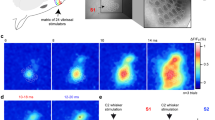
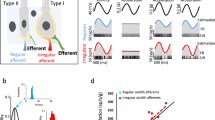
Abstract
The anatomical connections from the whiskers to the rodent somatosensory (barrel) cortex form two parallel (lemniscal and paralemniscal) pathways1,2. It is unclear whether the paralemniscal pathway is directly involved in tactile processing, because paralemniscal neuronal responses show poor spatial resolution, labile latencies and strong dependence on cortical feedback3,4,5. Here we show that the paralemniscal system can transform temporally encoded vibrissal information into a rate code. We recorded the representations of the frequency of whisker movement along the two pathways in anaesthetized rats. In response to varying stimulus frequencies, the lemniscal neurons exhibited amplitude modulations and constant latencies. In contrast, paralemniscal neurons in both thalamus and cortex coded the input frequency as changes in latency. Because the onset latencies increased and the offset latencies remained constant, the latency increments were translated into a rate code: increasing onset latencies led to lower spike counts. A thalamocortical loop that includes cortical oscillations and thalamic gating can account for these results. Thus, variable latencies and effective cortical feedback in the paralemniscal system can serve the processing of temporal sensory cues, such as those that encode object location during whisking. In contrast, fixed time locking in the lemniscal system is crucial for reliable spatial processing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woolsey, T. A. in Encyclopedia of Neuroscience (eds Adelman, G. & Smith, B.) 195–199 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1997 ).
Diamond, M. E. & Armstrong-James, M. Role of parallel sensory pathways and cortical columns in learning. Concepts Neurosci. 3, 55–78 (1992).
Diamond, M. E., Armstrong-James, M. & Ebner, F. F. Somatic sensory responses in the rostral sector of the posterior group (POm) and in the ventral posterior medial nucleus (VPM) of the rat thalamus. J. Comp. Neurol. 318, 462–476 (1992).
Diamond, M. E., Armstrong-James, M., Budway, M. J. & Ebner, F. F. Somatic sensory responses in the rostral sector of the posterior group (POm) and in the ventral posterior medial nucleus (VPM) of the rat thalamus: dependence on the barrel field cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 319, 66–84 (1992).
Hoogland, P. V., Welker, E., Van der Loos, H. & Wouterlood, F. G. in Cellular Thalamic Mechanisms (eds Bentivoglio, M. & Spreafico, R.) 152–162 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1988).
Chmielowska, J., Carvell, G. E. & Simons, D. J. Spatial organization of thalamocortical and corticothalamic projection systems in the rat SmI barrel cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 285, 325–338 ( 1989).
Lu, S. M. & Lin, R. C. Thalamic afferents of the rat barrel cortex: a light- and electron-microscopic study using Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin as an anterograde tracer. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 10, 1–16 ( 1993).
Koralek, K. A., Jensen, K. F. & Killackey, H. P. Evidence for two complementary patterns of thalamic input to the rat somatosensory cortex. Brain Res. 463 , 346–351 (1988).
Carvell, G. E. & Simons, D. J. Biometric analyses of vibrissal tactile discrimination in the rat. J. Neurosci. 10, 2638–2648 (1990).
Hartings, J. A. & Simons, D. J. Thalamic relay of afferent responses to 1- to 12-Hz whisker stimulation in the rat. J. Neurophysiol. 80, 1016–1019 (1998).
Nicolelis, M. A. & Chapin, J. K. Spatiotemporal structure of somatosensory responses of many-neuron ensembles in the rat ventral posterior medial nucleus of the thalamus. J. Neurosci. 14, 3511–3532 (1994).
Welker, W. I. Analysis of sniffing of the albino rat. Behaviour 22 , 223–244 (1964).
Fanselow, E. E. & Nicolelis, M. A. L. Behavioral modulation of tactile responses in the rat somatosensory system. J. Neurosci. 19, 7603–7616 (1999).
Friedberg, M. H., Lee, S. M. & Ebner, F. F. Modulation of receptive field properties of thalamic somatosensory neurons by the depth of anesthesia. J. Neurophysiol. 81, 2243–2252 ( 1999).
Simons, D. J., Carvell, G. E., Hershey, A. E. & Bryant, D. P. Responses of barrel cortex neurons in awake rats and effects of urethane anesthesia. Exp. Brain Res. 91, 259– 272 (1992).
Chiaia, N. L., Rhoades, R. W., Fish, S. E. & Killackey, H. P. Thalamic processing of vibrissal information in the rat: II. Morphological and functional properties of medial ventral posterior nucleus and posterior nucleus neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 314, 217 –236 (1991).
Crabtree, J. W., Collingridge, G. L. & Isaac, J. T. A new intrathalamic pathway linking modality-related nuclei in the dorsal thalamus. Nature Neurosci. 1, 389–394 (1998).
Ahissar, E. Temporal-code to rate-code conversion by neuronal phase-locked loops. Neural Comput. 10, 597–650 (1998).
Kleinfeld, D., Berg, R. W. & O'Connor, S. M. Anatomical loops and their electrical dynamics in relation to whisking by rat. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 16, 69–88 (1999).
White, E. L. & Keller, A. Intrinsic circuitry involving the local axon collaterals of corticothalamic projection cells in mouse SmI cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 262, 13– 26 (1987).
Swadlow, H. A. Influence of VPM afferents on putative inhibitory interneurons in s1 of the awake rabbit—evidence from cross-correlation, microstimulaton, and latencies to peripheral sensory stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 73, 1584–1599 (1995).
Silva, L. R., Amitai, Y. & Connors, B. W. Intrinsic oscillations of neocortex generated by layer 5 pyramidal neurons. Science 251, 432–435 (1991).
Nicolelis, M. A. L., Baccala, L. A., Lin, R. C. S. & Chapin, J. K. Sensorimotor encoding by synchronous neural ensemble activity at multiple levels of the somatosensory system. Science 268, 1353–1358 (1995).
Ahissar, E., Haidarliu, S. & Zacksenhouse, M. Decoding temporally encoded sensory input by cortical oscillations and thalamic phase comparators. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 11633–11638 ( 1997).
Sherman, S. M. & Guillery, R. W. Functional organization of thalamocortical relays. J. Neurophysiol. 76, 1367–1395 (1996).
Zucker, E. & Welker, W. I. Coding of somatic sensory input by vibrissae neurons in the rat's trigeminal ganglion. Brain Res. 12, 138–156 ( 1969).
Carr, C. E. Processing of temporal information in the brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 16, 223–243 ( 1993).
Haidarliu, S., Sosnik, R. & Ahissar, E. Simultaneous multi-site recordings and iontophoretic drug and dye applications along the trigeminal system of anesthetized rats. J. Neurosci. Methods 94, 27– 40 (1999).
Williams, M. N., Zahm, D. S. & Jacquin, M. F. Differential foci and synaptic organization of the principal and spinal trigeminal projections to the thalamus in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 6, 429–453 (1994).
Bourassa, J., Pinault, D. & Deschenes, M. Corticothalamic projections from the cortical barrel field to the somatosensory thalamus in rats: a single-fibre study using biocytin as an anterograde tracer. Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 19–30 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Ahissar, and S. Barash for suggestions; A. Arieli, F. F. Ebner, K. O. Johnson, R. Malach and D. J. Simons for comments and discussions; M. E. Diamond for assistance during our initial thalamic recordings; and B. Schick for reviewing the manuscript. This work was supported by the US–Israel Binational Science Foundation and by the MINERVA Foundation, Germany. S.H. was supported by The Centre for Absorption of Scientists, Ministry of Absorption, Israel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahissar, E., Sosnik, R. & Haidarliu, S. Transformation from temporal to rate coding in a somatosensory thalamocortical pathway. Nature 406, 302–306 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35018568
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35018568
This article is cited by
-
Thalamocortical loops as temporal demodulators across senses
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Bayesian prediction of psychophysical detection responses from spike activity in the rat sensorimotor cortex
Journal of Computational Neuroscience (2023)
-
High-frequency burst spiking in layer 5 thick-tufted pyramids of rat primary somatosensory cortex encodes exploratory touch
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Effects of basal forebrain stimulation on the vibrotactile responses of neurons from the hindpaw representation in the rat SI cortex
Brain Structure and Function (2020)
-
Propagation of temporal and rate signals in cultured multilayer networks
Nature Communications (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.