Abstract
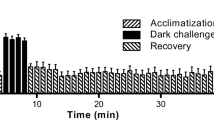
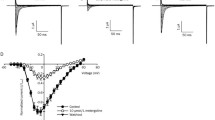
The discovery of endocannabinoids such as anandamide and the wide spread localization of cannabinoid receptors in the brain and peripheral tissues, suggests that the cannabinoid system represents a previously unrecognized ubiquitous net work in the nervous system, whose physiology and function is unfolding. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that some of the actions of anandamide are independent of a cannabinoid receptor mechanism. This was accomplished by the use of cannabinoid agonist and antagonist interaction in an in-vitro and in-vivo test systems. In-vitro, we used Xenopus laevis oocytes expression system and two-voltage clamp technique in combination with differential display polymerase chain reaction to determine whether the differential display of genes following treatment with anandamide may be linked to AMPA glutamate receptor. The differential expression of genes in vivo after the sub-acute administration of anandamide could not be directly linked with the AMPA glutamate receptor. In the voltage clamp studies we investigated the effects of anandamide on recombinant AMPA GluR3 sub-unit currents generated by kainic acid in oocytes expressing the AMPA glutamate receptor. In the in-vitro studies, we present evidence that anandamide inhibited the kainate activated currents in oocytes expressing AMPA glutamate receptor involves cAMP transduction via a cannabinoid receptor independent mechanism. In the in-vivo studies, SR141716A, the CB1 antagonist, induced anxiolysis, that was dependent on the mouse strain used in the anxiety model and blocked the anxiogenic effects of anandamide or methanandamide whereas SR141716A had no effect on the anandamide inhibition of kainate activated currents in-vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Miles, M. F. 1995. Alcohol's effects on gene expression. Alcohol health and research world. 19:237–243.
Valenzuela, C. F. 1997. Alcohol and neurotransmitter interactions. Alcohol health and research world. 21:144–148.
Chakrabarti, A., Onaivi, E. S., Sulser, F., and Akinshola, B. E. 1997. Interaction of cannabinoids with NMDA and non-NMDA glutamate receptors. Soc. Neurosc. Absts., 23:376.11.
Hampson, A. J., Bornheim, L. M., Scanziani, M., Yost C. S., Gray, A. T., Hansen, B. M., Leonoudakis, D. J., and Bickler, P. E. 1998. Dual effects of anandamide on NMDA receptor-mediated responses and neurotransmission. J. Neurochem., 70:671–676.
Mailleux, P., and Vanderhaeghen J-J. 1994. Glutamatergic regulation of cannabinoid receptor gene expression in the caudateputamen. European J. Pharmacol., 266:193–196.
Tabuchi, S., Kume, K., Aihara, M., Ishii, S., Mishina, M., and Shimizu., T. (1997) Lipid mediators modulate NMDA receptor currents in a Xenopus oocyte expression system. Neuroscience letters, 237:13–16.
Bliss, T. V., and Collingridge, G. L. 1993. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature, 361:31–39.
Di, Marzo, V., Fontana, A., Cadas, H., Schinelli, S., Cimino, G., Schwartz, J. C., and Piomelli, D. 1994. Formation and inactivation of endogenous cannabinoid anandamide in central neuron. Nature, 372:686–691.
Devane, W. A., Hanus, L., Breuer, A., Pertwee, R. G., Stevenson, L. A., Griffin, G., Gibson, D., Mandelbaum, A., Etinger, A., and Mechoulam, R. 1993. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science, 258:1946–1949.
Axelrod, J., and Felder, C. C. 1998. Cannabinoid receptors and their endogenous agonist, anandamide. Neurochemical Research, 23:575–581.
Onaivi, E. S., Chakrabarti, A., and Chaudhuri, G. 1996. Cannabinoid receptor genes. Prog. Neurobiol., 48:275–305.
Pertwee, R. G. 1997. Pharmacology of cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Pharmacol. Ther., 74:129–180.
Chakrabarti, A., Ekuta, J. E., and Onaivi, E. S. 1998. Neurobehavioral effects anandamide and cannabinoid receptor gene expression in mice. Brain Res. Bull., 45:67–74.
Matsuda, L. A. 1997. Molecular aspects of cannabinoid receptors. Critical Reviews in Neurobiology. 11:143–166.
Quick, M. W., and Lester, H. A. 1994. Methods for expression of excitability protein in Xenopus oocyte, in Methods in Neuroscience Science, Vol. 19 (Conn. P. M., ed.), P261-P279). Academic Press, San Diego.
DeLean, A., Munson, P. J., and Rodbard, D. 1978. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am. J. Physiol., 235:97–102.
Burstein, S., and Hunter, S. A. 1978. Prostaglandins and cannabis. VI. Release of arachidonic acid from HeLa cells by delta-1-tetrahydrocannabinol and other cannabinoids. Biochem. Pharmacol., 27:1275–1280.
Reichman, M., Nen, W., and Hokin, L. E. 1988. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol increases arachidonate levels in guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol. Pharmacol., 34:823–828.
Reichman, M., Nen, W., and Hokin, L. E. 1991. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol inhibits arachidonic acylation of phospholipids and triacylglycerols in guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol. Pharmacol., 40:547–555.
Felder, C. C., Nielsen, A., Briley, E. M., Palkovits, M., Priller, J., Axelrod, J., Nguyen, D. N., Richardson, J. M., Riggin, R. M., Koppel, G. A., Paul, S. M., and Becker, G. W. 1996. Isolation and measurement of the endogenous cannabinoid receptor agonist, anandamide, in brain and peripheral tissues of human and rat. FEBS Lett., 393:231–235.
Lake, K. D., Martin, B. R., Kunos, G., and Karoly, V. 1997. Cardiovascular effects of anandamide in anesthetized and conscious normotensive rats. Hypertension, 29:1204–1210.
Venance, L., Piomelli, D., Glowinski, J., and Giaume, C. 1995. Inhibition by anandamide of gap junctions and intercellular calcium signalling in striatal astrocytes. Nature, 376:590–597.
Rhee, M-H., Bayewitch, M., Avidor-Reiss, T., Levy, R., and Vogel, Z. 1998. Cannabinoid receptor activation differentially regulates the various adenylyl cyclase isozymes. J. Neurochemistry, 71:1525–1534.
Keller, B. U., Hollmann, M., Heinmann, S., and Konnerth, A. 1992. Calcium influx through subunits GluR1/GluR3 of kainate/AMPA receptor channels is regulated by cAMP dependent protein kinase. EMBO J., 11:891–896.
Onaivi, E. S., Green, M. R., and Martin, B. R. 1990. Pharmacological characterization of cannabinoids in the elevated plus maze. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 253:1002–1009.
Onaivi, E. S., and Akinshola, B. E. 1999. In-vitro and in-vivo actions of cannabinoids. Faseb J., 13(5):823.2.
Onaivi, E. S., and Martin, B. R. 1989. A neuropharmacological and physiological validation of a computer-controlled two compartment black and white box for the assessment of anxiety. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. & Biol. Psychiatry, 13:963–976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akinshola, B.E., Chakrabarti, A. & Onaivi, E.S. In-Vitro and In-Vivo Action of Cannabinoids. Neurochem Res 24, 1233–1240 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020968922151
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020968922151