Abstract
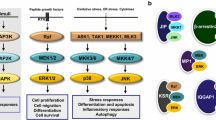
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase (MKP)-1 provides a negative feedback mechanism for regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity and thus a variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, growth and apoptosis. MKP-1 is established as a central regulator of a variety of functions in the immune, metabolic and cardiovascular systems, and it is now increasingly acknowledged as having a role to play in the nervous system. It has been implicated in regulating processes of neuronal cell development and death as well as in glial cell function. Reduced MKP-1 levels have been observed in models of neurological conditions including Huntington’s disease, multiple sclerosis, ischemia and cerebral hypoxia. It has also been suggested to have a role to play in psychiatric disorders such as major depressive disorder. Here, we discuss the role of MKP-1 in nervous system development and disease and examine current evidence providing insight into MKP-1 as a potential therapeutic target for various diseases of the central nervous system.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nishida E, Gotoh Y (1993) The MAP kinase cascade is essential for diverse signal transduction pathways. Trends Biochem Sci 18(4):128–131
Boutros T, Chevet E, Metrakos P (2008) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase regulation: roles in cell growth, death, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev 60(3):261–310
Duan W, Wong WSF (2006) Targeting mitogen-activated protein kinases for asthma. Curr Drug Targets 7(6):691–698
Jeffrey KL, Camps M, Rommel C, Mackay CR (2007) Targeting dual-specificity phosphatases: manipulating MAP kinase signalling and immune responses. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(5):391–403
Theodosiou A, Ashworth A (2002) MAP kinase phosphatases. Genome Biol 3(7):1–10
Wancket LM, Frazier WJ, Liu Y (2012) Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase (MKP)-1 in immunology, physiology, and disease. Life Sci 90(7–8):237–248
Farooq A, Zhou MM (2004) Structure and regulation of MAPK phosphatases. Cell Signal 16(7):769–779
Lang R, Hammer M, Mages J (2006) DUSP meet immunology: dual specificity MAPK phosphatases in control of the inflammatory response. J Immunol 177(11):7497–7504
Keyse SM (2000) Protein phosphatases and the regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12(2):186–192
Sun H, Charles CH, Lau LF, Tonks NK (1993) MKP-1 (3CH134), an immediate early gene product, is a dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates MAP kinase in vivo. Cell 75(3):487–493
Franklin CC, Kraft AS (1997) Conditional expression of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase MKP-1 preferentially inhibits p38 MAPK and stress-activated protein kinase in U937 cells. J Biol Chem 272(27):16917–16923
Lawan A, Shi H, Gatzke F, Bennett AM (2013) Diversity and specificity of the mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 functions. Cell Mol Life Sci 70(2):223–237. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1041-2
Chen P, Li J, Barnes J, Kokkonen GC, Lee JC, Liu Y (2002) Restraint of proinflammatory cytokine biosynthesis by mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J Immunol 169(11):6408–6416
Chi H, Barry SP, Roth RJ, Wu JJ, Jones EA, Bennett AM, Flavell RA (2006) Dynamic regulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines by MAPK phosphatase 1 (MKP-1) in innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(7):2274–2279. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510965103
Salojin KV, Owusu IB, Millerchip KA, Potter M, Platt KA, Oravecz T (2006) Essential role of MAPK phosphatase-1 in the negative control of innate immune responses. J Immunol 176(3):1899–1907
Hammer M, Mages J, Dietrich H, Servatius A, Howells N, Cato AC, Lang R (2006) Dual specificity phosphatase 1 (DUSP1) regulates a subset of LPS-induced genes and protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock. J Exp Med 203(1):15–20. doi:10.1084/jem.20051753
Sakaue H, Ogawa W, Nakamura T, Mori T, Nakamura K, Kasuga M (2004) Role of MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) in adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 279(38):39951–39957. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407353200
Roth RJ, Le AM, Zhang L, Kahn M, Samuel VT, Shulman GI, Bennett AM (2009) MAPK phosphatase-1 facilitates the loss of oxidative myofibers associated with obesity in mice. J Clin Invest 119(12):3817–3829. doi:10.1172/JCI39054
Wu JJ, Roth RJ, Anderson EJ, Hong EG, Lee MK, Choi CS, Neufer PD, Shulman GI, Kim JK, Bennett AM (2006) Mice lacking MAP kinase phosphatase-1 have enhanced MAP kinase activity and resistance to diet-induced obesity. Cell Metab 4(1):61–73. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.05.010
Bennett AM, Tonks NK (1997) Regulation of distinct stages of skeletal muscle differentiation by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Science 278(5341):1288–1291
Liu Y, Shepherd EG, Nelin LD (2007) MAPK phosphatases—regulating the immune response. Nat Rev Immunol 7(3):202–212. doi:10.1038/nri2035
Loda M, Capodieci P, Mishra R, Yao H, Corless C, Grigioni W, Wang Y, Magi-Galluzzi C, Stork PJ (1996) Expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in the early phases of human epithelial carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol 149(5):1553–1564
Rojo F, Gonzalez-Navarrete I, Bragado R, Dalmases A, Menendez S, Cortes-Sempere M, Suarez C, Oliva C, Servitja S, Rodriguez-Fanjul V, Sanchez-Perez I, Campas C, Corominas JM, Tusquets I, Bellosillo B, Serrano S, Perona R, Rovira A, Albanell J (2009) Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in human breast cancer independently predicts prognosis and is repressed by doxorubicin. Clin Cancer Res 15(10):3530–3539. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2070
Wang HY, Cheng Z, Malbon CC (2003) Overexpression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases MKP1, MKP2 in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett 191(2):229–237
Vicent S, Garayoa M, Lopez-Picazo JM, Lozano MD, Toledo G, Thunnissen FB, Manzano RG, Montuenga LM (2004) Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and is an independent predictor of outcome in patients. Clin Cancer Res 10(11):3639–3649. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0771
Wu GS (2007) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases (MKPs) in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26(3–4):579–585. doi:10.1007/s10555-007-9079-6
Valjent E, Caboche J, Vanhoutte P (2001) Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase induced gene regulation in brain: a molecular substrate for learning and memory? Mol Neurobiol 23(2–3):83–99. doi:10.1385/MN:23:2-3:083
Nolan Y, Vereker E, Lynch AM, Lynch MA (2003) Evidence that lipopolysaccharide-induced cell death is mediated by accumulation of reactive oxygen species and activation of p38 in rat cortex and hippocampus. Exp Neurol 184(2):794–804. doi:10.1016/S0014-4886(03)00301-7
Roth TL, Sweatt JD (2008) Rhythms of memory. Nat Neurosci 11(9):993–994. doi:10.1038/nn0908-993
Kim EK, Choi EJ (2010) Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(4):396–405. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.12.009
Peinado-Ramon P, Wallen A, Hallbook F (1998) MAP kinase phosphatase-1 mRNA is expressed in embryonic sympathetic neurons and is upregulated after NGF stimulation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 56(1–2):256–267
Reffas S, Schlegel W (2000) Compartment-specific regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) by ERK-dependent and non-ERK-dependent inductions of MAPK phosphatase (MKP)-3 and MKP-1 in differentiating P19 cells. Biochem J 352(Pt 3):701–708
Jeanneteau F, Deinhardt K, Miyoshi G, Bennett AM, Chao MV (2010) The MAP kinase phosphatase MKP-1 regulates BDNF-induced axon branching. Nat Neurosci 13(11):1373–1379
Collins LM, O’Keeffe GW, Long-Smith CM, Wyatt SL, Sullivan AM, Toulouse A, Nolan YM (2013) Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase (MKP)-1 as a neuroprotective agent: promotion of the morphological development of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Neuromol Med 15(2):435–446. doi:10.1007/s12017-013-8230-5
Choi BH, Hur EM, Lee JH, Jun DJ, Kim KT (2006) Protein kinase Cdelta-mediated proteasomal degradation of MAP kinase phosphatase-1 contributes to glutamate-induced neuronal cell death. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 7):1329–1340. doi:10.1242/jcs.02837
Kawahara N, Wang Y, Mukasa A, Furuya K, Shimizu T, Hamakubo T, Aburatani H, Kodama T, Kirino T (2004) Genome-wide gene expression analysis for induced ischemic tolerance and delayed neuronal death following transient global ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24(2):212–223. doi:10.1097/01.WCB.0000106012.33322.A2
Rininger A, Dejesus C, Totten A, Wayland A, Halterman MW (2012) MKP-1 antagonizes C/EBPbeta activity and lowers the apoptotic threshold after ischemic injury. Cell Death Differ 19(10):1634–1643. doi:10.1038/cdd.2012.41
Koga S, Kojima S, Kishimoto T, Kuwabara S, Yamaguchi A (2012) Over-expression of map kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) suppresses neuronal death through regulating JNK signaling in hypoxia/re-oxygenation. Brain Res 1436:137–146. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.12.004
Mishra OP, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M (2004) Effect of hypoxia on the expression and activity of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase-phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) and MKP-3 in neuronal nuclei of newborn piglets: the role of nitric oxide. Neuroscience 129(3):665–673
Kristiansen M, Hughes R, Patel P, Jacques TS, Clark AR, Ham J (2010) Mkp1 is a c-Jun target gene that antagonizes JNK-dependent apoptosis in sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci 30(32):10820–10832. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2824-10.2010
Huang H, Fan S, Ji X, Zhang Y, Bao F, Zhang G (2009) Recombinant human erythropoietin protects against experimental spinal cord trauma injury by regulating expression of the proteins MKP-1 and p-ERK. J Int Med Res 37(2):511–519
Wu J, Pan Z, Wang Z, Zhu W, Shen Y, Cui R, Lin J, Yu H, Wang Q, Qian J, Yu Y, Zhu D, Lou Y (2012) Ginsenoside Rg1 protection against beta-amyloid peptide-induced neuronal apoptosis via estrogen receptor alpha and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent anti-protein nitration pathway. Neuropharmacology 63(3):349–361. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.04.005
Taylor DM, Moser R, Régulier E, Breuillaud L, Dixon M, Beesen AA, Elliston L, Silva Santos MF, Kim J, Jones L, Goldstein DR, Ferrante RJ, Luthi-Carter R (2013) MAP kinase phosphatase 1 (MKP-1/DUSP1) is neuroprotective in Huntington’s disease via additive effects of JNK and p38 inhibition. J Neurosci 33(6):2313–2325. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.4965-11.2013
Ndong C, Landry RP, DeLeo JA, Romero-Sandoval EA (2012) Mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 prevents the development of tactile sensitivity in a rodent model of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 8:34. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-8-34
Huo Y, Rangarajan P, Ling EA, Dheen ST (2011) Dexamethasone inhibits the Nox-dependent ROS production via suppression of MKP-1-dependent MAPK pathways in activated microglia. BMC Neurosci 12:49. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-12-49
Rayan NA, Baby N, Pitchai D, Indraswari F, Ling EA, Lu J, Dheen T (2011) Costunolide inhibits proinflammatory cytokines and iNOS in activated murine BV2 microglia. Front Biosci 3:1079–1091, Elite Ed
Kim J, Shim J, Lee S, Lim SS, Lee KW, Lee HJ (2013) Licorice-derived dehydroglyasperin C increases MKP-1 expression and suppresses inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration. Neurochem Int 63(8):732–740. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2013.09.013
Crittenden PL, Filipov NM (2011) Manganese modulation of MAPK pathways: effects on upstream mitogen activated protein kinase kinases and mitogen activated kinase phosphatase-1 in microglial cells. J Appl Toxicol 31(1):1–10. doi:10.1002/jat.1552
Eljaschewitsch E, Witting A, Mawrin C, Lee T, Schmidt PM, Wolf S, Hoertnagl H, Raine CS, Schneider-Stock R, Nitsch R, Ullrich O (2006) The endocannabinoid anandamide protects neurons during CNS inflammation by induction of MKP-1 in microglial cells. Neuron 49(1):67–79
Krishnan G, Chatterjee N (2014) Endocannabinoids affect innate immunity of Muller glia during HIV-1 Tat cytotoxicity. Mol Cell Neurosci 59C:10–23. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2014.01.001
Romero-Sandoval EA, Horvath R, Landry RP, DeLeo JA (2009) Cannabinoid receptor type 2 activation induces a microglial anti-inflammatory phenotype and reduces migration via MKP induction and ERK dephosphorylation. Mol Pain 5:25. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-5-25
Juknat A, Pietr M, Kozela E, Rimmerman N, Levy R, Gao F, Coppola G, Geschwind D, Vogel Z (2013) Microarray and pathway analysis reveal distinct mechanisms underlying cannabinoid-mediated modulation of LPS-induced activation of BV-2 microglial cells. PLoS ONE 8(4):e61462. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061462
Li W, Hertzberg EL, Spray DC (2005) Regulation of connexin43-protein binding in astrocytes in response to chemical ischemia/hypoxia. J Biol Chem 280(9):7941–7948. doi:10.1074/jbc.M410548200
Tournier C, Thomas G, Pierre J, Jacquemin C, Pierre M, Saunier B (1997) Mediation by arachidonic acid metabolites of the H2O2-induced stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase). Eur J Biochem 244(2):587–595
Herrera-Molina R, Flores B, Orellana JA, von Bernhardi R (2012) Modulation of interferon-gamma-induced glial cell activation by transforming growth factor beta1: a role for STAT1 and MAPK pathways. J Neurochem 123(1):113–123. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07887.x
Flores B, von Bernhardi R (2012) Transforming growth factor beta1 modulates amyloid beta-induced glial activation through the Smad3-dependent induction of MAPK phosphatase-1. J Alzheimers Dis 32(2):417–429. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-120721
Lee JH, Kim H, Woo JH, Joe EH, Jou I (2012) 5, 8, 11, 14-eicosatetraynoic acid suppresses CCL2/MCP-1 expression in IFN-gamma-stimulated astrocytes by increasing MAPK phosphatase-1 mRNA stability. J Neuroinflammation 9:34. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-9-34
Lee JH, Woo JH, Woo SU, Kim KS, Park SM, Joe EH, Jou I (2008) The 15-deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 suppresses monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in IFN-gamma-stimulated astrocytes through induction of MAPK phosphatase-1. J Immunol 181(12):8642–8649
Freeman SE, Patil VV, Durham PL (2008) Nitric oxide-proton stimulation of trigeminal ganglion neurons increases mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatase expression in neurons and satellite glial cells. Neuroscience 157(3):542–555. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.09.035
Cady RJ, Denson JE, Durham PL (2013) Inclusion of cocoa as a dietary supplement represses expression of inflammatory proteins in spinal trigeminal nucleus in response to chronic trigeminal nerve stimulation. Mol Nutr Food Res 57(6):996–1006. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201200630
Cady RJ, Hirst JJ, Durham PL (2010) Dietary grape seed polyphenols repress neuron and glia activation in trigeminal ganglion and trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Mol Pain 6:91. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-6-91
Clark R, Stewart M, Miskimins WK, Miskimins R (1998) Involvement of MAP kinase in the cyclic AMP induction of myelin basic protein gene expression. Int J Dev Neurosci 16(5):323–331
Davis S, Vanhoutte P, Pages C, Caboche J, Laroche S (2000) The MAPK/ERK cascade targets both Elk-1 and cAMP response element-binding protein to control long-term potentiation-dependent gene expression in the dentate gyrus in vivo. J Neurosci 20(12):4563–4572
Zhou J, Wang L, Ling S, Zhang X (2007) Expression changes of growth-associated protein-43 (GAP-43) and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) and in hippocampus of streptozotocin-induced diabetic cognitive impairment rats. Exp Neurol 206(2):201–208. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.04.013
Chen MF, Huang TY, Kuo YM, Yu L, Chen HI, Jen CJ (2013) Early postinjury exercise reverses memory deficits and retards the progression of closed-head injury in mice. J Physiol 591(Pt 4):985–1000. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.241125
Duric V, Banasr M, Licznerski P, Schmidt HD, Stockmeier CA, Simen AA, Newton SS, Duman RS (2010) A negative regulator of MAP kinase causes depressive behavior. Nat Med 16(11):1328–1332
Iio W, Matsukawa N, Tsukahara T, Kohari D, Toyoda A (2011) Effects of chronic social defeat stress on MAP kinase cascade. Neurosci Lett 504(3):281–284
Budziszewska B, Szymanska M, Leskiewicz M, Basta-Kaim A, Jaworska-Feil L, Kubera M, Jantas D, Lason W (2010) The decrease in JNK-and p38-MAP kinase activity is accompanied by the enhancement of PP2A phosphatase level in the brain of prenatally stressed rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 61(2):207
Lee H-R, Hwang I-S, Kim J-E, Choi S-I, Lee Y-J, Goo J-S, Lee E-P, Choi H-W, Kim H-S, Lee J-H (2012) Altered expression of γ-secretase components in animal model of major depressive disorder induced by reserpine administration. Lab Anim Res 28(2):109
Vogt A, Tamewitz A, Skoko J, Sikorski RP, Giuliano KA, Lazo JS (2005) The benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloid, sanguinarine, is a selective, cell-active inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1. J Biol Chem 280(19):19078–19086. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501467200
Chen Y, Wang H, Zhang R, Wang H, Peng Z, Sun R, Tan Q (2012) Microinjection of sanguinarine into the ventrolateral orbital cortex inhibits Mkp-1 and exerts an antidepressant-like effect in rats. Neurosci Lett 506(2):327–331. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2011.11.038
Jia W, Liu R, Shi J, Wu B, Dang W, Du Y, Zhou Q, Wang J, Zhang R (2013) Differential regulation of MAPK phosphorylation in the dorsal hippocampus in response to prolonged morphine withdrawal-induced depressive-like symptoms in mice. PLoS ONE 8(6):e66111. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066111
Sasaki K, El Omri A, Kondo S, Han J, Isoda H (2013) Rosmarinus officinalis polyphenols produce anti-depressant like effect through monoaminergic and cholinergic functions modulation. Behav Brain Res 238:86–94. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2012.10.010
Acknowledgments
Work in the authors’ laboratories is supported by grants from Science Foundation Ireland (12/IA/1537 and RFP/NSC1298; YN) and the College of Medicine and Health, UCC (LC/AT/ED/YN).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collins, L.M., Downer, E.J., Toulouse, A. et al. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase (MKP)-1 in Nervous System Development and Disease. Mol Neurobiol 51, 1158–1167 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8786-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8786-6