Abstract
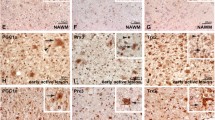
Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts protein-1 (MLC1) is a membrane protein expressed by perivascular astrocytes. MLC1 mutations cause MLC, an incurable leukodystrophy characterized by macrocephaly, brain edema, cysts, myelin vacuolation, and astrocytosis, leading to cognitive/motor impairment and epilepsy. Although its function is unknown, MLC1 favors regulatory volume decrease after astrocyte osmotic swelling and down-regulates intracellular signaling pathways controlling astrocyte activation and proliferation. By combining analysis of human brain tissues with in vitro experiments, here we investigated MLC1 role in astrocyte activation during neuroinflammation, a pathological condition exacerbating patient symptoms. MLC1 upregulation was observed in brain tissues from multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, and Creutzfeld-Jacob disease, all pathologies characterized by strong astrocytosis and release of inflammatory cytokines, particularly IL-1β. Using astrocytoma lines overexpressing wild-type (WT) or mutated MLC1 and astrocytes from control and Mlc1 knock-out (KO) mice, we found that IL-1β stimulated WT-MLC1 plasma membrane expression in astrocytoma cells and control primary astrocytes. In astrocytoma, WT-MLC1 inhibited the activation of IL-1β–induced inflammatory signals (pERK, pNF-kB) that, conversely, were constitutively activated in mutant expressing cells or abnormally upregulated in KO astrocytes. WT-MLC1+ cells also expressed reduced levels of the astrogliosis marker pSTAT3. We then monitored MLC1 expression timing in a demyelinating/remyelinating murine cerebellar organotypic culture model where, after the demyelination and release of inflammatory cytokines, recovery processes occur, revealing MLC1 upregulation in these latter phases. Altogether, these findings suggest that by modulating specific pathways, MLC1 contributes to restore astrocyte homeostasis after inflammation, providing the opportunity to identify drug target molecules to slow down disease progression.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sofroniew MV, Vinters HV (2010) Astrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 119:7–35
Pekny M, Pekna M (2014) Astrocyte reactivity and reactive astrogliosis: costs and benefits. Physiol Rev 94:1077–1098
Pekny M, Wilhelmsson U, Pekna M (2014) The dual role of astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Neurosci Lett 565:30–38
Liddelow SA, Barres BA (2017) Reactive astrocytes: production, function, and therapeutic potential. Immunity. 46:957–967
Pekny M, Pekna M (2016) Reactive gliosis in the pathogenesis of CNS diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862:483–491
Pekny M, Pekna M, Messing A, Steinhauser C, Lee JM, Parpura V, Hol EM, Sofroniew MV et al (2016) Astrocytes: a central element in neurological diseases. Acta Neuropathol 131:323–345
Ben Haim L, Carrillo-de Sauvage MA, Ceyzeriat K, Escartin C (2015) Elusive roles for reactive astrocytes in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 9:278
Ferrer I (2017) Diversity of astroglial responses across human neurodegenerative disorders and brain aging. Brain Pathol 27:645–674
Lanciotti A, Brignone MS, Bertini E, Petrucci TC, Aloisi F, Ambrosini E (2013) Astrocytes: emerging stars in leukodystrophy pathogenesis. Transl Neurosci 4. https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-013-0118-1
Leegwater PA, Boor PK, Yuan BQ, van der Steen J, Visser A, Konst AA, Oudejans CB, Schutgens RB et al (2002) Identification of novel mutations in MLC1 responsible for megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Hum Genet 110:279–283
Leegwater PA, Yuan BQ, van der Steen J, Mulders J, Konst AA, Boor PK, Mejaski-Bosnjak V, van der Maarel SM et al (2001) Mutations of MLC1 (KIAA0027), encoding a putative membrane protein, cause megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Am J Hum Genet 68:831–838
Yalcinkaya C, Yuksel A, Comu S, Kilic G, Cokar O, Dervent A (2003) Epilepsy in vacuolating megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Seizure. 12:388–396
van der Knaap MS, Barth PG, Vrensen GF, Valk J (1996) Histopathology of an infantile-onset spongiform leukoencephalopathy with a discrepantly mild clinical course. Acta Neuropathol 92:206–212
Pascual-Castroviejo I, van der Knaap MS, Pronk JC, Garcia-Segura JM, Gutierrez-Molina M, Pascual-Pascual SI (2005) Vacuolating megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy: 24 year follow-up of two siblings. Neurologia. 20:33–40
Duarri A, Lopez de Heredia M, Capdevila-Nortes X, Ridder MC, Montolio M, Lopez-Hernandez T, Boor I, Lien CF et al (2011) Knockdown of MLC1 in primary astrocytes causes cell vacuolation: a MLC disease cell model. Neurobiol Dis 43:228–238
Ridder MC, Boor I, Lodder JC, Postma NL, Capdevila-Nortes X, Duarri A, Brussaard AB, Estevez R et al (2011) Megalencephalic leucoencephalopathy with cysts: defect in chloride currents and cell volume regulation. Brain. 134:3342–3354
Dubey M, Bugiani M, Ridder MC, Postma NL, Brouwers E, Polder E, Jacobs JG, Baayen JC et al (2015) Mice with megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with cysts: a developmental angle. Ann Neurol 77:114–131
Jayakumar AR, Rao KV, Panickar KS, Moriyama M, Reddy PV, Norenberg MD (2008) Trauma-induced cell swelling in cultured astrocytes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:417–427
Pasantes-Morales H, Vazquez-Juarez E (2012) Transporters and channels in cytotoxic astrocyte swelling. Neurochem Res 37:2379–2387
Brosnan CF, Raine CS (2013) The astrocyte in multiple sclerosis revisited. Glia. 61:453–465
Bugiani M, Moroni I, Bizzi A, Nardocci N, Bettecken T, Gartner J, Uziel G (2003) Consciousness disturbances in megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Neuropediatrics. 34:211–214
Mejaski-Bosnjak V, Besenski N, Brockmann K, Pouwels PJ, Frahm J, Hanefeld FA (1997) Cystic leukoencephalopathy in a megalencephalic child: clinical and magnetic resonance imaging/magnetic resonance spectroscopy findings. Pediatr Neurol 16:347–350
Lanciotti A, Brignone MS, Visentin S, De Nuccio C, Catacuzzeno L, Mallozzi C, Petrini S, Caramia M et al (2016) Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts protein-1 regulates epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in astrocytes. Hum Mol Genet 25:1543–1558
Gao WL, Tian F, Zhang SQ, Zhang H, Yin ZS (2014) Epidermal growth factor increases the expression of Nestin in rat reactive astrocytes through the Ras-Raf-ERK pathway. Neurosci Lett 562:54-59
Burda JE, Sofroniew MV (2014) Reactive gliosis and the multicellular response to CNS damage and disease. Neuron. 81:229–248
Wei T, Yi M, Gu W, Hou L, Lu Q, Yu Z, Chen H (2017) The Potassium Channel KCa3.1 represents a valid pharmacological target for Astrogliosis-induced neuronal impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Front Pharmacol 7:528
Yi M, Wei T, Wang Y, Lu Q, Chen G, Gao X, Geller HM, Chen H et al (2017) The potassium channel KCa3.1 constitutes a pharmacological target for astrogliosis associated with ischemia stroke. J Neuroinflammation 14:203–017-0973-8
Elorza-Vidal X, Sirisi S, Gaitan-Penas H, Perez-Rius C, Alonso-Gardon M, Armand-Ugon M, Lanciotti A, Brignone MS et al (2018) GlialCAM/MLC1 modulates LRRC8/VRAC currents in an indirect manner: implications for megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy. Neurobiol Dis 119:88–99
Petrini S, Minnone G, Coccetti M, Frank C, Aiello C, Cutarelli A, Ambrosini E, Lanciotti A et al (2013) Monocytes and macrophages as biomarkers for the diagnosis of megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Mol Cell Neurosci 56:307–321
Agresti C, Aloisi F, Levi G (1991) Heterotypic and homotypic cellular interactions influencing the growth and differentiation of bipotential oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocyte progenitors in culture. Dev Biol 144:16–29
Lanciotti A, Brignone MS, Molinari P, Visentin S, De Nuccio C, Macchia G, Aiello C, Bertini E et al (2012) Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts protein 1 functionally cooperates with the TRPV4 cation channel to activate the response of astrocytes to osmotic stress: dysregulation by pathological mutations. Hum Mol Genet 21:2166–2180
Lanciotti A, Brignone MS, Camerini S, Serafini B, Macchia G, Raggi C, Molinari P, Crescenzi M et al (2010) MLC1 trafficking and membrane expression in astrocytes: role of caveolin-1 and phosphorylation. Neurobiol Dis 37:581–595
Brignone MS, Lanciotti A, Visentin S, De Nuccio C, Molinari P, Camerini S, Diociaiuti M, Petrini S et al (2014) Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts protein-1 modulates endosomal pH and protein trafficking in astrocytes: relevance to MLC disease pathogenesis. Neurobiol Dis 66:1–18
Ambrosini E, Serafini B, Lanciotti A, Tosini F, Scialpi F, Psaila R, Raggi C, Di Girolamo F et al (2008) Biochemical characterization of MLC1 protein in astrocytes and its association with the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Mol Cell Neurosci 37:480–493
Eleuteri C, Olla S, Veroni C, Umeton R, Mechelli R, Romano S, Buscarinu MC, Ferrari F et al (2017) A staged screening of registered drugs highlights remyelinating drug candidates for clinical trials. Sci Rep 7:45780
Lassmann H (2018) Multiple sclerosis pathology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 8. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a028936
Stadelmann C (2011) Multiple sclerosis as a neurodegenerative disease: pathology, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Curr Opin Neurol 24:224–229
Boor PK, de Groot K, Waisfisz Q, Kamphorst W, Oudejans CB, Powers JM, Pronk JC, Scheper GC et al (2005) MLC1: a novel protein in distal astroglial processes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:412–419
Stephenson J, Nutma E, van der Valk P, Amor S (2018) Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology. 154:204–219
Zenaro E, Piacentino G, Constantin G (2017) The blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 107:41–56
Iwasaki Y, Mori K, Ito M, Tatsumi S, Mimuro M, Yoshida M (2013) An autopsied case of progressive supranuclear palsy presenting with cerebellar ataxia and severe cerebellar involvement. Neuropathology. 33:561–567
Lewicki H, Tishon A, Homann D, Mazarguil H, Laval F, Asensio VC, Campbell IL, DeArmond S et al (2003) T cells infiltrate the brain in murine and human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. J Virol 77:3799–3808
Verkhratsky A, Zorec R, Rodriguez JJ, Parpura V (2016) Astroglia dynamics in ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol 26:74–79
Gomez-Arboledas A, Davila JC, Sanchez-Mejias E, Navarro V, Nunez-Diaz C, Sanchez-Varo R, Sanchez-Mico MV, Trujillo-Estrada L et al (2018) Phagocytic clearance of presynaptic dystrophies by reactive astrocytes in Alzheimer's disease. Glia. 66:637–653
Van Everbroeck B, Dewulf E, Pals P, Lubke U, Martin JJ, Cras P (2002) The role of cytokines, astrocytes, microglia and apoptosis in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurobiol Aging 23:59–64
Rubio-Perez JM, Morillas-Ruiz JM (2012) A review: inflammatory process in Alzheimer's disease, role of cytokines. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012:756357
Lucas SM, Rothwell NJ, Gibson RM (2006) The role of inflammation in CNS injury and disease. Br J Pharmacol 147(Suppl 1):S232–S240
Parker LC, Luheshi GN, Rothwell NJ, Pinteaux E (2002) IL-1 beta signalling in glial cells in wildtype and IL-1RI deficient mice. Br J Pharmacol 136:312–320
Nadjar A, Combe C, Busquet P, Dantzer R, Parnet P (2005) Signaling pathways of interleukin-1 actions in the brain: anatomical distribution of phospho-ERK1/2 in the brain of rat treated systemically with interleukin-1beta. Neuroscience. 134:921–932
Meini A, Sticozzi C, Massai L, Palmi M (2008) A nitric oxide/Ca(2+)/calmodulin/ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is involved in the mitogenic effect of IL-1beta in human astrocytoma cells. Br J Pharmacol 153:1706–1717
Summers L, Kangwantas K, Nguyen L, Kielty C, Pinteaux E (2010) Adhesion to the extracellular matrix is required for interleukin-1 beta actions leading to reactive phenotype in rat astrocytes. Mol Cell Neurosci 44:272–281
Marcus JS, Karackattu SL, Fleegal MA, Sumners C (2003) Cytokine-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in astroglia: role of Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB. Glia. 41:152–160
Wang T, Yuan W, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Zhou X, Ning G, Zhang L et al (2015) The role of the JAK-STAT pathway in neural stem cells, neural progenitor cells and reactive astrocytes after spinal cord injury. Biomed Rep 3:141–146
Ben Haim L, Ceyzeriat K, Carrillo-de Sauvage MA, Aubry F, Auregan G, Guillermier M, Ruiz M, Petit F et al (2015) The JAK/STAT3 pathway is a common inducer of astrocyte reactivity in Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases. J Neurosci 35:2817–2829
Konnikova L, Kotecki M, Kruger MM, Cochran BH (2003) Knockdown of STAT3 expression by RNAi induces apoptosis in astrocytoma cells. BMC Cancer 3:23–2407-3-23
Lindemann C, Hackmann O, Delic S, Schmidt N, Reifenberger G, Riemenschneider MJ (2011) SOCS3 promoter methylation is mutually exclusive to EGFR amplification in gliomas and promotes glioma cell invasion through STAT3 and FAK activation. Acta Neuropathol 122:241–251
Barateiro A, Afonso V, Santos G, Cerqueira JJ, Brites D, van Horssen J, Fernandes A (2016) S100B as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in multiple sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol 53:3976–3991
Birgbauer E, Rao TS, Webb M (2004) Lysolecithin induces demyelination in vitro in a cerebellar slice culture system. J Neurosci Res 78:157–166
Brignone MS, Lanciotti A, Macioce P, Macchia G, Gaetani M, Aloisi F, Petrucci TC, Ambrosini E (2011) The beta1 subunit of the Na,K-ATPase pump interacts with megalencephalic leucoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts protein 1 (MLC1) in brain astrocytes: New insights into MLC pathogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 20:90–103
Sofroniew MV (2015) Astrocyte barriers to neurotoxic inflammation. Nat Rev Neurosci 16:249–263
Griffin WS (2006) Inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Am J Clin Nutr 83:470S–474S
Griffin WS, Liu L, Li Y, Mrak RE, Barger SW (2006) Interleukin-1 mediates Alzheimer and Lewy body pathologies. J Neuroinflammation 3:5–2094-3-5
Rezaie P, Lantos PL (2001) Microglia and the pathogenesis of spongiform encephalopathies. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 35:55–72
Amor S, Peferoen LA, Vogel DY, Breur M, van der Valk P, Baker D, van Noort JM (2014) Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases--an update. Immunology. 142:151–166
Rozemuller AJ, Jansen C, Carrano A, van Haastert ES, Hondius D, van der Vies SM, Hoozemans JJ (2012) Neuroinflammation and common mechanism in Alzheimer's disease and prion amyloidosis: amyloid-associated proteins, neuroinflammation and neurofibrillary degeneration. Neurodegener Dis 10:301–304
Heneka MT (2017) Inflammasome activation and innate immunity in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Pathol 27:220–222
Guillot-Sestier MV, Town T (2017) Let's make microglia great again in neurodegenerative disorders. J Neural Transm (Vienna)
Stoeck K, Schmitz M, Ebert E, Schmidt C, Zerr I (2014) Immune responses in rapidly progressive dementia: a comparative study of neuroinflammatory markers in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflammation 11:170–014-0170-y
Aguzzi A, Liu Y (2017) A role for astroglia in prion diseases. J Exp Med 214:3477–3479
Avila-Munoz E, Arias C (2014) When astrocytes become harmful: functional and inflammatory responses that contribute to Alzheimer's disease. Ageing Res Rev 18:29–40
Alam Q, Alam MZ, Mushtaq G, Damanhouri GA, Rasool M, Kamal MA, Haque A (2016) Inflammatory process in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: Central role of cytokines. Curr Pharm Des 22:541–548
Frost GR , Li YM (2017) The role of astrocytes in amyloid production and Alzheimer's disease. Open Biol 7(12)
Taib T, Leconte C, Van Steenwinckel J, Cho AH, Palmier B, Torsello E, Lai Kuen R, Onyeomah S et al (2017) Neuroinflammation, myelin and behavior: temporal patterns following mild traumatic brain injury in mice. PLoS One 12:e0184811
Zetterstrom M, Sundgren-Andersson AK, Ostlund P, Bartfai T (1998) Delineation of the proinflammatory cytokine cascade in fever induction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 856:48–52
Sun M, Brady RD, Wright DK, Kim HA, Zhang SR, Sobey CG, Johnstone MR, O'Brien TJ et al (2017) Treatment with an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist mitigates neuroinflammation and brain damage after polytrauma. Brain Behav Immun 66:359–371
Lu KT, Wang YW, Yang JT, Yang YL, Chen HI (2005) Effect of interleukin-1 on traumatic brain injury-induced damage to hippocampal neurons. J Neurotrauma 22:885–895
Sticozzi C, Belmonte G, Meini A, Carbotti P, Grasso G, Palmi M (2013) IL-1beta induces GFAP expression in vitro and in vivo and protects neurons from traumatic injury-associated apoptosis in rat brain striatum via NFkappaB/Ca(2)(+)-calmodulin/ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Neuroscience. 252:367–383
Fields J, Cisneros IE, Borgmann K, Ghorpade A (2013) Extracellular regulated kinase 1/2 signaling is a critical regulator of interleukin-1beta-mediated astrocyte tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 expression. PLoS One 8:e56891
Cheng P, Alberts I, Li X (2013) The role of ERK1/2 in the regulation of proliferation and differentiation of astrocytes in developing brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 31:783–789
Sun J, Nan G (2017) The extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway in neurological diseases: a potential therapeutic target (review). Int J Mol Med 39:1338–1346
Rama Rao KV, Jayakumar AR, Tong X, Alvarez VM, Norenberg MD (2010) Marked potentiation of cell swelling by cytokines in ammonia-sensitized cultured astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation 7:66–2094-7-66
Mori T, Wang X, Aoki T, Lo EH (2002) Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and attenuation of edema via inhibition of ERK mitogen activated protein kinase in traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 19:1411–1419
Hui H, Rao W, Zhang L, Xie Z, Peng C, Su N, Wang K, Wang L et al (2016) Inhibition of Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl(−) cotransporter-1 attenuates traumatic brain injury-induced neuronal apoptosis via regulation of Erk signaling. Neurochem Int 94:23–31
Yang Z, Fan R, Sun P, Cui H, Peng W, Luo J, Zhang C, Xiong X et al (2018) Rhubarb attenuates cerebral edema via inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway following traumatic brain injury in rats. Pharmacogn Mag 14:134–139
van der Knaap MS, Boor I, Estevez R (2012) Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts: chronic white matter oedema due to a defect in brain ion and water homoeostasis. Lancet Neurol 11:973–985
Liu S, Zhu S, Zou Y, Wang T, Fu X (2015) Knockdown of IL-1beta improves hypoxia-ischemia brain associated with IL-6 up-regulation in cell and animal models. Mol Neurobiol 51:743–752
Eng LF, Ghirnikar RS (1994) GFAP and astrogliosis. Brain Pathol 4:229–237
Ceyzeriat K, Abjean L, Carrillo-de Sauvage MA, Ben Haim L, Escartin C (2016) The complex STATes of astrocyte reactivity: how are they controlled by the JAK-STAT3 pathway? Neuroscience. 330:205–218
Toutounchian JJ, McCarty JH (2017) Selective expression of eGFP in mouse perivascular astrocytes by modification of the Mlc1 gene using T2A-based ribosome skipping. Genesis. 55. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvg.23071
Estevez R, Elorza-Vidal X, Gaitan-Penas H, Perez-Rius C, Armand-Ugon M, Alonso-Gardon M, Xicoy-Espaulella E, Sirisi S et al (2018) Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts: a personal biochemical retrospective. Eur J Med Genet 61:50–60
Sirisi S, Elorza-Vidal X, Arnedo T, Armand-Ugon M, Callejo G, Capdevila-Nortes X, Lopez-Hernandez T, Schulte U et al (2017) Depolarization causes the formation of a ternary complex between GlialCAM, MLC1 and ClC-2 in astrocytes: implications in megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy. Hum Mol Genet 26:2436–2450
Dubey M, Brouwers E, Hamilton EMC, Stiedl O, Bugiani M, Koch H, Kole MHP, Boschert U et al (2018) Seizures and disturbed brain potassium dynamics in the leukodystrophy megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Ann Neurol 83:636–649
Tzour A, Leibovich H, Barkai O, Biala Y, Lev S, Yaari Y, Binshtok AM (2017) KV 7/M channels as targets for lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory neuronal hyperexcitability. J Physiol 595:713–738
Neprasova H, Anderova M, Petrik D, Vargova L, Kubinova S, Chvatal A, Sykova E (2007) High extracellular K(+) evokes changes in voltage-dependent K(+) and Na (+) currents and volume regulation in astrocytes. Pflugers Arch 453:839–849
Okazaki R, Doi T, Hayakawa K, Morioka K, Imamura O, Takishima K, Hamanoue M, Sawada Y et al (2016) The crucial role of Erk2 in demyelinating inflammation in the central nervous system. J Neuroinflammation 13:235–016-0690-8
Hamilton EMC, Tekturk P, Cialdella F, van Rappard DF, Wolf NI, Yalcinkaya C, Cetincelik U, Rajaee A et al (2018) Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts: characterization of disease variants. Neurology. 90:e1395–e1403
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Antonella Bernardo for providing rat astrocyte cultures, Dr. Barbara Rosicarelli for technical assistance in the immunohistochemical work, and the UK Multiple Sclerosis Tissue Bank (http://www.imperial.ac.uk/medicine/multiple-sclerosis-and-parkinsons-tissue-bank) for providing brain tissue samples.
Funding
This work was supported by Italian Ministry of Health, Ricerca Finalizzata, (Grant N. GR-2013-02355882 to A.L.); European Leukodystrophies Association (ELA) (Grant N. ELA 2016-002F3 to M.S.B and ELA2012-014C2B to R.E.); TELETHON (Grant N. GEP14134 to E.A.); Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (MICINN) (SAF2015–70377 to R.E.); and the Generalitat de Catalunya (SGR2014–1178 to R.E.), (ERARE to R.E.). R.E. is a recipient of an ICREA Academia prize.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brignone, M.S., Lanciotti, A., Serafini, B. et al. Megalencephalic Leukoencephalopathy with Subcortical Cysts Protein-1 (MLC1) Counteracts Astrocyte Activation in Response to Inflammatory Signals. Mol Neurobiol 56, 8237–8254 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01657-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01657-y