Abstract
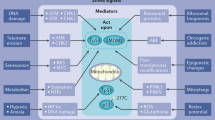
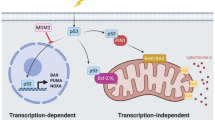
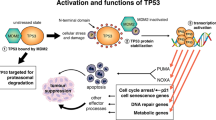
The protein p53 is a key tumour-suppressor, as evidenced by its frequent inactivation in human cancers. Animal models have indicated that attenuation of p53-dependent cell death (apoptosis) can contribute to both the initiation and progression of cancer, but the molecular mechanisms are unknown. Although p53-mediated transcriptional activation is one possible explanation, none of the known p53-responsive genes has been shown to function in p53-dependent apoptosis. Here we test the role of the death-promoting gene bax in a transgenic mouse brain tumour, a model in which p53-mediated apoptosis attenuates tumour growth. Inactivation of p53 causes a dramatic acceleration of tumour growth owing to a reduction in apoptosis of over ninety per cent1. We show that p53-dependent expression of bax is induced in slow-growing apoptotic tumours. Moreover, tumour growth is accelerated and apoptosis drops by fifty per cent in Bax-deficient mice, indicating that it is required for a full p53-mediated response. To our knowledge this is the first demonstration that Bax acts as a tumour suppressor, and our findings indicate that Bax could be a component of the p53-mediated apoptotic response in this system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Symonds, H. et al. Cell 78, 703–711 (1994).
Oltvai, Z., Milliman, C. & Korsmeyer, S. Cell 74, 609–619 (1993).
Knudson, C. M., Tung, K. S. K., Tourtellotte, W. G., Brown, G. A. J. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Science 270, 96–99 (1995).
Miyashita, T. et al. Oncogene 9, 1799–1805 (1994).
Han, J. H. et al. Genes Dev. 10, 461–477 (1996).
Miyashita, T. & Reed, J. C. Cell 80, 293–299 (1995).
Clarke, A. R. et al. Nature 362, 849–852 (1993).
Lowe, S. W., Schmitt, E. M., Smith, S. W., Osborne, B. A. & Jacks, T. Nature 362, 847–849 (1993).
Donehower, L. A. et al. Nature 356, 215–221 (1992).
Van Dyke, T. A. in Molecular Genetics of Nervous System Tumors (eds Levine, A. J. & Schmidek, H. H.) 287–301 (Wiley-Liss, New York, 1993).
Saenz-Robles, M. T., Symonds, H., Chen, J. & Van Dyke, T. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 2686–2698 (1994).
Pipas, J. M., Peden, K. W. & Nathans, D. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3, 203–213 (1983).
Gavrieli, Y., Sherman, Y. & Ben-Sasson, S. A. J. Cell Biol. 119, 493–501 (1992).
Lane, D. P. Nature 358, 15–16 (1992).
Yin, Y., Tainsky, M. A., Bischoff, F. Z., Strong, L. C. & Wahl, G. M. Cell 70, 937–948 (1992).
Livingstone, L. R. et al. Cell 70, 923–935 (1992).
McCurrach, M. E., Connor, T. M. F, Knuson, C. M., Korsmeyer, S. E. & Lowe, S. W. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA (submitted).
Chen, X., Ko, L. J., Jayaraman, L. & Prives, C. Gene Dev. 10, 2438–2451 (1996).
Brady, H. J. M., Salomons, G. S., Bobeldijk, R. C. & Berns, A. J. M. EMBO J. 15, 1221–1230 (1996).
Symonds, H. S., McCarthy, S. A., Chen, J., Pipas, J. M. & Van Dyke, T. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 3255–3265 (1993).
Yan, C., Costa, R. H., Darnell, J. E., Chen, J. D. & Van Dyke, T. A. EMBO J. 9, 869–878 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, C., Knudson, C., Korsmeyer, S. et al. Bax suppresses tumorigenesis and stimulates apoptosis in vivo. Nature 385, 637–640 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/385637a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/385637a0
This article is cited by
-
Melatonin and 5-fluorouracil combination chemotherapy: opportunities and efficacy in cancer therapy
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Conversion of senescent cartilage into a pro-chondrogenic microenvironment with antibody-functionalized copper sulfate nanoparticles for efficient osteoarthritis therapy
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2023)
-
Promoter hypermethylation and comprehensive regulation of ncRNA lead to the down-regulation of ZNF880, providing a new insight for the therapeutics and research of colorectal cancer
BMC Medical Genomics (2023)
-
Epigenetic alterations of miR-155 and global DNA methylation as potential mediators of ochratoxin A cytotoxicity and carcinogenicity in human lung fibroblasts
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
-
The role of the DFF40/CAD endonuclease in genomic stability
Apoptosis (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.