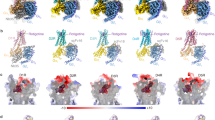
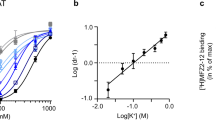
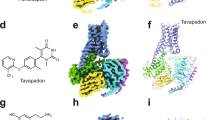
Abstract
DOPAMINE receptors belong to a superfamily of receptors that exert their biological effects through guanine nucleotide-binding (G) proteins. Two main dopamine receptor subtypes have been identified, D1 and D2, which differ in their pharmacological and biochemical characteristics. D1 stimulates adenylyl cyclase activity, whereas D2 inhibits it1–3. Both receptors are primary targets for drugs used to treat many psychomotor diseases, including Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia4,5. Whereas the dopamine D, receptor has been cloned6–9, biochemical and behavioural data indicate that dopamine D1-like receptors exist which either are not linked to adenylyl cyclase or display different pharmacological activities10,11. We report here the cloning of a gene encoding a 477-amino-acid protein with strong homology to the cloned Dt receptor. The receptor, called D5, binds drugs with a pharmacological profile similar to that of the cloned Dl receptor, but displays a 10-fold higher affinity for the endogenous agonist, dopamine. As with D1, the dopamine D5 receptor stimulates adenylyl cyclase activity. Northern blot and in situ hybridization analyses reveal that the receptor is neuron-specific, localized primarily within limbic regions of the brain; no messenger RNA was detected in kidney, liver, heart or parathyroid gland. The existence of a dopamine D1-like receptor with these characteristics had not been predicted and may represent an alternative pathway for dopamine-mediated events and regulation of D2 receptor activity12–14.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kebabian, J. W. & Calne, D. B. Nature 277, 93–96 (1979).
Seeman, P. Pharmac. Rev. 32, 229–313 (1980).
Niznik, H. B. Molec. cell. Endocrin. 54, 1–22 (1987).
Seeman, P. Synapse 1, 133–152 (1987).
Seeman, P. & Niznik, H. B. FASEB J. 4(10), 2737–2744 (1990).
Sunahara, R. K. et al. Nature 347, 80–83 (1990).
Zhou, Q.-Y. et al. Nature 347, 76–79 (1990).
Dearry, A. G. et al. Nature 347, 72–76 (1990).
Monsma, F. J., Mahan, L. C., McVittie, L. D., Gerfen, C. R. & Sibley, D. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 6723–6727 (1990).
Andersen, P. H. et al. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 11, 231–234 (1990).
Felder, R. A., Felder, C. C., Eisner, G. M. & Jose, P. A. Am. J. Physiol. 257, F315–F327 (1989).
Waddington, J. L. & O'Boyle, K. M. Pharmac. Ther. 43, 1–52 (1989).
Clark, D. & White, F. J. Synapse 1, 347–388 (1987).
Seeman, P., Niznik, H. B., Guan, H.-C., Booth, G. & Ulpian, C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 10156–10160 (1989).
O'Dowd, B. F., Lefkowitz, R. J. & Caron, M. G. A. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 67–83 (1989).
Kozak, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 857–873 (1984).
Bunzow, J. R. et al. Nature 336, 783–787 (1988).
Sokoloff, P., Giros, B., Martres, M. P., Bouthenet, M. L. & Schwartz, J. C. Nature 347, 146–151 (1990).
Van Tol, H. H. M. et al. Nature, 350, 610–614 (1991).
Selbie, L. A., Hayes, G. & Shine, J. DNA 8, 683–989 (1989).
Strader, C. D., Sigal, S. S. & Dixon, R. A. FASEB J. 3, 1825–1832 (1989).
O'Dowd, B. F., Hnatowich, M., Caron, M. G., Lefkowitz, R. J. & Bouvier, M. J. biol. Chem. 264, 7564–7569 (1989).
Bonner, T. I. et al. Neuron 1, 403–410 (1988).
Seeman, P. et al. Neuropsychopharmacology 1, 5–15 (1987).
Albert, P. R., Neve, K. A., Bunzow, J. R. & Civelli, O. J. biol. Chem. 265(4), 2098–2104 (1990).
Ehrlich, M. E., Kurihara, T. & Greengard, P. J. molec. Neurosci. 2, 1–10 (1990).
Kozak, M. J. Cell Biol. 103, 1–7 (1988).
Bjorklund, A., Lindvall, O. in Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy (eds Bjorklund, A. & Hokfeld, T.) Vol. 2(A) 55–122 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1984).
Savasta, M., Dubois, A. & Scatton, B. Brain Res. 375, 291–301 (1986).
Cortes, R., Gueye, B., Pazos, A., Probst, A. & Palacios, J. M. Neuroscience 28(2), 263–273 (1989).
Diop, L., Gottberg, E., Briere, R., Grondin, L. & Reader, T. M. Synapse 2, 395–405 (1988).
Besson, M.-J., Graybiel, A. M. & Nastuk, M. A. Neuroscience 1, 101–119 (1988).
Ongini, E. & Longo, V. G. Int Rev. Neurobiol. 31, 239–255 (1989).
Niznik, H. B. et al. Biochemistry 27, 7594–7599 (1988).
Niznik, H. B., Jarvie, K. R. & Brown, E. M. Biochemistry 28, 6925–6930 (1989).
O'Dowd, B. F. et al. FEBS Lett. 262(1), 8–12 (1990).
Chen, C. & Okayama, H. Molec. cell. Biol. 7, 2745–2752 (1987).
Salomon, Y. in Advances in Cyclic Nucleotide Research. (eds Brooker, G., Greengard, P. & Robison, G. A.) Vol. 10 (Raven, New York, 1979).
McMaster, G. K. & Carmichael, G. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 74, 4835 (1977).
Shivers, B. D., Schachter, B. S. & Pfaff, D. W. Meth. Enzym. 124, 497–510 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunahara, R., Guan, HC., O'Dowd, B. et al. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature 350, 614–619 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/350614a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/350614a0
This article is cited by
-
The dopamine receptor D1 inhibitor, SKF83566, suppresses GBM stemness and invasion through the DRD1-c-Myc-UHRF1 interactions
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2024)
-
G protein-coupled receptors in neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Behavioural effects of APH199, a selective dopamine D4 receptor agonist, in animal models
Psychopharmacology (2023)
-
Behavioral characteristics of dopamine D5 receptor knockout mice
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Therapeutic potential of dopamine agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.