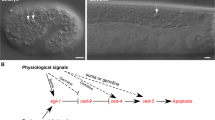
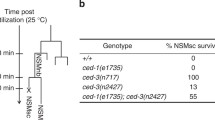
Abstract
Programmed cell death is used during developmental morphogenesis to eliminate superfluous cells or cells with inappropriate developmental potential (e.g., self-reactive immune cells, tumorigenic cells). Recent work in genetic models has led to a number of key observations, revealing signal transduction pathways and identifying new roles for genes previously studied in corpse removal (e.g., removal of broken synapses in the nervous system). Further, studies using mouse models have suggested a role for removal of apoptotic cells in the establishment or maintenance of immune tolerance. In this review, we survey current knowledge of phagocytic pathways derived from studies in the nematode (Caenorhabditis elegans), the fly (Drosophila melanogaster), and mouse (Mus musculus) model systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABCA1/7:
-
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A, member 1 or 7
- ABL-1:
-
Related to oncogene Abl 1
- ABI-1:
-
Abl interactor homologue 1
- BAI1:
-
Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor-1
- Ccz1:
-
Caffeine, calcium and zinc sensitive 1
- CED (ced):
-
Cell death abnormal
- CrkII:
-
v-crk Sarcoma virus CT10 oncogene homologue
- Dock180:
-
Dedicator of cytokinesis (180 kDa), also called Dock1
- DStim:
-
Drosophila stromal interaction molecule
- DYN-1:
-
Dynamin related 1
- ELMO:
-
Engulfment and cell motility
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- GEF:
-
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
- GULP:
-
Engulfment adapter, PTB domain containing 1
- ITAM:
-
Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif
- LXR:
-
Liver × receptor
- LRP1:
-
Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1
- MEGF10:
-
Multiple EGF-like domains 10
- MFG-E8:
-
Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 (also called lactadherin)
- MIG-2:
-
Abnormal cell migration 2
- MOM-5:
-
More of MS 5
- MTM-1:
-
MTM (myotubularin) family 1
- Mon1:
-
Monensin sensitivity protein 1
- ORAI:
-
ORAI calcium release-activated calcium modulator
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PPAR:
-
Peroxisome proliferation-activated receptor
- PtdSer:
-
Phosphatidylserine
- RABX-5:
-
Rab exchange factor
- Rac1:
-
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1
- RhoG:
-
Ras homologue gene family, member G
- RME-6:
-
Receptor-mediated endocytosis 6
- SAND-1:
-
SAND endocytosis protein family
- SR-A:
-
Scavenger receptor, types I and II, isoform A
- Syk:
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase
- TAG-333:
-
Temporarily assigned gene name 333
- TBC-2:
-
TBC (Tre-2/Bub2/Cvc16) domain family 2
- TIM:
-
T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain containing
- Ub:
-
Ubiquitin
- Vps34:
-
Vacuolar protein sorting factor 34
- UNC-73:
-
Uncoordinated 73
- ZAP-70:
-
Zeta-chain (TCR) associated protein kinase (70 kDa)
References
Park D, Hochreiter-Hufford A, Ravichandran KS (2009) The phosphatidylserine receptor TIM-4 does not mediate direct signaling. Curr Biol 19:346–351
Kobayashi N, Karisola P, Pena-Cruz V et al (2007) TIM-1 and TIM-4 glycoproteins bind phosphatidylserine and mediate uptake of apoptotic cells. Immunity 27:927–940
Nakayama M, Akiba H, Takeda K et al (2009) Tim-3 mediates phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cross-presentation. Blood 113:3821–3830
Hanayama R, Tanaka M, Miyasaka K et al (2004) Autoimmune disease and impaired uptake of apoptotic cells in MFG-E8-deficient mice. Science 304:1147–1150
Lacy-Hulbert A, Smith AM, Tissire H et al (2007) Ulcerative colitis and autoimmunity induced by loss of myeloid alphav integrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15823–15828
Scott RS, McMahon EJ, Pop SM et al (2001) Phagocytosis and clearance of apoptotic cells is mediated by MER. Nature 411:207–211
Kinchen JM, Ravichandran KS (2007) Journey to the grave: signaling events regulating removal of apoptotic cells. J Cell Sci 120:2143–2149
Stuart LM, Ezekowitz RA (2008) Phagocytosis and comparative innate immunity: learning on the fly. Nat Rev Immunol 8:131–141
Mangahas PM, Zhou Z (2005) Clearance of apoptotic cells in Caenorhabditis elegans. Semin Cell Dev Biol 16:295–306
Zhou Z, Mangahas PM, Yu X (2004) The genetics of hiding the corpse: engulfment and degradation of apoptotic cells in C. elegans and D. melanogaster. Curr Top Dev Biol 63:91–143
Hoeppner DJ, Spector MS, Ratliff TM et al (2004) eor-1 and eor-2 are required for cell-specific apoptotic death in C. elegans. Dev Biol 274:125–138
Reece-Hoyes JS, Deplancke B, Barrasa MI et al (2009) The C. elegans Snail homolog CES-1 can activate gene expression in vivo and share targets with bHLH transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res 37:3689–3698
Cameron S, Clark SG, McDermott JB, Aamodt E, Horvitz HR (2002) PAG-3, a Zn-finger transcription factor, determines neuroblast fate in C. elegans. Development 129:1763–1774
Abraham MC, Lu Y, Shaham S (2007) A morphologically conserved nonapoptotic program promotes linker cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Cell 12:73–86
Lettre G, Hengartner MO (2006) Developmental apoptosis in C. elegans: a complex CEDnario. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:97–108
Ravichandran KS, Lorenz U (2007) Engulfment of apoptotic cells: signals for a good meal. Nat Rev Immunol 7:964–974
Kinchen JM, Cabello J, Klingele D et al (2005) Two pathways converge at CED-10 to mediate actin rearrangement and corpse removal in C. elegans. Nature 434:93–99
Zhou Z, Hartwieg E, Horvitz HR (2001) CED-1 is a transmembrane receptor that mediates cell corpse engulfment in C. elegans. Cell 104:43–56
Su HP, Nakada-Tsukui K, Tosello-Trampont AC et al (2002) Interaction of CED-6/GULP, an adapter protein involved in engulfment of apoptotic cells with CED-1 and CD91/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). J Biol Chem 277:11772–11779
Kiss RS, Ma Z, Nakada-Tsukui K et al (2006) The lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP) adapter protein GULP mediates trafficking of the LRP ligand prosaposin, leading to sphingolipid and free cholesterol accumulation in late endosomes and impaired efflux. J Biol Chem 281:12081–12092
Yu X, Lu N, Zhou Z (2008) Phagocytic receptor CED-1 initiates a signaling pathway for degrading engulfed apoptotic cells. PLoS Biol 6:e61
Kiss RS, Elliott MR, Ma Z, Marcel YL, Ravichandran KS (2006) Apoptotic cells induce a phosphatidylserine-dependent homeostatic response from phagocytes. Curr Biol 16:2252–2258
Brooks-Wilson A, Marcil M, Clee SM et al (1999) Mutations in ABC1 in Tangier disease and familial high-density lipoprotein deficiency. Nat Genet 22:336–345
Wu YC, Horvitz HR (1998) The C. elegans cell corpse engulfment gene CED-7 encodes a protein similar to ABC transporters. Cell 93:951–960
Venegas V, Zhou Z (2007) Two alternative mechanisms that regulate the presentation of apoptotic cell engulfment signal in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell 18:3180–3192
Franc NC, Dimarcq JL, Lagueux M, Hoffmann J, Ezekowitz RA (1996) Croquemort, a novel Drosophila hemocyte/macrophage receptor that recognizes apoptotic cells. Immunity 4:431–443
Franc NC, Heitzler P, Ezekowitz RA, White K (1999) Requirement for croquemort in phagocytosis of apoptotic cells in Drosophila. Science 284:1991–1994
Freeman MR, Delrow J, Kim J, Johnson E, Doe CQ (2003) Unwrapping glial biology: Gcm target genes regulating glial development, diversification, and function. Neuron 38:567–580
Manaka J, Kuraishi T, Shiratsuchi A et al (2004) Draper-mediated and phosphatidylserine-independent phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by Drosophila hemocytes/macrophages. J Biol Chem 279:48466–48476
Awasaki T, Tatsumi R, Takahashi K et al (2006) Essential role of the apoptotic cell engulfment genes draper and ced-6 in programmed axon pruning during Drosophila metamorphosis. Neuron 50:855–867
MacDonald JM, Beach MG, Porpiglia E, Sheehan AE, Watts RJ, Freeman MR (2006) The Drosophila cell corpse engulfment receptor Draper mediates glial clearance of severed axons. Neuron 50:869–881
Kurant E, Axelrod S, Leaman D, Gaul U (2008) Six-microns-under acts upstream of Draper in the glial phagocytosis of apoptotic neurons. Cell 133:498–509
Wu HH, Bellmunt E, Scheib JL et al (2009) Glial precursors clear sensory neuron corpses during development via Jedi-1, an engulfment receptor. Nat Neurosci 12:1534–1541
Hamon Y, Trompier D, Ma Z et al (2006) Cooperation between engulfment receptors: the case of ABCA1 and MEGF10. PLoS One 1:e120
Platt N, Suzuki H, Kurihara Y, Kodama T, Gordon S (1996) Role for the class A macrophage scavenger receptor in the phagocytosis of apoptotic thymocytes in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12456–12460
Gardai SJ, McPhillips KA, Frasch SC et al (2005) Cell-surface calreticulin initiates clearance of viable or apoptotic cells through trans-activation of LRP on the phagocyte. Cell 123:321–334
Doherty J, Logan MA, Tasdemir OE, Freeman MR (2009) Ensheathing glia function as phagocytes in the adult Drosophila brain. J Neurosci 29:4768–4781
Ziegenfuss JS, Biswas R, Avery MA et al (2008) Draper-dependent glial phagocytic activity is mediated by Src and Syk family kinase signalling. Nature 453:935–939
Fadok VA, Voelker DR, Campbell PA, Cohen JJ, Bratton DL, Henson PM (1992) Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J Immunol 148:2207–2216
Hanayama R, Tanaka M, Miwa K, Shinohara A, Iwamatsu A, Nagata S (2002) Identification of a factor that links apoptotic cells to phagocytes. Nature 417:182–187
Park SY, Jung MY, Kim HJ et al (2008) Rapid cell corpse clearance by stabilin-2, a membrane phosphatidylserine receptor. Cell Death Differ 15:192–201
Park D, Tosello-Trampont AC, Elliott MR et al (2007) BAI1 is an engulfment receptor for apoptotic cells upstream of the ELMO/Dock180/Rac module. Nature 450:430–434
Schutters K, Reutelingsperger CP (2010) Phosphatidylserine targeting for diagnosis and treatment of human diseases. Apoptosis (current issue)
Miyanishi M, Tada K, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Kitamura T, Nagata S (2007) Identification of Tim4 as a phosphatidylserine receptor. Nature 450:435–439
Wang X, Wang J, Gengyo-Ando K et al (2007) C. elegans mitochondrial factor WAH-1 promotes phosphatidylserine externalization in apoptotic cells through phospholipid scramblase SCRM-1. Nat Cell Biol 9:541–549
Kuraishi T, Nakagawa Y, Nagaosa K et al (2009) Pretaporter, a Drosophila protein serving as a ligand for Draper in the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. EMBO J 28:3868–3878
Kuraishi T, Manaka J, Kono M et al (2007) Identification of calreticulin as a marker for phagocytosis of apoptotic cells in Drosophila. Exp Cell Res 313:500–510
Ogden CA, deCathelineau A, Hoffmann PR et al (2001) C1q and mannose binding lectin engagement of cell surface calreticulin and CD91 initiates macropinocytosis and uptake of apoptotic cells. J Exp Med 194:781–795
Mirnikjoo B, Balasubramanian K, Schroit AJ (2009) Suicidal membrane repair regulates phosphatidylserine externalization during apoptosis. J Biol Chem 284:22512–22516
Brugnera E, Haney L, Grimsley C et al (2002) Unconventional Rac-GEF activity is mediated through the Dock180-ELMO complex. Nat Cell Biol 4:574–582
Lu M, Kinchen JM, Rossman KL et al (2004) PH domain of ELMO functions in trans to regulate Rac activation via Dock180. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:756–762
Lu M, Kinchen JM, Rossman KL et al (2005) A steric-inhibition model for regulation of nucleotide exchange via the Dock180 family of GEFs. Curr Biol 15:371–377
Cote JF, Motoyama AB, Bush JA, Vuori K (2005) A novel and evolutionarily conserved PtdIns(3, 4, 5)P3-binding domain is necessary for DOCK180 signalling. Nat Cell Biol 7:797–807
Reddien PW, Horvitz HR (2000) CED-2/CrkII and CED-10/Rac control phagocytosis and cell migration in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Cell Biol 2:131–136
Wu Y, Singh S, Georgescu MM, Birge RB (2005) A role for Mer tyrosine kinase in alphavbeta5 integrin-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. J Cell Sci 118:539–553
Akakura S, Singh S, Spataro M et al (2004) The opsonin MFG-E8 is a ligand for the alphavbeta5 integrin and triggers DOCK180-dependent Rac1 activation for the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Exp Cell Res 292:403–416
Albert ML, Kim JI, Birge RB (2000) alphavbeta5 integrin recruits the CrkII-Dock180-rac1 complex for phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Nat Cell Biol 2:899–905
Hsu TY, Wu YC (2010) Engulfment of apoptotic cells in C. elegans is mediated by integrin alpha/SRC signaling. Curr Biol 20:477–486
Gumienny TL, Brugnera E, Tosello-Trampont AC et al (2001) CED-12/ELMO, a novel member of the CrkII/Dock180/Rac pathway, is required for phagocytosis and cell migration. Cell 107:27–41
Cabello J, Neukomm LJ, Gunesdogan U et al (2010) The Wnt pathway controls cell death engulfment, spindle orientation, and migration through CED-10/Rac. PLoS Biol 8(2):e1000297
Angers S, Moon RT (2009) Proximal events in Wnt signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:468–477
Silva E, Au-Yeung HW, Van Goethem E, Burden J, Franc NC (2007) Requirement for a Drosophila E3-ubiquitin ligase in phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Immunity 27:585–596
Cuttell L, Vaughan A, Silva E et al (2008) Undertaker, a Drosophila Junctophilin, links Draper-mediated phagocytosis and calcium homeostasis. Cell 135:524–534
Yang Y, Lu J, Rovnak J, Quackenbush SL, Lundquist EA (2006) SWAN-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans WD repeat protein of the AN11 family, is a negative regulator of Rac GTPase function. Genetics 174:1917–1932
Hurwitz ME, Vanderzalm PJ, Bloom L, Goldman J, Garriga G, Horvitz HR (2009) Abl kinase inhibits the engulfment of apoptotic [corrected] cells in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Biol 7:e99
deBakker CD, Haney LB, Kinchen JM et al (2004) Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells is regulated by a UNC-73/TRIO-MIG-2/RhoG signaling module and armadillo repeats of CED-12/ELMO. Curr Biol 14:2208–2216
Tosello-Trampont AC, Kinchen JM, Brugnera E, Haney LB, Hengartner MO, Ravichandran KS (2007) Identification of two signaling submodules within the CrkII/ELMO/Dock180 pathway regulating engulfment of apoptotic cells. Cell Death Differ 14(5):963–972
Feller SM, Knudsen B, Hanafusa H (1994) c-Abl kinase regulates the protein binding activity of c-Crk. EMBO J 13:2341–2351
Ren R, Ye ZS, Baltimore D (1994) Abl protein-tyrosine kinase selects the Crk adapter as a substrate using SH3-binding sites. Genes Dev 8:783–795
Sheffield M, Loveless T, Hardin J, Pettitt J (2007) C. elegans enabled exhibits novel interactions with N-WASP, Abl, and cell-cell junctions. Curr Biol 17:1791–1796
Ravid T, Hochstrasser M (2008) Diversity of degradation signals in the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:679–690
Dikic I, Wakatsuki S, Walters KJ (2009) Ubiquitin-binding domains: from structures to functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:659–671
Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD (2000) The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:11–21
Lu Q, Zhang Y, Hu T, Guo P, Li W, Wang X (2008) C. elegans Rab GTPase 2 is required for the degradation of apoptotic cells. Development 135:1069–1080
Mangahas PM, Yu X, Miller KG, Zhou Z (2008) The small GTPase Rab2 functions in the removal of apoptotic cells in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Cell Biol 180:357–373
Kinchen JM, Doukoumetzidis K, Almendinger J et al (2008) A pathway for phagosome maturation during engulfment of apoptotic cells. Nat Cell Biol 10:556–566
Kinchen JM, Ravichandran KS (2008) Phagosome maturation: going through the acid test. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:781–795
Yu X, Odera S, Chuang CH, Lu N, Zhou Z (2006) C. elegans Dynamin mediates the signaling of phagocytic receptor CED-1 for the engulfment and degradation of apoptotic cells. Dev Cell 10:743–757
Kinchen JM, Ravichandran KS (2010) Identification of two evolutionarily conserved genes regulating processing of engulfed apoptotic cells. Nature 464(7289):778–782
Grosshans BL, Ortiz D, Novick P (2006) Rabs and their effectors: achieving specificity in membrane traffic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:11821–11827
Seabra MC, Wasmeier C (2004) Controlling the location and activation of Rab GTPases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:451–457
Xiao H, Chen D, Fang Z et al (2009) Lysosome biogenesis mediated by vps-18 affects apoptotic cell degradation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell 20:21–32
Li W, Zou W, Zhao D et al (2009) C. elegans Rab GTPase activating protein TBC-2 promotes cell corpse degradation by regulating the small GTPase RAB-5. Development 136:2445–2455
Zou W, Lu Q, Zhao D et al (2009) Caenorhabditis elegans myotubularin MTM-1 negatively regulates the engulfment of apoptotic cells. PLoS Genet 5:e1000679
Fuentes-Medel Y, Logan MA, Ashley J, Ataman B, Budnik V, Freeman MR (2009) Glia and muscle sculpt neuromuscular arbors by engulfing destabilized synaptic boutons and shed presynaptic debris. PLoS Biol 7:e1000184
Erwig LP, Henson PM (2007) Immunological consequences of apoptotic cell phagocytosis. Am J Pathol 171:2–8
Elliott MR, Chekeni FB, Trampont PC et al (2009) Nucleotides released by apoptotic cells act as a find-me signal to promote phagocytic clearance. Nature 461:282–286
Lauber K, Bohn E, Krober SM et al (2003) Apoptotic cells induce migration of phagocytes via caspase-3-mediated release of a lipid attraction signal. Cell 113:717–730
Truman LA, Ford CA, Pasikowska M et al (2008) CX3CL1/fractalkine is released from apoptotic lymphocytes to stimulate macrophage chemotaxis. Blood 112:5026–5036
Peter C, Wesselborg S, Herrmann M, Lauber K (2010) Dangerous attraction: phagocyte recruitment and danger signals of apoptotic and necrotic cells. Apoptosis (this issue)
Cohen PL, Caricchio R, Abraham V et al (2002) Delayed apoptotic cell clearance and lupus-like autoimmunity in mice lacking the c-mer membrane tyrosine kinase. J Exp Med 196:135–140
Ishimoto Y, Ohashi K, Mizuno K, Nakano T (2000) Promotion of the uptake of PS liposomes and apoptotic cells by a product of growth arrest-specific gene, gas6. J Biochem 127:411–417
Sather S, Kenyon KD, Lefkowitz JB et al (2007) A soluble form of the Mer receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits macrophage clearance of apoptotic cells and platelet aggregation. Blood 109:1026–1033
Mukundan L, Odegaard JI, Morel CR et al (2009) PPAR-delta senses and orchestrates clearance of apoptotic cells to promote tolerance. Nat Med 15:1266–1272
A-Gonzalez N, Bensinger SJ, Hong C et al (2009) Apoptotic cells promote their own clearance and immune tolerance through activation of the nuclear receptor LXR. Immunity 31:245–258
Franz S, Gaipl US, Munoz LE et al (2006) Apoptosis and autoimmunity: when apoptotic cells break their silence. Curr Rheumatol Rep 8:245–247
Korb LC, Ahearn JM (1997) C1q binds directly and specifically to surface blebs of apoptotic human keratinocytes: complement deficiency and systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. J Immunol 158:4525–4528
Mevorach D (1999) The immune response to apoptotic cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 887:191–198
Devitt A, Parker KG, Ogden CA et al (2004) Persistence of apoptotic cells without autoimmune disease or inflammation in CD14−/− mice. J Cell Biol 167:1161–1170
Krysko DV, D’Herde K, Vandenabeele P (2006) Clearance of apoptotic and necrotic cells and its immunological consequences. Apoptosis 11:1709–1726
Patel VA, Lee DJ, Longacre-Antoni A et al (2009) Apoptotic and necrotic cells as sentinels of local tissue stress and inflammation: response pathways initiated in nearby viable cells. Autoimmunity 42:317–321
Torchinsky MB, Garaude J, Blander JM (2010) Infection and apoptosis as a combined inflammatory trigger. Curr Opin Immunol 22:55–62
Torchinsky MB, Garaude J, Martin AP, Blander JM (2009) Innate immune recognition of infected apoptotic cells directs T(H)17 cell differentiation. Nature 458:78–82
Blander JM, Medzhitov R (2006) Toll-dependent selection of microbial antigens for presentation by dendritic cells. Nature 440:808–812
Blander JM, Medzhitov R (2004) Regulation of phagosome maturation by signals from toll-like receptors. Science 304:1014–1018
Kirsch T, Woywodt A, Beese M et al (2007) Engulfment of apoptotic cells by microvascular endothelial cells induces proinflammatory responses. Blood 109:2854–2862
Canbay A, Feldstein AE, Higuchi H et al (2003) Kupffer cell engulfment of apoptotic bodies stimulates death ligand and cytokine expression. Hepatology 38:1188–1198
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank K. S. Ravichandran and Cynthia Grimsley-Myers for helpful comments and discussion on this review. JMK is supported by a Scientist Development Grant from the American Heart Association and a grant from the American Cancer Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kinchen, J.M. A model to die for: signaling to apoptotic cell removal in worm, fly and mouse. Apoptosis 15, 998–1006 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0509-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0509-5