Abstract
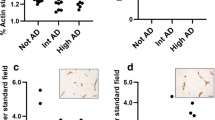
Alterations in the blood brain barrier and brain vasculature may be involved in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. We sought to determine if vascular remodeling characterized by angiogenic vessels or increased vascular density, occurred in pathologically confirmed Alzheimer’s disease (AD) postmortem human brain tissues. We examined brains of deceased, older catholic clergy from the Religious Order Study, a longitudinal clinical–pathological study of aging and AD. The hippocampus, midfrontal cortex, substantia nigra, globus pallidus and locus ceruleus were examined for integrin αvβ3 immunoreactivity, a marker of angiogenesis, and vascular densities. Activated microglia cell counts were also performed. All areas except the globus pallidus exhibited elevated αvβ3 immunoreactivity in AD cases compared with controls. Only in the hippocampus did the ongoing angiogenesis result in increased vascular density compared with controls. Vascular density was correlated with Aβ load in the hippocampus and αvβ3 reactivity was correlated with neurofibrillary tangles in the midfrontal cortex and in the substantia nigra. These data indicate that ongoing angiogenesis is present in brain regions affected by AD pathology and may be related to tissue injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott NJ (2000) Inflammatory mediators and modulation of blood–brain barrier permeability. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20:131–147
Akiyama H, Kawamata T, Dedhar S, McGeer PL (1991) Immunohistochemical localization of vitronectin, its receptor and beta-3 integrin in Alzheimer brain tissue. J Neuroimmunol 32:19–28
Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Kondo H, McGeer PL (1992) Thrombin accumulation in brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 146:152–154
Alzheimer A, Stelzmann RA, Schnitzlein HN, Murtagh FR (1995) An English translation of Alzheimer’s 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”. Clin Anat 8:429–431
Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Wilson RS, Bienias JL, Arnold SE (2004) Neurofibrillary tangles mediate the association of amyloid load with clinical Alzheimer disease and level of cognitive function. Arch Neurol 61:378–384
Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Kelly JF, Aggarwal NT, Shah RC, Wilson RS (2006) Neuropathology of older persons without cognitive impairment from two community-based studies. Neurology 66:1837–1844
Boscolo E, Folin M, Nico B, Grandi C, Mangieri D, Longo V, Scienza R, Zampieri P, Conconi MT, Parnigotto PP, Ribatti D (2007) Beta amyloid angiogenic activity in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med 19:581–587
Braak H, Braak E (1995) Staging of Alzheimer’s disease-related neurofibrillary changes. Neurobiol Aging 16:271–278 discussion 278–284
Braak H, Braak E (1997) Frequency of stages of Alzheimer-related lesions in different age categories. Neurobiol Aging 18:351–357
Brilliant MJ, Elble RJ, Ghobrial M, Struble RG (1997) The distribution of amyloid beta protein deposition in the corpus striatum of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 23:322–325
Brooks PC (1996) Role of integrins in angiogenesis. Eur J Cancer 32A:2423–2429
Cantara S, Donnini S, Morbidelli L, Giachetti A, Schulz R, Memo M, Ziche M (2004) Physiological levels of amyloid peptides stimulate the angiogenic response through FGF-2. Faseb J 18:1943–1945
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407:249–257
Carmeliet P, Storkebaum E (2002) Vascular and neuronal effects of VEGF in the nervous system: implications for neurological disorders. Semin Cell Dev Biol 13:39–53
Carvey PM, Zhao CH, Hendey B, Lum H, Trachtenberg J, Desai BS, Snyder J, Zhu YG, Ling ZD (2005) 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced alterations in blood–brain barrier permeability. Eur J Neurosci 22:1158–1168
Cheresh DA, Stupack DG (2008) Regulation of angiogenesis: apoptotic cues from the ECM. Oncogene 27:6285–6298
Croll SD, Ransohoff RM, Cai N, Zhang Q, Martin FJ, Wei T, Kasselman LJ, Kintner J, Murphy AJ, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ (2004) VEGF-mediated inflammation precedes angiogenesis in adult brain. Exp Neurol 187:388–402
Deane R, Zlokovic BV (2007) Role of the blood–brain barrier in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 4:191–197
Folkman J (2004) Endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors. APMIS 112:496–507
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Horton M (1990) Vitronectin receptor: tissue specific expression or adaptation to culture? Int J Exp Pathol 71:741–759
Jain RK (2001) Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med 7:987–989
Jain RK (2005) Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307:58–62
Kalaria RN (1992) The blood–brain barrier and cerebral microcirculation in Alzheimer disease. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 4:226–260
Kalaria RN, Cohen DL, Premkumar DR, Nag S, LaManna JC, Lust WD (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor in Alzheimer’s disease and experimental cerebral ischemia. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 62:101–105
Kalinowski L, Dobrucki LW, Meoli DF, Dione DP, Sadeghi MM, Madri JA, Sinusas AJ (2008) Targeted imaging of hypoxia-induced integrin activation in myocardium early after infarction. J Appl Physiol 104:1504–1512
Kanaan NM, Kordower JH, Collier TJ (2008) Age and region-specific responses of microglia, but not astrocytes, suggest a role in selective vulnerability of dopamine neurons after 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine exposure in monkeys. Glia 56:1199–1214
Lahdenranta J, Sidman RL, Pasqualini R, Arap W (2007) Treatment of hypoxia-induced retinopathy with targeted proapoptotic peptidomimetic in a mouse model of disease. Faseb J 21:3272–3278
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1995) The inflammatory response system of brain: implications for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 21:195–218
Meyer EP, Ulmann-Schuler A, Staufenbiel M, Krucker T (2008) Altered morphology and 3D architecture of brain vasculature in a mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:3587–3592
Milner R, Frost E, Nishimura S, Delcommenne M, Streuli C, Pytela R, Ffrench-Constant C (1997) Expression of alpha vbeta3 and alpha vbeta8 integrins during oligodendrocyte precursor differentiation in the presence and absence of axons. Glia 21:350–360
Mitchell TW, Nissanov J, Han LY, Mufson EJ, Schneider JA, Cochran EJ, Bennett DA, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Arnold SE (2000) Novel method to quantify neuropil threads in brains from elders with or without cognitive impairment. J Histochem Cytochem 48:1627–1638
Nagy JA, Benjamin L, Zeng H, Dvorak AM, Dvorak HF (2008) Vascular permeability, vascular hyperpermeability and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 11:109–119
Nakajima M, Yuasa S, Ueno M, Takakura N, Koseki H, Shirasawa T (2003) Abnormal blood vessel development in mice lacking presenilin-1. Mech Dev 120:657–667
Naldini A, Carraro F (2005) Role of inflammatory mediators in angiogenesis. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4:3–8
NIA Working Group (1997) Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol Aging 18:S1–S2
Paik DC, Fu C, Bhattacharya J, Tilson MD (2004) Ongoing angiogenesis in blood vessels of the abdominal aortic aneurysm. Exp Mol Med 36:524–533
Paris D, Patel N, DelleDonne A, Quadros A, Smeed R, Mullan M (2004a) Impaired angiogenesis in a transgenic mouse model of cerebral amyloidosis. Neurosci Lett 366:80–85
Paris D, Townsend K, Quadros A, Humphrey J, Sun J, Brem S, Wotoczek-Obadia M, DelleDonne A, Patel N, Obregon DF, Crescentini R, Abdullah L, Coppola D, Rojiani AM, Crawford F, Sebti SM, Mullan M (2004b) Inhibition of angiogenesis by Abeta peptides. Angiogenesis 7:75–85
Phares TW, Kean RB, Mikheeva T, Hooper DC (2006) Regional differences in blood–brain barrier permeability changes and inflammation in the apathogenic clearance of virus from the central nervous system. J Immunol 176:7666–7675
Pinkstaff JK, Detterich J, Lynch G, Gall C (1999) Integrin subunit gene expression is regionally differentiated in adult brain. J Neurosci 19:1541–1556
Pogue AI, Lukiw WJ (2004) Angiogenic signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 15:1507–1510
Sato W, Kosugi T, Zhang L, Roncal CA, Heinig M, Campbell-Thompson M, Yuzawa Y, Atkinson MA, Grant MB, Croker BP, Nakagawa T (2008) The pivotal role of VEGF on glomerular macrophage infiltration in advanced diabetic nephropathy. Lab Invest 88:949–961
Schmid-Brunclik N, Burgi-Taboada C, Antoniou X, Gassmann M, Ogunshola OO (2008) Astrocyte responses to injury: VEGF simultaneously modulates cell death and proliferation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295:R864–R873
Schneider JA, Li JL, Li Y, Wilson RS, Kordower JH, Bennett DA (2006) Substantia nigra tangles are related to gait impairment in older persons. Ann Neurol 59:166–173
Schneider JA, Boyle PA, Arvanitakis Z, Bienias JL, Bennett DA (2007) Subcortical infarcts, Alzheimer’s disease pathology, and memory function in older persons. Ann Neurol 62:59–66
Schultheiss C, Blechert B, Gaertner FC, Drecoll E, Mueller J, Weber GF, Drzezga A, Essler M (2006) In vivo characterization of endothelial cell activation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Angiogenesis 9:59–65
Siedlak SL, Cras P, Kawai M, Richey P, Perry G (1991) Basic fibroblast growth factor binding is a marker for extracellular neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease. J Histochem Cytochem 39:899–904
Streit WJ, Mrak RE, Griffin WS (2004) Microglia and neuroinflammation: a pathological perspective. J Neuroinflammation 1:14
Tarkowski E, Issa R, Sjogren M, Wallin A, Blennow K, Tarkowski A, Kumar P (2002) Increased intrathecal levels of the angiogenic factors VEGF and TGF-beta in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Neurobiol Aging 23:237–243
Thirumangalakudi L, Samany PG, Owoso A, Wiskar B, Grammas P (2006) Angiogenic proteins are expressed by brain blood vessels in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 10:111–118
Tsopanoglou NE, Maragoudakis ME (1999) On the mechanism of thrombin-induced angiogenesis. Potentiation of vascular endothelial growth factor activity on endothelial cells by up-regulation of its receptors. J Biol Chem 274:23969–23976
Vagnucci AH Jr, Li WW (2003) Alzheimer’s disease and angiogenesis. Lancet 361:605–608
Wei L, Erinjeri JP, Rovainen CM, Woolsey TA (2001) Collateral growth and angiogenesis around cortical stroke. Stroke 32:2179–2184
Williams RW, Rakic P (1988) Three-dimensional counting: an accurate and direct method to estimate numbers of cells in sectioned material. J Comp Neurol 278:344–352
Willmann JK, Lutz AM, Paulmurugan R, Patel MR, Chu P, Rosenberg J, Gambhir SS (2008) Dual-targeted contrast agent for US assessment of tumor angiogenesis in vivo. Radiology 248:936–944
Yang SP, Bae DG, Kang HJ, Gwag BJ, Gho YS, Chae CB (2004) Co-accumulation of vascular endothelial growth factor with beta-amyloid in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 25:283–290
Zarow C, Barron E, Chui HC, Perlmutter LS (1997) Vascular basement membrane pathology and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 826:147–160
Zarow C, Lyness SA, Mortimer JA, Chui HC (2003) Neuronal loss is greater in the locus coeruleus than nucleus basalis and substantia nigra in Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Arch Neurol 60:337–341
Zetterberg H, Andreasen N, Blennow K (2004) Increased cerebrospinal fluid levels of transforming growth factor-beta1 in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 367:194–196
Zlokovic BV (2008) The blood–brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57:178–201
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by RO1AI51619 (BH), K08AG00084 (JAS), P30AG10161 (JAS), R01AG15819 (JAS), and the Kenneth Douglas Foundation (PMC). We thank Dr. Sue Leurgans for her statistical expertise. We thank the nuns, priests, and brothers from the following groups participating in the Religious Orders Study: Archdiocesan priests of Chicago, Dubuque, and Milwaukee; Benedictine Monks, Lisle, IL, and Collegeville, MN; Benedictine Sisters of Erie, Erie, PA; Benedictine Sisters of the Sacred Heart, Lisle, IL; Capuchins, Appleton, WI; Christian Brothers, Chicago, IL, and Memphis, TN; Diocesan priests of Gary, IN; Dominicans, River Forest, IL; Felician Sisters, Chicago, IL; Franciscan Handmaids of Mary, New York, NY; Franciscans, Chicago, IL; Holy Spirit Missionary Sisters, Techny, IL; Maryknolls, Los Altos, CA and Maryknoll, NY; Norbertines, DePere, WI; Oblate Sisters of Providence, Baltimore, MD; Passionists, Chicago, IL; Presentation Sisters, Dubuque, BVM., IA; Servites, Chicago, IL; Sinsinawa Dominican Sisters, Chicago, IL, and Sinsinawa, WI; Sisters of Charity, B.V.M., Chicago, IL, and Dubuque, IA; Sisters of the Holy Family, New Orleans, LA; Sisters of the Holy Family of Nazareth, Des Plaines, IL; Sisters of Mercy of the Americas, Chicago and Aurora, IL, Erie, PA; Sisters of St. Benedict, St. Cloud and St. Joseph, MN; Sisters of St. Casimir, Chicago, IL; Sisters of St. Francis of Mary Immaculate, Joliet, IL; Sisters of St. Joseph of LaGrange, LaGrange Park, IL; Society of Divine Word, Techny, IL; Trappists, Gethsemani, KY, and Peosta, IA; Wheaton Franciscan Sisters, Wheaton, IL. We thank T. Colvin and J. Bach, Religious Orders Study Coordinators; data and analytic programmers, Karen Skish, Veronica Flores, Davik Shah, Benjamin Spirtovic, Wayne Longman and Yu Li for technical assistance and the Rush Institute for Healthy Aging staff.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desai, B.S., Schneider, J.A., Li, JL. et al. Evidence of angiogenic vessels in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 116, 587–597 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0226-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0226-9