Abstract
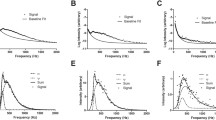
The ECoG background activity of cerebral cortex in states of rest and slow wave sleep resembles broadband noise. The power spectral density (PSD) then may often conform to a power-law distribution: a straight line in coordinates of log power vs. log frequency. The exponent, x, of the distribution, 1/fx, ranges between 2 and 4. These findings are explained with a model of the neural source of the background activity in mutual excitation among pyramidal cells. The dendritic response of a population of interactive excitatory neurons to an impulse input is a rapid exponential rise and a slow exponential decay, which can be fitted with the sum of two exponential terms. When that function is convolved as the kernel with pulses from a Poisson process and summed, the resulting “brown” or “black noise conforms to the ECoG time series and the PSD in rest and sleep. The PSD slope is dependent on the rate of rise. The variation in the observed slope is attributed to variation in the level of the background activity that is homeostatically regulated by the refractory periods of the excitatory neurons. Departures in behavior from rest and sleep to action are accompanied by local peaks in the PSD, which manifest emergent nonrandom structure in the ECoG, and which prevent reliable estimation of the 1/fx exponents in active states. We conclude that the resting ECoG truly is low-dimensional noise, and that the resting state is an optimal starting point for defining and measuring both artifactual and physiological structures emergent in the activated ECoG.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles M (1991) Corticonics: neural circuits of the cerebral cortex. Cambridge UP, New York
Barrie JM, Freeman WJ, Lenhart M (1996) Modulation by discriminative training of spatial patterns of gamma EEG amplitude and phase in neocortex of rabbits. J Neurophysiol 76:520–539
Elul R (1972) The genesis of the EEG. Int Rev Neurobiol 15:227–272. doi:10.1016/S0074-7742(08)60333-5
Freeman WJ (1974) A model for mutual excitation in a neuron population in olfactory bulb. Trans IEEE Biomed Eng 21:350–358. doi:10.1109/TBME.1974.324403
Freeman WJ (1975) Mass action in the nervous system. Academic Press, New York. © 2004: http://sulcus.berkeley.edu/MANSWWW/MANSWWW.html
Freeman WJ (1979) Nonlinear gain mediating cortical stimulus-response relations. Biol Cybern 33:237–247
Freeman WJ (2004a) Origin, structure, and role of background EEG activity. Part 1. Analytic amplitude. Clin Neurophysiol 115: 2077–2088. http://repositories.cdlib.org/postprints/1006
Freeman WJ (2004b) Origin, structure, and role of background EEG activity. Part 2. Analytic phase. Clin Neurophysiol 115:2089–2107
Freeman WJ (2005) Origin, structure, and role of background EEG activity. Part 3. Neural frame classification. Clin Neurophysiol 116(5):1118–1129. http://authors.elsevier.com/sd/article/S1388245705000064
Freeman WJ (2006a) Origin, structure, and role of background EEG activity. Part 4. Neural frame simulation. Clin Neurophysiol 117:572–589
Freeman WJ (2006b) Definitions of state variables and state space for brain-computer interface. Part 1. Multiple hierarchical levels of brain function. Cogn Neurodyn 1(1):13–14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11571-006-9001-x
Freeman WJ (2007) Definitions of state variables and state space for brain-computer interface. Part 2. Extraction and classification of feature vectors. Cogn Neurodyn 1(2):85–96
Freeman WJ, Cao Y (2008) Proposed renormalization group analysis of nonlinear brain dynamics at critically, Chapter 27. In: Wang R et al (eds) Advances in cognitive neurodynamics ICCN 2007. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 147–158
Freeman WJ, Zhai J (2007) Deriving 1/f form of human EEG spectrum from summed random pulse trains. International workshop on nonlinear brain dynamics (IWNBD’07) 9-10 June 2007, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Freeman WJ, Holmes MD, West GA, Vanhatalo S (2006) Fine spatiotemporal structure of phase in human intracranial EEG. Clin Neurophysiol 117:1228–1243
Percival DB, Walden AT (1993) Spectral analysis for physical applications: multitaper and conventional univariate techniques. Cambridge University Press
Raichle ME (2006) The brain’s dark energy. Science 314:1249–1250
Schroeder M (1991) Fractals, chaos, power laws. Minutes from an infinite paradise. WH Freeman, San Francisco
Siklós L, Rickmann M, Joó F, Freeman WJ, Wolff JR (1995) Chloride is preferentially accumulated in a subpopulation of dendrites and periglomerular cells of the main olfactory bulb in adult rats. Neuroscience 64:165–172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freeman, W.J., Zhai, J. Simulated power spectral density (PSD) of background electrocorticogram (ECoG). Cogn Neurodyn 3, 97–103 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-008-9064-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-008-9064-y