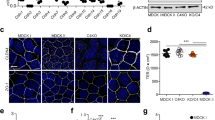
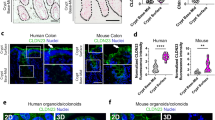
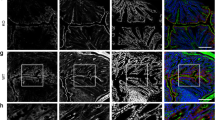
Abstract
The tight junction (zonula occludens), a belt-like region of contact between cells of polarized epithelia, serves as a selective barrier to small molecules and as a total barrier to large molecules1,2, and is involved in the separation between lumenal and basolateral compartments of the epithelium3,4. In the electron microscope, tight junctions show focal regions of apparent fusion between the adjoining cell membranes, and freeze-fractured membranes display an elaborate network of branching and anastomosing strands1,5–8. Very little is known about the molecular composition and architecture of tight junctions. The first specific zonula occludens-associated protein, designated ZO-1, has recently been identified in mammalian epithelial and endothelial cells9. Here we describe the identification and purification of a new component of this junc-tional complex in avian brush-border cells, which we name cingulin. Cingulin is an acidic, heat-stable protein, with a highly elongated shape. Immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy of brush-border cells with anti-cingulin antibodies show that cingulin is localized in the apical zone of the terminal web, at the endofacial surfaces of the zonula occludens.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farquhar, M. G. & Palade, G. J. cell Biol. 17, 375–412 (1963).
Staehelin, L. A. Int. Rev. Cytol. 39, 191–283 (1974).
Simons, K. & Fuller, S. D. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 1, 243–288 (1985).
Van Meer, G. & Simons, K. EMBO J. 5, 1455–1464 (1986).
Goodenough, D. A. & Revel, J. P. J. cell Biol. 45, 272–290 (1970).
Kachar, B. & Reese, T. S. Nature 296, 464–466 (1982).
Pinto da Silva, P. & Kachar, B. Cell 28, 441–450 (1982).
Stevenson, B. R. & Goodeneough, D. A. J. cell Biol. 98, 1209–1221 (1984).
Stevenson, B. R., Siliciano, J. D., Mooseker, M. S. & Goodenough, D. A. J. cell Biol. 103, 755–766 (1986).
Matsudaira, P. T. & Burgess, D. R. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 46, 845–854 (1982).
Mooseker, M. S. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 1, 209–241 (1985).
Hull, B. E. & Staehelin, L. A. J. cell Biol. 81, 67–82 (1979).
Citi, S. & Kendrick-Jones, J. J. cell Biol. 103, Pt2, 394a (1986).
Geiger, B., Dutton, A. H., Tokuyasu, K. T. & Singer, S. J. J. cell Biol. 91, 614–628 (1981).
Marston, S. B. & Smith, W. J. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 6, 669–708 (1985).
Lowey, S., Slayter, H. S., Weeds, A. & Baker, H. J. molec. Biol. 42, 1–29 (1969).
Jockush, B. M. & Isenberg, G. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 46, 613–623 (1981).
Geiger, B. in International Cell Biology 1980–1981 761–773 (Springer, Berlin 1981).
Ebashi, S. & Ebashi, F. J. biochem, Tokyo 58, 7–12 (1965).
Glenney, J. R., Glenney, P. & Weber, K. J. biol. Chem. 257, 9781–9787 (1982).
Cohen, C. & Parry, D. A. D. Trends biochem. Sci. 11, 245–248 (1986).
De Lanerolle, P., Adelstein, R. S., Feramisco, J. R. & Burridge, K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 4738–4742 (1981).
Glenney, J. R., Glenney, P. & Weber, K. J. cell Biol. 96, 1491–1496 (1983).
Hirokawa, N., Cheney, R. E. & Willard, M. Cell 32, 953–965 (1983).
Stewart, M. & Edwards, P. FEBS Lett. 168, 75–78 (1984).
Caspar, D. L. D., Cohen, C. & Longley, W. J. molec. Biol. 41, 87–107 (1969).
Glenney, J. R., Glenney, P. & Weber, K. J. molec. Biol. 167, 275–293 (1983).
Bretscher, A. J. biol. Chem. 259, 12873–12880 (1984).
Citi, S. & Kendrick-Jones, J. Eur. J. Biochem. 165, 315–325 (1987).
Citi, S. & Kendrick-Jones, J. J. molec. Biol. 188, 369–382 (1986).
Bretscher, A. & Weber, K. J. cell Biol. 86, 335–340 (1980).
Volk, T. & Geiger, B. J. cell Biol. 103, 1441–1450 (1986).
Matsudaira, P. T. & Burgess, D. R. Analyt. Biochem. 87, 386–396 (1978).
Burnette, W. N. Analyt. Biochem. 112, 195–203 (1981).
Burke, B. E. & Shotton, D. M. EMBO J. 1, 505–508 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Citi, S., Sabanay, H., Jakes, R. et al. Cingulin, a new peripheral component of tight junctions. Nature 333, 272–276 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/333272a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/333272a0
This article is cited by
-
Paracellular permeability and tight junction regulation in gut health and disease
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2023)
-
Fenofibrate reduces glucose-induced barrier dysfunction in feline enteroids
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
RNA sequencing-based analysis of the magnum tissues revealed the novel genes and biological pathways involved in the egg-white formation in the laying hen
BMC Genomics (2021)
-
Bioavailability of arsenic, cadmium, lead and mercury as measured by intestinal permeability
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Expression of periaxin (PRX) specifically in the human cerebrovascular system: PDZ domain-mediated strengthening of endothelial barrier function
Scientific Reports (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.