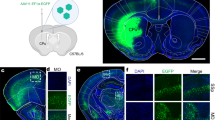
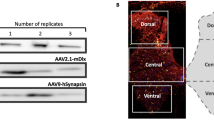
Abstract
The treatment of axonal disorders, such as diseases associated with axonal injury and degeneration, is limited by the inability to directly target therapeutic protein expression to injured axons. Current gene therapy approaches rely on infection and transcription of viral genes in the cell body. Here, we describe an approach to target gene expression selectively to axons. Using a genetically engineered mouse containing epitope-labeled ribosomes, we find that neurons in adult animals contain ribosomes in distal axons. To use axonal ribosomes to alter local protein expression, we utilized a Sindbis virus containing an RNA genome that has been modified so that it can be directly used as a template for translation. Selective application of this virus to axons leads to local translation of heterologous proteins. Furthermore, we demonstrate that selective axonal protein expression can be used to modify axonal signaling in cultured neurons, enabling axons to grow over inhibitory substrates typically encountered following axonal injury. We also show that this viral approach also can be used to achieve heterologous expression in axons of living animals, indicating that this approach can be used to alter the axonal proteome in vivo. Together, these data identify a novel strategy to manipulate protein expression in axons, and provides a novel approach for using gene therapies for disorders of axonal function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Filbin MT . Myelin-associated inhibitors of axonal regeneration in the adult mammalian CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci 2003; 4: 703–713.
Liu K, Tedeschi A, Park KK, He Z . Neuronal intrinsic mechanisms of axon regeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci 2011; 34: 131–152.
Franz S, Weidner N, Blesch A . Gene therapy approaches to enhancing plasticity and regeneration after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 2011 (in press).
Davidson BL, Breakefield XO . Viral vectors for gene delivery to the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 2003; 4: 353–364.
Lowery LA, Van Vactor D . The trip of the tip: understanding the growth cone machinery. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009; 10: 332–343.
Piper M, Holt C . RNA translation in axons. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2004; 20: 505–523.
Hengst U, Deglincerti A, Kim HJ, Jeon NL, Jaffrey SR . Axonal elongation triggered by stimulus-induced local translation of a polarity complex protein. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 1024–1030.
Hengst U, Jaffrey SR . Function and translational regulation of mRNA in developing axons. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2007; 18: 209–215.
Zelena J . Ribosomes in myelinated axons of dorsal root ganglia. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 1972; 124: 217–229.
Conradi S, Ronnevi LO . Ultrastructure and synaptology of the initial axon segment of cat spinal motoneurons during early postnatal development. J Neurocytol 1977; 6: 195–210.
Li YC, Cheng CX, Li YN, Shimada O, Atsumi S . Beyond the initial axon segment of the spinal motor axon: fasciculated microtubules and polyribosomal clusters. J Anat 2005; 206: 535–542.
Pannese E, Ledda M . Ribosomes in myelinated axons of the rabbit spinal ganglion neurons. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 1991; 23: 33–38.
Koenig E, Martin R, Titmus M, Sotelo-Silveira JR . Cryptic peripheral ribosomal domains distributed intermittently along mammalian myelinated axons. J Neurosci 2000; 20: 8390–8400.
Palay SL, Sotelo C, Peters A, Orkand PM . The axon hillock and the initial segment. J Cell Biol 1968; 38: 193–201.
Kun A, Otero L, Sotelo-Silveira JR, Sotelo JR . Ribosomal distributions in axons of mammalian myelinated fibers. J Neurosci Res 2007; 85: 2087–2098.
Heiman M, Schaefer A, Gong S, Peterson JD, Day M, Ramsey KE et al. A translational profiling approach for the molecular characterization of CNS cell types. Cell 2008; 135: 738–748.
Doyle JP, Dougherty JD, Heiman M, Schmidt EF, Stevens TR, Ma G et al. Application of a translational profiling approach for the comparative analysis of CNS cell types. Cell 2008; 135: 749–762.
Ramirez LF, Kalil K . Critical stages for growth in the development of cortical neurons. J Comp Neurol 1985; 237: 506–518.
Steward O, Levy WB . Preferential localization of polyribosomes under the base of dendritic spines in granule cells of the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 1982; 2: 284–291.
Tennyson VM . The fine structure of the axon and growth cone of the dorsal root neuroblast of the rabbit embryo. J Cell Biol 1970; 44: 62–79.
Strauss JH, Strauss EG . The alphaviruses: gene expression, replication, and evolution. Microbiol Rev 1994; 58: 491–562.
Jeromin A, Yuan LL, Frick A, Pfaffinger P, Johnston D . A modified Sindbis vector for prolonged gene expression in neurons. J Neurophysiol 2003; 90: 2741–2745.
Waehler R, Russell SJ, Curiel DT . Engineering targeted viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 573–587.
Ehrengruber MU, Lundstrom K, Schweitzer C, Heuss C, Schlesinger S, Gahwiler BH . Recombinant Semliki forest virus and Sindbis virus efficiently infect neurons in hippocampal slice cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 7041–7046.
Wu KY, Hengst U, Cox LJ, Macosko EZ, Jeromin A, Urquhart ER et al. Local translation of RhoA regulates growth cone collapse. Nature 2005; 436: 1020–1024.
Martinez-Salas E . Internal ribosome entry site biology and its use in expression vectors. Curr Opin Biotechnol 1999; 10: 458–464.
Dryga SA, Dryga OA, Schlesinger S . Identification of mutations in a Sindbis virus variant able to establish persistent infection in BHK cells: the importance of a mutation in the nsP2 gene. Virology 1997; 228: 74–83.
Taylor AM, Blurton-Jones M, Rhee SW, Cribbs DH, Cotman CW, Jeon NL . A microfluidic culture platform for CNS axonal injury, regeneration and transport. Nat Methods 2005; 2: 599–605.
Xiong C, Levis R, Shen P, Schlesinger S, Rice CM, Huang HV . Sindbis virus: an efficient, broad host range vector for gene expression in animal cells. Science 1989; 243: 1188–1191.
Thuret S, Moon LD, Gage FH . Therapeutic interventions after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006; 7: 628–643.
Pearse DD, Pereira FC, Marcillo AE, Bates ML, Berrocal YA, Filbin MT et al. cAMP and Schwann cells promote axonal growth and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nat Med 2004; 10: 610–616.
Menniti FS, Faraci WS, Schmidt CJ . Phosphodiesterases in the CNS: targets for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006; 5: 660–670.
Spencer GE, Syed NI, van Kesteren E, Lukowiak K, Geraerts WP, van Minnen J . Synthesis and functional integration of a neurotransmitter receptor in isolated invertebrate axons. J Neurobiol 2000; 44: 72–81.
Chen Y, Cann MJ, Litvin TN, Iourgenko V, Sinclair ML, Levin LR et al. Soluble adenylyl cyclase as an evolutionarily conserved bicarbonate sensor. Science 2000; 289: 625–628.
Gao Y, Deng K, Hou J, Bryson JB, Barco A, Nikulina E et al. Activated CREB is sufficient to overcome inhibitors in myelin and promote spinal axon regeneration in vivo. Neuron 2004; 44: 609–621.
Cai D, Qiu J, Cao Z, McAtee M, Bregman BS, Filbin MT . Neuronal cyclic AMP controls the developmental loss in ability of axons to regenerate. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 4731–4739.
Silver J, Miller JH . Regeneration beyond the glial scar. Nat Rev Neurosci 2004; 5: 146–156.
McKeon RJ, Schreiber RC, Rudge JS, Silver J . Reduction of neurite outgrowth in a model of glial scarring following CNS injury is correlated with the expression of inhibitory molecules on reactive astrocytes. J Neurosci 1991; 11: 3398–3411.
Borisoff JF, Chan CC, Hiebert GW, Oschipok L, Robertson GS, Zamboni R et al. Suppression of Rho-kinase activity promotes axonal growth on inhibitory CNS substrates. Mol Cell Neurosci 2003; 22: 405–416.
Sivasankaran R, Pei J, Wang KC, Zhang YP, Shields CB, Xu XM et al. PKC mediates inhibitory effects of myelin and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans on axonal regeneration. Nat Neurosci 2004; 7: 261–268.
Tom VJ, Steinmetz MP, Miller JH, Doller CM, Silver J . Studies on the development and behavior of the dystrophic growth cone, the hallmark of regeneration failure, in an in vitro model of the glial scar and after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 6531–6539.
Sherman DL, Brophy PJ . Mechanisms of axon ensheathment and myelin growth. Nat Rev Neurosci 2005; 6: 683–690.
Ohno N, Kidd GJ, Mahad D, Kiryu-Seo S, Avishai A, Komuro H et al. Myelination and axonal electrical activity modulate the distribution and motility of mitochondria at CNS nodes of Ranvier. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 7249–7258.
Hillefors M, Gioio AE, Mameza MG, Kaplan BB . Axon viability and mitochondrial function are dependent on local protein synthesis in sympathetic neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2007; 27: 701–716.
Court FA, Hendriks WT, MacGillavry HD, Alvarez J, van Minnen J . Schwann cell to axon transfer of ribosomes: toward a novel understanding of the role of glia in the nervous system. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 11024–11029.
Milner TA, Thompson LI, Wang G, Kievits JA, Martin E, Zhou P et al. Distribution of estrogen receptor beta containing cells in the brains of bacterial artificial chromosome transgenic mice. Brain Res 2010; 1351: 74–96.
Banker G, Goslin K . Culturing Nerve Cells, 2nd edn MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, 1998.
Delree P, Leprince P, Schoenen J, Moonen G . Purification and culture of adult rat dorsal root ganglia neurons. J Neurosci Res 1989; 23: 198–206.
Goldenberg SS, De Boni U . Pure population of viable neurons from rabbit dorsal root ganglia, using gradients of Percoll. J Neurobiol 1983; 14: 195–206.
Kim J, Dittgen T, Nimmerjahn A, Waters J, Pawlak V, Helmchen F et al. Sindbis vector SINrep(nsP2S726): a tool for rapid heterologous expression with attenuated cytotoxicity in neurons. J Neurosci Methods 2004; 133: 81–90.
Acknowledgements
We thank S Schlesinger and A Jeromin for Sindbis plasmids, Joe Harris (UC Irvine), for preparing masters for casting microfluidic chambers, MS Cohen, A Deglincerti, L Levin and J Buck (Weill Cornell Medical College) for useful comments and suggestions. This work was supported by the Christopher Reeve Paralysis Foundation, the New York State Spinal Cord Injury Board, NIH Grants NINDS NS56306 (SRJ), DA08259 (TAM), ML096571 (TAM), ML098351 (TAM), the Biomembrane Plasticity Research Center (2011-0000841) through the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NLJ) and training grant T32DA007274 (BAW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Gene Therapy website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walker, B., Hengst, U., Kim, H. et al. Reprogramming axonal behavior by axon-specific viral transduction. Gene Ther 19, 947–955 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.217
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.217
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Local translation in neurons: visualization and function
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2019)
-
Targeting Axonal Protein Synthesis in Neuroregeneration and Degeneration
Neurotherapeutics (2015)
-
Peripheral nerve axons contain machinery for co-translational secretion of axonally-generated proteins
Neuroscience Bulletin (2013)
-
Axonal mRNA localization and local protein synthesis in nervous system assembly, maintenance and repair
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2012)