Abstract
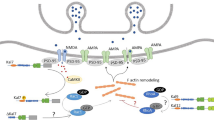
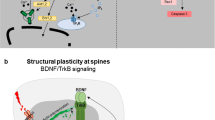
Spine morphogenesis and plasticity are intimately linked to cognition, and there is strong evidence that aberrant regulation of spine plasticity is associated with physiological, behavioral, and pathological conditions. The neuronal guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) kalirin is emerging as a key regulator of structural and functional plasticity at dendritic spines. Here, we review recent studies that have genetically and functionally linked kalirin signaling to a number of human disorders. Kalirin signaling may thus represent a disease mechanism and provide a novel therapeutic target.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlisle HJ, Kennedy MB (2005) Spine architecture and synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci 28:182–187
Alvarez VA, Sabatini BL (2007) Anatomical and physiological plasticity of dendritic spines. Annu Rev Neurosci 30:79–97
Chklovskii DB, Mel BW, Svoboda K (2004) Cortical rewiring and information storage. Nature 431:782–788
Chen JL, Nedivi E (2010) Neuronal structural remodeling: is it all about access? Curr Opin Neurobiol 20:557–562
Penzes P, Cahill ME, Jones KA, VanLeeuwen JE, Woolfrey KM (2011) Dendritic spine pathology in neuropsychiatric disorders. Nat Neurosci 14:285–293
Kaufmann WE, Moser HW (2000) Dendritic anomalies in disorders associated with mental retardation. Cereb Cortex 10:981–991
Zhou Z, Hong EJ, Cohen S, Zhao WN, Ho HY, Schmidt L, Chen WG, Lin Y, Savner E, Griffith EC, Hu L, Steen JA, Weitz CJ, Greenberg ME (2006) Brain-specific phosphorylation of MeCP2 regulates activity-dependent Bdnf transcription, dendritic growth, and spine maturation. Neuron 52:255–269
Bagni C, Greenough WT (2005) From mRNP trafficking to spine dysmorphogenesis: the roots of fragile X syndrome. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:376–387
Hutsler JJ, Zhang H (2010) Increased dendritic spine densities on cortical projection neurons in autism spectrum disorders. Brain Res 1309:83–94
Glantz LA, Lewis DA (2000) Decreased dendritic spine density on prefrontal cortical pyramidal neurons in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:65–73
Sweet RA, Henteleff RA, Zhang W, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (2009) Reduced dendritic spine density in auditory cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:374–389
Robinson TE, Kolb B (1997) Persistent structural modifications in nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex neurons produced by previous experience with amphetamine. J Neurosci 17:8491–8497
Robinson TE, Kolb B (2004) Structural plasticity associated with exposure to drugs of abuse. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):33–46
Zhou FC, Anthony B, Dunn KW, Lindquist WB, Xu ZC, Deng P (2007) Chronic alcohol drinking alters neuronal dendritic spines in the brain reward center nucleus accumbens. Brain Res 1134:148–161
Knobloch M, Mansuy IM (2008) Dendritic spine loss and synaptic alterations in alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 37:73–82
Day M, Wang Z, Ding J, An X, Ingham CA, Shering AF, Wokosin D, Ilijic E, Sun Z, Sampson AR, Mugnaini E, Deutch AY, Sesack SR, Arbuthnott GW, Surmeier DJ (2006) Selective elimination of glutamatergic synapses on striatopallidal neurons in Parkinson disease models. Nat Neurosci 9:251–259
Spires TL, Grote HE, Garry S, Cordery PM, Van Dellen A, Blakemore C, Hannan AJ (2004) Dendritic spine pathology and deficits in experience-dependent dendritic plasticity in R6/1 Huntington’s disease transgenic mice. Eur J Neurosci 19:2799–2807
Tolias KF, Duman JG, Um K (2011) Control of synapse development and plasticity by Rho GTPase regulatory proteins. Prog Neurobiol 94:133–148
Ramakers GJ (2002) Rho proteins, mental retardation and the cellular basis of cognition. Trends Neurosci 25:191–199
Newey SE, Velamoor V, Govek EE, Van Aelst L (2005) Rho GTPases, dendritic structure, and mental retardation. J Neurobiol 64:58–74
Penzes P, Jones KA (2008) Dendritic spine dynamics—a key role for kalirin-7. Trends Neurosci 31:419–427
Penzes P, Johnson RC, Sattler R, Zhang X, Huganir RL, Kambampati V, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2001) The neuronal Rho-GEF Kalirin-7 interacts with PDZ domain-containing proteins and regulates dendritic morphogenesis. Neuron 29:229–242
Penzes P, Beeser A, Chernoff J, Schiller MR, Eipper BA, Mains RE, Huganir RL (2003) Rapid induction of dendritic spine morphogenesis by trans-synaptic ephrinB-EphB receptor activation of the Rho-GEF kalirin. Neuron 37:263–274
Xie Z, Srivastava DP, Photowala H, Kai L, Cahill ME, Woolfrey KM, Shum CY, Surmeier DJ, Penzes P (2007) Kalirin-7 controls activity-dependent structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines. Neuron 56:640–656
Kolomeets NS, Orlovskaya DD, Rachmanova VI, Uranova NA (2005) Ultrastructural alterations in hippocampal mossy fiber synapses in schizophrenia: a postmortem morphometric study. Synapse 57:47–55
Steen RG, Mull C, McClure R, Hamer RM, Lieberman JA (2006) Brain volume in first-episode schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging studies. Br J Psychiatry 188:510–518
Hill JJ, Hashimoto T, Lewis DA (2006) Molecular mechanisms contributing to dendritic spine alterations in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 11:557–566
Ikeda M et al (2011) Genome-wide association study of schizophrenia in a Japanese population. Biol Psychiatry 69:472–478
St Jean PL (2008) Genes associated with schizophrenia identified using a whole genome scan. http://www.freepatentsonline.com/y2008/0176240.html Accessed 8 August 2010
Kushima I, Nakamura Y, Aleksic B, Ikeda M, Ito Y, Shiino T, Okochi T, Fukuo Y, Ujike H, Suzuki M, Inada T, Hashimoto R, Takeda M, Kaibuchi K, Iwata N, Ozaki N (2010) Resequencing and association analysis of the KALRN and EPHB1 genes and their contribution to schizophrenia susceptibility. Schizophr Bull [Epub ahead of print]
Millar JK, Christie S, Porteous DJ (2003) Yeast two-hybrid screens implicate DISC1 in brain development and function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:1019–1025
Hayashi-Takagi A, Takaki M, Graziane N, Seshadri S, Murdoch H, Dunlop AJ, Makino Y, Seshadri AJ, Ishizuka K, Srivastava DP, Xie Z, Baraban JM, Houslay MD, Tomoda T, Brandon NJ, Kamiya A, Yan Z, Penzes P, Sawa A (2010) Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) regulates spines of the glutamate synapse via Rac1. Nat Neurosci 13:327–332
Golimbet VE, Lavrushina OM, Kaleda VG, Abramova LI, Lezheiko TV (2007) Supportive evidence for the association between the T102C 5-HTR2A gene polymorphism and schizophrenia: a large-scale case–control and family-based study. Eur Psychiatry 22:167–170
Jones KA, Srivastava DP, Allen JA, Strachan RT, Roth BL, Penzes P (2009) Rapid modulation of spine morphology by the 5-HT2A serotonin receptor through kalirin-7 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19575–19580
Cahill ME, Jones KA, Rafalovich I, Xie Z, Barros CS, Muller U, Penzes P (2011) Control of interneuron dendritic growth through NRG1/erbB4-mediated kalirin-7 disinhibition. Mol Psychiatry [Epub ahead of print]
Mei L, Xiong WC (2008) Neuregulin 1 in neural development, synaptic plasticity and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:437–452
Walsh T et al (2008) Rare structural variants disrupt multiple genes in neurodevelopmental pathways in schizophrenia. Science 320:539–543
Barros CS, Calabrese B, Chamero P, Roberts AJ, Korzus E, Lloyd K, Stowers L, Mayford M, Halpain S, Muller U (2009) Impaired maturation of dendritic spines without disorganization of cortical cell layers in mice lacking NRG1/ErbB signaling in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:4507–4512
Ma XM, Johnson RC, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2001) Expression of kalirin, a neuronal GDP/GTP exchange factor of the trio family, in the central nervous system of the adult rat. J Comp Neurol 429:388–402
Lewis DA, Hashimoto T, Volk DW (2005) Cortical inhibitory neurons and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:312–324
Ma XM, Wang Y, Ferraro F, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2008) Kalirin-7 is an essential component of both shaft and spine excitatory synapses in hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci 28:711–724
Li B, Woo RS, Mei L, Malinow R (2007) The neuregulin-1 receptor erbB4 controls glutamatergic synapse maturation and plasticity. Neuron 54:583–597
Morrow EM, Kane A, Goff DC, Walsh CA (2008) Sequence analysis of P21-activated kinase 3 (PAK3) in chronic schizophrenia with cognitive impairment. Schizophr Res 106:265–267
Mulle JG, Dodd AF, McGrath JA, Wolyniec PS, Mitchell AA, Shetty AC, Sobreira NL, Valle D, Rudd MK, Satten G, Cutler DJ, Pulver AE, Warren ST (2010) Microdeletions of 3q29 confer high risk for schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 87:229–236
Cahill ME, Xie Z, Day M, Photowala H, Barbolina MV, Miller CA, Weiss C, Radulovic J, Sweatt JD, Disterhoft JF, Surmeier DJ, Penzes P (2009) Kalirin regulates cortical spine morphogenesis and disease-related behavioral phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13058–13063
Durstewitz D, Seamans JK, Sejnowski TJ (2000) Neurocomputational models of working memory. Nat Neurosci 3(Suppl):1184–1191
Lewis DA, Gonzalez-Burgos G (2008) Neuroplasticity of neocortical circuits in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:141–165
Penzes P, Cahill ME, Jones KA, Srivastava DP (2008) Convergent CaMK and RacGEF signals control dendritic structure and function. Trends Cell Biol 18:405–413
Niwa M, Kamiya A, Murai R, Kubo K, Gruber AJ, Tomita K, Lu L, Tomisato S, Jaaro-Peled H, Seshadri S, Hiyama H, Huang B, Kohda K, Noda Y, O’Donnell P, Nakajima K, Sawa A, Nabeshima T (2010) Knockdown of DISC1 by in utero gene transfer disturbs postnatal dopaminergic maturation in the frontal cortex and leads to adult behavioral deficits. Neuron 65:480–489
Ma XM, Kiraly DD, Gaier ED, Wang Y, Kim EJ, Levine ES, Eipper BA, Mains RE (2008) Kalirin-7 is required for synaptic structure and function. J Neurosci 28:12368–12382
Rabiner CA, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2005) Kalirin: a dual Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor that is so much more than the sum of its many parts. Neuroscientist 11:148–160
Tashiro A, Minden A, Yuste R (2000) Regulation of dendritic spine morphology by the rho family of small GTPases: antagonistic roles of Rac and Rho. Cereb Cortex 10:927–938
Xie Z, Cahill ME, Radulovic J, Wang J, Campbell SL, Miller CA, Sweatt JD, Penzes P (2011) Hippocampal phenotypes in kalirin-deficient mice. Mol Cell Neurosci 46:45–54
DeKosky ST, Scheff SW (1990) Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer’s disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Ann Neurol 27:457–464
Selkoe DJ (2002) Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science 298:789–791
Arendt T (2009) Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 118:167–179
Fiala JC, Spacek J, Harris KM (2002) Dendritic spine pathology: cause or consequence of neurological disorders? Brain Res Brain Res Rev 39:29–54
Penzes P, Vanleeuwen JE (2011) Impaired regulation of synaptic actin cytoskeleton in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Rev 67:184–192
Youn H, Ji I, Ji HP, Markesbery WR, Ji TH (2007) Under-expression of Kalirin-7 Increases iNOS activity in cultured cells and correlates to elevated iNOS activity in Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus. J Alzheimers Dis 12:271–281
Youn H, Jeoung M, Koo Y, Ji H, Markesbery WR, Ji I, Ji TH (2007) Kalirin is under-expressed in Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus. J Alzheimers Dis 11:385–397
Viola KL, Velasco PT, Klein WL (2008) Why Alzheimer’s is a disease of memory: the attack on synapses by A beta oligomers (ADDLs). J Nutr Health Aging 12:51S–57S
Simon AM, de Maturana RL, Ricobaraza A, Escribano L, Schiapparelli L, Cuadrado-Tejedor M, Perez-Mediavilla A, Avila J, Del Rio J, Frechilla D (2009) Early changes in hippocampal Eph receptors precede the onset of memory decline in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 17:773–786
Lacor PN, Buniel MC, Furlow PW, Clemente AS, Velasco PT, Wood M, Viola KL, Klein WL (2007) Abeta oligomer-induced aberrations in synapse composition, shape, and density provide a molecular basis for loss of connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 27:796–807
Cisse M, Halabisky B, Harris J, Devidze N, Dubal DB, Sun B, Orr A, Lotz G, Kim DH, Hamto P, Ho K, Yu GQ, Mucke L (2011) Reversing EphB2 depletion rescues cognitive functions in Alzheimer model. Nature 469:47–52
Zhao L, Ma QL, Calon F, Harris-White ME, Yang F, Lim GP, Morihara T, Ubeda OJ, Ambegaokar S, Hansen JE, Weisbart RH, Teter B, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2006) Role of p21-activated kinase pathway defects in the cognitive deficits of Alzheimer disease. Nat Neurosci 9:234–242
Ratovitski EA, Alam MR, Quick RA, McMillan A, Bao C, Kozlovsky C, Hand TA, Johnson RC, Mains RE, Eipper BA, Lowenstein CJ (1999) Kalirin inhibition of inducible nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 274:993–999
Mitrovic B, Ignarro LJ, Vinters HV, Akers MA, Schmid I, Uittenbogaart C, Merrill JE (1995) Nitric oxide induces necrotic but not apoptotic cell death in oligodendrocytes. Neuroscience 65:531–539
Lesch KP, Timmesfeld N, Renner TJ, Halperin R, Roser C, Nguyen TT, Craig DW, Romanos J, Heine M, Meyer J, Freitag C, Warnke A, Romanos M, Schafer H, Walitza S, Reif A, Stephan DA, Jacob C (2008) Molecular genetics of adult ADHD: converging evidence from genome-wide association and extended pedigree linkage studies. J Neural Transm 115:1573–1585
Xie Z, Photowala H, Cahill ME, Srivastava DP, Woolfrey KM, Shum CY, Huganir RL, Penzes P (2008) Coordination of synaptic adhesion with dendritic spine remodeling by AF-6 and kalirin-7. J Neurosci 28:6079–6091
Group THsDCR (1993) A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. The Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group. Cell 72:971–983
Li SH, Schilling G, Young WS 3rd, Li XJ, Margolis RL, Stine OC, Wagster MV, Abbott MH, Franz ML, Ranen NG et al (1993) Huntington’s disease gene (IT15) is widely expressed in human and rat tissues. Neuron 11:985–993
Li XJ, Li SH, Sharp AH, Nucifora FC Jr, Schilling G, Lanahan A, Worley P, Snyder SH, Ross CA (1995) A huntingtin-associated protein enriched in brain with implications for pathology. Nature 378:398–402
Colomer V, Engelender S, Sharp AH, Duan K, Cooper JK, Lanahan A, Lyford G, Worley P, Ross CA (1997) Huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1) binds to a Trio-like polypeptide, with a rac1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor domain. Hum Mol Genet 6:1519–1525
Hyman SE, Malenka RC, Nestler EJ (2006) Neural mechanisms of addiction: the role of reward-related learning and memory. Annu Rev Neurosci 29:565–598
Kiraly DD, Ma XM, Mazzone CM, Xin X, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2010) Behavioral and morphological responses to cocaine require kalirin7. Biol Psychiatry 68:249–255
Mains RE, Kiraly DD, Eipper-Mains JE, Ma XM, Eipper BA (2011) Kalrn promoter usage and isoform expression respond to chronic cocaine exposure. BMC Neurosci 12:20
Li W, Li QJ, An SC (2010) Preventive effect of estrogen on depression-like behavior induced by chronic restraint stress. Neurosci Bull 26:140–146
Wang L, Hauser ER, Shah SH, Pericak-Vance MA, Haynes C, Crosslin D, Harris M, Nelson S, Hale AB, Granger CB, Haines JL, Jones CJ, Crossman D, Seo D, Gregory SG, Kraus WE, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, Vance JM (2007) Peakwide mapping on chromosome 3q13 identifies the kalirin gene as a novel candidate gene for coronary artery disease. Am J Hum Genet 80:650–663
Ikram MA et al (2009) Genomewide association studies of stroke. N Engl J Med 360:1718–1728
Krug T et al (2010) Kalirin: a novel genetic risk factor for ischemic stroke. Hum Genet 127:513–523
Olsson S, Jood K, Melander O, Sjogren M, Norrving B, Nilsson M, Lindgren A, Jern C (2011) Lack of association between genetic variations in the KALRN region and ischemic stroke. Clin Biochem 44:1018–1020
Beresewicz M, Kowalczyk JE, Zablocka B (2008) Kalirin-7, a protein enriched in postsynaptic density, is involved in ischemic signal transduction. Neurochem Res 33:1789–1794
Jourdain P, Nikonenko I, Alberi S, Muller D (2002) Remodeling of hippocampal synaptic networks by a brief anoxia–hypoglycemia. J Neurosci 22:3108–3116
Acknowledgments
We thank Kelly Jones, Mike Cahill, Jon VanLeeuwen, and Zhong Xie for their useful input. This work was supported by a grant from NIH-NIMH to P.P. (R01MH071316).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penzes, P., Remmers, C. Kalirin Signaling: Implications for Synaptic Pathology. Mol Neurobiol 45, 109–118 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8223-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8223-z