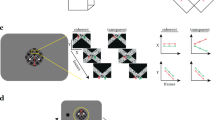
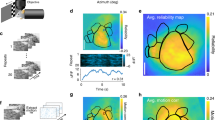
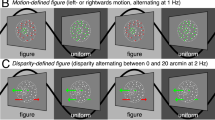
Abstract
THE primate visual system incorporates a highly specialized subsystem for the analysis of motion in the visual field1–6. A key element of this subsystem is the middle temporal (MT) cortical area, which contains a majority of direction-selective neurons1–3. MT neurons are also selective for binocular disparity (depth), which is perplexing given that they are not sensitive to motion through depth7. What is the role of disparity in MT? Our data suggest an important link between disparity and transparent motion detection. Motion signals in different directions tend to inhibit each other within a given MT receptive field8. This inhibition has an averaging effect which minimizes MT responses to random motion signals created by light intensity changes and other non-motion stimuli (motion noise) 9. But, in the absence of disparity cues, inhibition may also occur between surfaces moving in different directions through the same part of the visual field (transparent motion), thus impairing the detection of either surface. Here we show that inhibition in MT occurs mainly between motion signals with similar disparities. Transparent surface movements at different depths are thus represented independently in MT (that is, without inhibiting each other) whereas spurious motion signals from a given surface tend to cancel out. To our knowledge, these results provide the first evidence for a functional integration of motion and disparity in MT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maunsell, J. H. R. & Van Essen, D. C. J. Neurophysiol. 49, 1127–1147 (1983).
Albright, T. D. J. Neurophysiol. 52, 1106–1130 (1984).
Allman, J. M. & Kaas, J. H. Brain Res. 31, 84–105 (1971).
Roy, J. P., Komatsu, H. & Wurtz, R. H. J. Neurosci. 12, 2478–2492 (1992).
Hubel, D. H. & Wiesel, T. N. J. Physiol. 195, 215–243 (1968).
Nakayama, K. Vision Res. 25, 625–660 (1985).
Maunsell, J. H. R. & Van Essen, D. C. J. Neurophysiol. 49, 1148–1167 (1983).
Snowden, R. J., Treue, S., Erickson, R. G. & Andersen, R. A. J. Neurosci. 11, 2768–2785 (1991).
Qian, N. & Andersen, R. A. J. Neurosci. 14, 7367–7380 (1994).
Qian, N., Andersen, R. A. & Adelson, E. H. J. Neurosci. 14, 7357–7366 (1994).
Snowden, R. J. J. opt. Soc. Am. A6, 1096–1101 (1989).
Mather, G. & Moulden, B. Q. J. exp. Psychol. 35A, 513–518 (1983).
Lindsey, D. T. & Todd, J. T. Invest. Ophthal. Vis. Sci. 35, 1389 (1994).
Newsome, W. T., Britten, K. H. & Movshon, J. A. Nature 341, 52–54 (1989).
Stoner, G. R. & Albright, T. D. Nature 358, 412–414 (1992).
Logothetis, N. K. & Schall, J. D. Science 245, 761–763 (1989).
Van Essen, D. C., Felleman, D. J., DeYoe, E. A., Olavarria, J. & Knierim, J. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 55, 679–696 (1990).
Livingstone, M. S. & Hubel, D. H. J. Neurosci. 7, 3416–3468 (1987).
Judge, S. J., Richmond, B. J. & Chu, F. C. Vision Res. 20, 535–537 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bradley, D., Qian, N. & Andersen, R. Integration of motion and stereopsis in middle temporal cortical area of macaques. Nature 373, 609–611 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/373609a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/373609a0
This article is cited by
-
Interocular contrast difference drives illusory 3D percept
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
The Pulfrich effect in the clinic
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2011)
-
Disparity- and velocity-based signals for three-dimensional motion perception in human MT+
Nature Neuroscience (2009)
-
Integrating motion and depth via parallel pathways
Nature Neuroscience (2008)
-
A neural representation of depth from motion parallax in macaque visual cortex
Nature (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.