III, and the inferior longitudinal fascicle. Given the location of EmC within the language zone, specifically Broca’s area in the frontal lobe, and Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe and inferior parietal lobule, it is suggested that the extreme capsule could have a role in language function.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariens-Kappers CU, Huber GC, Crosby EC (1936) The comparative anatomy of the nervous system of vertebrates including man. MacMillan, New York
Azuma M, Suzuki H (1984) Properties and distribution of auditory neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the alert monkey. Brain Res 298(2):343–346. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(84)91434-3
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111:209–219. doi:10.1006/jmrb.1996.0086
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15(7–8):435–455. doi:10.1002/nbm.782
Benson DA, Hienz RD, Goldstein MH Jr (1981) Single-unit activity in the auditory cortex of monkeys actively localizing sound sources: spatial tuning and behavioral dependency. Brain Res 219(2):249–267. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(81)90290-0
Berke JJ (1960) The claustrum, the external capsule and the extreme capsule of Macaca mulatto. J Comp Neurol 115(3):297–331. doi:10.1002/cne.901150304
Catani M, Howard RJ, Pajevic S, Jones DK (2002) Virtual in vivo interactive dissection of white matter fasciculi in the human brain. Neuroimage 17(1):77–94. doi:10.1006/nimg.2002.1136
Catani M, Jones DK, ffytche DH (2005) Perisylvian language networks of the human brain. Ann Neurol 57(1):8–16. doi:10.1002/ana.20319
Caviness VSJ, Makris N, Meyer J, Kennedy DN (1996) MRI-based parcellation of human neocortex: an anatomically specified method with estimate of reliability. J Cogn Neurosci 8:566–588
Clarke S, Bellmann Thiran A, Maeder P, Adriani M, Vernet O, Regli L, Cuisenaire O, Thiran JP (2002) What and where in human audition: selective deficits following focal hemispheric lesions. Exp Brain Res 147(1):8–15. doi:10.1007/s00221-002-1203-9
Clarke S, Thiran AB (2004) Auditory neglect: what and where in auditory space. Cortex 40(2):291–300. doi:10.1016/S0010-9452(08)70124-2
Crosby EC, Schnizlein HN (1982) Comparative correlative neuroanatomy of the vertebrate telencephalon. Macmillan, New York
Dejerine J (1895) Anatomie des Centres Nerveux. Tome 1. Paris, France, Rueff et Cie
Dejerine J (1901) Anatomie des Centres Nerveux. Tome 2. Paris, France, Rueff et Cie
Ding G, Jiang Q, Li L, Zhang L, Zhang ZG, Ledbetter KA, Panda S, Davarani SP, Athiraman H, Li Q, Ewing JR, Chopp M (2008) Magnetic resonance imaging investigation of axonal remodeling and angiogenesis after embolic stroke in sildenafil-treated rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28(8):1440–1448. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2008.33
Filipek PA, Richelme C, Kennedy DN, Caviness VS Jr (1994) The young adult human brain: an MRI-based morphometric analysis. Cereb Cortex 4:344–360. doi:10.1093/cercor/4.4.344
Fullerton BC, Pandya DN (2007) Architectonic analysis of the auditory-related areas of the superior temporal region in human brain. J Comp Neurol 504(5):470–498. doi:10.1002/cne.21432
Frey S, Campbell JS, Pike GB, Petrides M (2008) Dissociating the human language pathways with high angular resolution diffusion fiber tractography. J Neurosci 28(45):11435–11444
Geschwind N (1965a) Disconnexion syndromes in animals and man. I. Brain 88(2):237–294. doi:10.1093/brain/88.2.237
Geschwind N (1965b) Disconnexion syndromes in animals and man. II. Brain 88(3):585–644. doi:10.1093/brain/88.3.585
Hackett TA, Preuss TM, Kaas JH (2001) Architectonic identification of the core region in auditory cortex of macaques, chimpanzees, and humans. J Comp Neurol 441(3):197–222. doi:10.1002/cne.1407
Hackett TA, Stepniewska I, Kaas JH (1999) Prefrontal connections of the parabelt auditory cortex in macaque monkeys. Brain Res 817(1–2):45–58. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(98)01182-2
Jiang Q, Zhang ZG, Ding GL, Silver B, Zhang L, Meng H, Lu M, Pourabdillah-Nejed DS, Wang L, Savant-Bhonsale S, Li L, Bagher-Ebadian H, Hu J, Arbab AS, Vanguri P, Ewing JR, Ledbetter KA, Chopp M (2006) MRI detects white matter reorganization after neural progenitor cell treatment of stroke. Neuroimage 32(3):1080–1089. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.05.025
Kaas JH, Hackett TA (1999) ‘What’ and ‘where’ processing in auditory cortex. Nat Neurosci 2(12):1045–1047. doi:10.1038/15967
Kaas JH, Hackett TA (2000) Subdivisions of auditory cortex and processing streams in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(22):11793–11799. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.22.11793
Klingberg T, Hedehus M, Temple E, Salz T, Gabrieli JD, Moseley ME, Poldrack RA (2000) Microstructure of temporo-parietal white matter as a basis for reading ability: evidence from diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Neuron 25(2):493–500. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80911-3
Krieg WJS (1963) Connections of the cerebral cortex. Brain Books, Evanston
Leinonen L, Hyvarinen J, Sovijarvi AR (1980) Functional properties of neurons in the temporo-parietal association cortex of awake monkey. Exp Brain Res 39(2):203–215. doi:10.1007/BF00237551
Lori NF, Akbudak E, Shimony JS, Cull TS, Snyder AZ, Guillory RK, Conturo TE (2002) Diffusion tensor fiber tracking of human brain connectivity: acquisition methods, reliability analysis and biological results. NMR Biomed 15(7–8):494–515. doi:10.1002/nbm.779
Makris N (1999) Delineation of human association fiber pathways using histologic and magnetic resonance methodologies. Behavioral neuroscience. Boston University, Boston, p 176
Makris N, Kennedy DN, McInerney S, Sorensen AG, Wang R, Caviness VS Jr, Pandya DN (2005) Segmentation of subcomponents within the superior longitudinal fascicle in humans: a quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. Cereb Cortex 15(6):854–869. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhh186
Makris N, Pandya DN, Normandin JJ (2002) Quantitative DT-MRI investigations of the human cingulum bundle. Cent Nerv Syst Spectrums 7(7):522–528
Makris N, Papadimitriou GM, Kaiser JR, Sorg S, Kennedy DN, Pandya DN (2008) Delineation of the middle longitudinal fascicle in humans: a quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. Cereb Cortex (in press)
Makris N, Papadimitriou GM, Sorg S, Kennedy DN, Caviness VS, Pandya DN (2007) The occipitofrontal fascicle in humans: a quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. Neuroimage 37(4):1100–1111. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.05.042
Makris N, Worth AJ, Sorensen AG, Papadimitriou GM, Wu O, Reese TG, Wedeen VJ, Davis TL, Stakes JW, Caviness VS, Kaplan E, Rosen BR, Pandya DN, Kennedy DN (1997) Morphometry of in vivo human white matter association pathways with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 42(6):951–962. doi:10.1002/ana.410420617
Martinkauppi S, Rama P, Aronen HJ, Korvenoja A, Carlson S (2000) Working memory of auditory localization. Cereb Cortex 10(9):889–898. doi:10.1093/cercor/10.9.889
Mesulam MM (1998) From sensation to cognition. Brain 121(Pt 6):1013–1052. doi:10.1093/brain/121.6.1013
Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, van Zijl PC (1999) Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 45(2):265–269. doi:10.1002/1531-8249(199902)45:2<265::AID-ANA21>3.0.CO;2-3
Morosan P, Rademacher J, Schleicher A, Amunts K, Schormann T, Zilles K (2001) Human primary auditory cortex: cytoarchitectonic subdivisions and mapping into a spatial reference system. Neuroimage 13(4):684–701. doi:10.1006/nimg.2000.0715
Ojemann G, Ojemann J, Lettich E, Berger M (1989) Cortical language localization in left, dominant hemisphere. An electrical stimulation mapping investigation in 117 patients. J Neurosurg 71(3):316–326
Ojemann JG, McKinstry RC, Mukherjee P, Park TS, Burton H (2005) Hand somatosensory cortex activity following selective dorsal rhizotomy: report of three cases with fMRI. Childs Nerv Syst 21(2):115–121. doi:10.1007/s00381-004-1051-y
Petrides M, Pandya DN (1984) Projections to the frontal cortex from the posterior parietal region in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 228(1):105–116. doi:10.1002/cne.902280110
Petrides M, Pandya DN (1988) Association fiber pathways to the frontal cortex from the superior temporal region in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 273(1):52–66. doi:10.1002/cne.902730106
Petrides M, Pandya DN (2006) Efferent association pathways originating in the caudal prefrontal cortex in the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol 498(2):227–251. doi:10.1002/cne.21048
Petrides M, Pandya DN (2007) Efferent association pathways from the rostral prefrontal cortex in the macaque monkey. J Neurosci 27(43):11573–11586. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2419-07.2007
Petrides M, Pandya DN (2008) Neural circuitry underlying language. In: Marien P, Abutalebi J (eds) Neuropsychological research: a review. Psychology Press, London, pp 22–60
Pierpaoli C, Barnett A, Pajevic S, Chen R, Penix LR, Virta A, Basser P (2001) Water diffusion changes in Wallerian degeneration and their dependence on white matter architecture. Neuroimage 13(6 Pt 1):1174–1185
Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ (1996) Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med 36(6):893–906. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910360612
Rademacher J, Galaburda AM, Kennedy DN, Filipek PA, VSj Caviness (1992) Human cerebral cortex: localization, parcellation, and morphometry with magnetic resonance imaging. J Cogn Neurosci 4(4):352–374. doi:10.1162/jocn.1992.4.4.352
Rauschecker J (1995) Compensatory plasticity and sensory substitution in the cerebral cortex. Trends Neurosci 18:36–43. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(95)93948-W
Rauschecker JP, Tian B (2000) Mechanisms and streams for processing of “what” and “where” in auditory cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(22):11800–11806. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.22.11800
Rilling JK, Glasser MF, Preuss TM, Ma X, Zhao T, Hu X, Behrens TE (2008) The evolution of the arcuate fasciculus revealed with comparative DTI. Nat Neurosci 11(4):426–428
Romanski LM, Bates JF, Goldman-Rakic PS (1999a) Auditory belt and parabelt projections to the prefrontal cortex in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 403(2):141–157. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19990111)403:2<141::AID-CNE1>3.0.CO;2-V
Romanski LM, Tian B, Fritz J, Mishkin M, Goldman-Rakic PS, Rauschecker JP (1999b) Dual streams of auditory afferents target multiple domains in the primate prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci 2(12):1131–1136. doi:10.1038/16056
Saur D, Kreher BW, Schnell S, Kummerer D, Kellmeyer P, Vry MS, Umarova R, Musso M, Glauche V, Abel S, Huber W, Rijntjes M, Hennig J, Weiller C (2008) Ventral and dorsal pathways for language. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(46):18035–18040
Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN (2006) Fiber pathways of the brain. Oxford University Press, New York
Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN, Wang R, Dai G, D’Arceuil HE, de Crespigny AJ, Wedeen VJ (2007) Association fibre pathways of the brain: parallel observations from diffusion spectrum imaging and autoradiography. Brain 130(Pt 3):630–653. doi:10.1093/brain/awl359
Seltzer B, Pandya DN (1984) Further observations on parieto-temporal connections in the rhesus monkey. Exp Brain Res 55(2):301–312. doi:10.1007/BF00237280
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc, New York
Vaadia E, Benson DA, Hienz RD, Goldstein MH Jr (1986) Unit study of monkey frontal cortex: active localization of auditory and of visual stimuli. J Neurophysiol 56(4):934–952
Wernicke C (1874) Der aphasiche Symptomenkomplex. Cohn und Weigert, Breslau
Werring DJ, Toosy AT, Clark CA, Parker GJ, Barker GJ, Miller DH, Thompson AJ (2000) Diffusion tensor imaging can detect and quantify corticospinal tract degeneration after stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69(2):269–272. doi:10.1136/jnnp.69.2.269
Acknowledgments
Preparation of this article was supported in part by grants from: the National Institutes of Health National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) to Dr. Nikos Makris. The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Edward H. Yeterian, Dr. Larry Seidman, Jonathan Kaiser, Danielle Sliva, George Papadimitriou, Steve Hodge, Thomas Benner and Dr. Andre van der Kouwe for their valuable contributions to the preparation of this manuscript. Offprints: Nikos Makris, M.D., Ph.D., Center for Morphometric Analysis, Massachusetts General Hospital, 149 13th St., Room 6017, Charlestown, MA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Human research statement: The experiments undertaken in this paper were performed with the understanding and written informed consent of each subject.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makris, N., Pandya, D.N. The extreme capsule in humans and rethinking of the language circuitry. Brain Struct Funct 213, 343–358 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-008-0199-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-008-0199-8