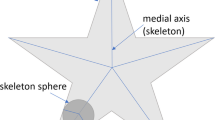
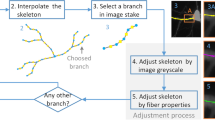
Abstract
Directional signal transmission is essential for neural circuit function and thus for connectomic analysis. The directions of signal flow can be obtained by experimentally identifying neuronal polarity (axons or dendrites). However, the experimental techniques are not applicable to existing neuronal databases in which polarity information is not available. To address the issue, we proposed SPIN: a method of Skeleton-based Polarity Identification for Neurons. SPIN was designed to work with large-scale neuronal databases in which tracing-line data are available. In SPIN, a classifier is first trained by neurons with known polarity in two steps: 1) identifying morphological features that most correlate with the polarity and 2) constructing a linear classifier by determining a discriminant axis (a specific combination of the features) and decision boundaries. Each polarity-undefined neuron is then divided into several morphological substructures (domains) and the corresponding polarities are determined using the classifier. Finally, the result is evaluated and warnings for potential errors are returned. We tested this method on fruitfly (Drosophila melanogaster) and blowfly (Calliphora vicina and Calliphora erythrocephala) unipolar neurons using data obtained from the Flycircuit and Neuromorpho databases, respectively. On average, the polarity of 84–92 % of the terminal points in each neuron could be correctly identified. An ideal performance with an accuracy between 93 and 98 % can be achieved if we fed SPIN with relatively “clean” data without artificial branches. Our result demonstrates that SPIN, as a computer-based semi-automatic method, provides quick and accurate polarity identification and is particularly suitable for analyzing large-scale data. We implemented SPIN in Matlab and released the codes under the GPLv3 license.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alivisatos, A. P., Chun, M., Church, G. M., Greenspan, R. J., Roukes, M. L., & Yuste, R. (2012). The brain activity map project and the challenge of functional connectomics. Neuron, 74(6), 970–974. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.06.006.
Ascoli, G. A., Donohue, D. E., & Halavi, M. (2007). NeuroMorpho.Org: a central resource for neuronal morphologies. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27(35), 9247–9251. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2055-07.2007.
Bas, E., & Erdogmus, D. (2011). Principal curves as skeletons of tubular objects: locally characterizing the structures of axons. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 181–191. doi:10.1007/s12021-011-9105-2.
Billeci, L., Magliaro, C., & Ahluwalia, A. (2013). NEuronMOrphological analysis tool: open-source software for quantitative morphometrics. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 7, 2. doi:10.3389/fninf.2013.00002.
Borst, A., & Haag, J. (1996). The intrinsic electrophysiological characteristics of fly lobula plate tangential cells: I. Passive membrane properties. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 3(4), 313–336. doi:10.1007/BF00161091.
Brown, K. M., Barrionuevo, G., Canty, A. J., Paola, V., Hirsch, J. A., Jefferis, G. S. X. E., et al. (2011). The DIADEM data sets: representative light microscopy images of neuronal morphology to advance automation of digital reconstructions. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 143–157. doi:10.1007/s12021-010-9095-5.
Campagne, M. V. L., Oestreicher, A. B., Henegouwen, P. M. P. V. B. E., & Gispen, W. H. (1990). Ultrastructural double localization of B-50/GAP43 and synaptophysin (p38) in the neonatal and adult rat hippocampus. Journal of Neurocytology, 19(6), 948–961. doi:10.1007/BF01186822.
Cannon, R., Turner, D., Pyapali, G., & Wheal, H. (1998). An on-line archive of reconstructed hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 84(1–2), 49–54. doi:10.1016/S0165-0270(98)00091-0.
Chiang, A.-S., Lin, C.-Y., Chang, H.-M., Hsieh, C.-H., Yeh, C.-W., & Hwang, J.-K. (2011). Three-dimensional reconstruction of brain-wide wiring networks in Drosophila at single-cell resolution. Current Biology, 21(1), 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2010.11.056.
Chothani, P., Mehta, V., & Stepanyants, A. (2011). Automated tracing of neurites from light microscopy stacks of images. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 263–278. doi:10.1007/s12021-011-9121-2.
Chou, Y.-H., Spletter, M. L., Yaksi, E., Leong, J. C. S., Wilson, R. I., & Luo, L. (2010). Diversity and wiring variability of olfactory local interneurons in the Drosophila antennal lobe. Nature Neuroscience, 13(4), 439–449. doi:10.1038/nn.2489.
Craig, A. M., & Banker, G. (1994). Neuronal polarity. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 17(1), 267–310. doi:10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.001411.
Cuntz, H., Forstner, F., Haag, J., & Borst, A. (2008). The morphological identity of insect dendrites. PLoS Computational Biology, 4(12), e1000251. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000251.
Cuntz, H., Forstner, F., Borst, A., & Häusser, M. (2010). One rule to grow them all: a general theory of neuronal branching and its practical application. PLoS Computational Biology, 6(8), e1000877. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000877.
Donohue, D. E., & Ascoli, G. A. (2011). Automated reconstruction of neuronal morphology: an overview. Brain Research Reviews, 67(1–2), 94–102. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.11.003.
Duchene, J., & Leclercq, S. (1988). An optimal transformation for discriminant and principal component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 10(6), 978–983. doi:10.1109/34.9121.
Feinberg, E. H., VanHoven, M. K., Bendesky, A., Wang, G., Fetter, R. D., Shen, K., et al. (2008). GFP reconstitution across synaptic partners (GRASP) defines cell contacts and synapses in living nervous systems. Neuron, 57(3), 353–363. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.030.
Fischbach, P. K.-F., & Dittrich, A. P. M. (1989). The optic lobe of Drosophila melanogaster. I. A Golgi analysis of wild-type structure. Cell and Tissue Research, 258(3), 441–475. doi:10.1007/BF00218858.
Gillette, T. A., Brown, K. M., & Ascoli, G. A. (2011). The DIADEM metric: comparing multiple reconstructions of the same neuron. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 233–245. doi:10.1007/s12021-011-9117-y.
Glaser, J. R., & Glaser, E. M. (1990). Neuron imaging with Neurolucida–a PC-based system for image combining microscopy. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics: the Official Journal of the Computerized Medical Imaging Society, 14(5), 307–317.
Gordon, M. D., & Scott, K. (2009). Motor control in a Drosophila taste circuit. Neuron, 61(3), 373–384. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2008.12.033.
Hanesch, U., Fischbach, K.-F., & Heisenberg, M. (1989). Neuronal architecture of the central complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell and Tissue Research, 257(2), 343–366. doi:10.1007/BF00261838.
Heinze, S., & Homberg, U. (2008). Neuroarchitecture of the central complex of the desert locust: intrinsic and columnar neurons. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 511(4), 454–478. doi:10.1002/cne.21842.
Ikeno, H., Kanzaki, R., Aonuma, H., Takahata, M., Mizunami, M., Yasuyama, K., et al. (2008). Development of invertebrate brain platform: Management of research resources for invertebrate neuroscience and neuroethology. In M. Ishikawa, K. Doya, H. Miyamoto, & T. Yamakawa (Eds.), Neural information processing (pp. 905–914). Springer: Berlin. Retrieved from http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-540-69162-4_94.
Ito, M., Masuda, N., Shinomiya, K., Endo, K., & Ito, K. (2013). Systematic analysis of neural projections reveals clonal composition of the Drosophila brain. Current Biology, 23(8), 644–655. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2013.03.015.
Jang, J.-S. R. (2012). Machine Learning Toolbox. http://mirlab.org/jang/matlab/toolbox/machineLearning. Accessed 12 June 2012.
Lee, P.-C., Chuang, C.-C., Chiang, A.-S., & Ching, Y.-T. (2012). High-throughput computer method for 3D neuronal structure reconstruction from the image stack of the Drosophila brain and its applications. PLoS Computational Biology, 8(9), e1002658. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002658.
Lin, C.-Y., Chuang, C.-C., Hua, T.-E., Chen, C.-C., Dickson, B. J., Greenspan, R. J., et al. (2013a). A comprehensive wiring diagram of the protocerebral bridge for visual information processing in the Drosophila brain. Cell Reports, 3(5), 1739–1753. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.04.022.
Lin, H.-H., Chu, L.-A., Fu, T.-F., Dickson, B. J., & Chiang, A.-S. (2013b). Parallel neural pathways mediate CO2 avoidance responses in Drosophila. Science, 340(6138), 1338–1341. doi:10.1126/science.1236693.
Luczak, A. (2010). Measuring neuronal branching patterns using model-based approach. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 4, 10. doi:10.3389/fncom.2010.00135.
Matus, A., Bernhardt, R., & Hugh-Jones, T. (1981). High molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins are preferentially associated with dendritic microtubules in brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 78(5), 3010–3014.
Müller, M., Homberg, U., & Kühn, A. (1997). Neuroarchitecture of the lower division of the central body in the brain of the locust (Schistocerca gregaria). Cell and Tissue Research, 288(1), 159–176.
Parekh, R., & Ascoli, G. A. (2013). Neuronal morphology goes digital: a research hub for cellular and system neuroscience. Neuron, 77(6), 1017–1038. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.03.008.
Pastrana, E. (2013). Focus on mapping the brain. Nature Methods, 10(6), 481. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2509.
Peng, H., Ruan, Z., Long, F., Simpson, J. H., & Myers, E. W. (2010). V3D enables real-time 3D visualization and quantitative analysis of large-scale biological image data sets. Nature Biotechnology, 28(4), 348–353. doi:10.1038/nbt.1612.
Robinson, I. M., Ranjan, R., & Schwarz, T. L. (2002). Synaptotagmins I and IV promote transmitter release independently of Ca2+ binding in the C2A domain. Nature, 418(6895), 336–340. doi:10.1038/nature00915.
Rolls, M. M. (2011). Neuronal polarity in Drosophila: sorting out axons and dendrites. Developmental Neurobiology, 71(6), 419–429. doi:10.1002/dneu.20836.
Rolls, M. M., Satoh, D., Clyne, P. J., Henner, A. L., Uemura, T., & Doe, C. Q. (2007). Polarity and intracellular compartmentalization of Drosophila neurons. Neural Development, 2(1), 7. doi:10.1186/1749-8104-2-7.
Scorcioni, R., Polavaram, S., & Ascoli, G. A. (2008). L-Measure: a web-accessible tool for the analysis, comparison and search of digital reconstructions of neuronal morphologies. Nature Protocols, 3(5), 866–876. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.51.
Squire, L. R., Berg, D., Bloom, F., Lac, S. du, & Ghosh, A. (2008). Subcellular organization of the nervous system: organelles and their functions. In Fundamental Neuroscience (3rd ed., pp. 59–86). Amsterdam; Boston: Elsevier/Academic Press.
Strausfeld, N. J., & Hausen, K. (1977). The resolution of neuronal assemblies after cobalt injection into neuropil. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 199(1136), 463–476. doi:10.1098/rspb.1977.0154.
Takemura, S., Bharioke, A., Lu, Z., Nern, A., Vitaladevuni, S., Rivlin, P. K., et al. (2013). A visual motion detection circuit suggested by Drosophila connectomics. Nature, 500(7461), 175–181. doi:10.1038/nature12450.
Türetken, E., González, G., Blum, C., & Fua, P. (2011). Automated reconstruction of dendritic and axonal trees by global optimization with geometric priors. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 279–302. doi:10.1007/s12021-011-9122-1.
Varshney, L. R., Chen, B. L., Paniagua, E., Hall, D. H., & Chklovskii, D. B. (2011). Structural properties of the Caenorhabditis elegans neuronal network. PLoS Computational Biology, 7(2), e1001066. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001066.
Wang, T., & Liao, D. (2011). Neuronal morphology classification based on SVM. In Computer Science and Service System (CSSS), 2011 International Conference on (pp. 3344–3347). doi:10.1109/CSSS.2011.5972187.
Wang, Y., Narayanaswamy, A., Tsai, C.-L., & Roysam, B. (2011b). A broadly applicable 3-D neuron tracing method based on open-curve snake. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 193–217. doi:10.1007/s12021-011-9110-5.
Wang, J., Ma, X., Yang, J. S., Zheng, X., Zugates, C. T., Lee, C.-H. J., et al. (2004). Transmembrane/juxtamembrane domain-dependent dscam distribution and function during mushroom body neuronal morphogenesis. Neuron, 43(5), 663–672. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.06.033.
White, J. G., Southgate, E., Thomson, J. N., & Brenner, S. (1986). The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B. Biological Sciences, 314(1165), 1–340. doi:10.1098/rstb.1986.0056.
Whitney, A. W. (1971). A direct method of nonparametric measurement selection. IEEE Transactions on Computers, C-20(9), 1100–1103. doi:10.1109/T-C.1971.223410.
Wichterle, H., Gifford, D., & Mazzoni, E. (2013). Mapping neuronal diversity one cell at a time. Science, 341(6147), 726–727. doi:10.1126/science.1235884.
Xiao, H., & Peng, H. (2013). APP2: automatic tracing of 3D neuron morphology based on hierarchical pruning of a gray-weighted image distance-tree. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 29(11), 1448–1454. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btt170.
Yu, H.-H., Awasaki, T., Schroeder, M. D., Long, F., Yang, J. S., He, Y., et al. (2013). Clonal development and organization of the adult Drosophila central brain. Current Biology, 23(8), 633–643. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2013.02.057.
Zhao, T., Xie, J., Amat, F., Clack, N., Ahammad, P., Peng, H., et al. (2011). Automated reconstruction of neuronal morphology based on local geometrical and global structural models. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 247–261. doi:10.1007/s12021-011-9120-3.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Science Council grants #NSC 101-2311-B-007-008-MY3 and Free Excellent Projects, and by the Aim for the Top University Project of the Ministry of Education, Taiwan. We thank the National Center for High-performance Computing for providing the Flycircuit data; Drs. Ann-Shyn Chiang and Hsiu-Ming Chang for helpful discussion. We also thank Dr. Chih-Yung Lin for providing PB data.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.08 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YH., Lin, YN., Chuang, CC. et al. SPIN: A Method of Skeleton-Based Polarity Identification for Neurons. Neuroinform 12, 487–507 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-014-9225-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-014-9225-6