Abstract
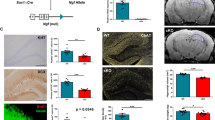
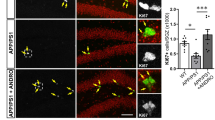
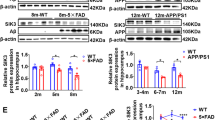
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) is crucial for the maintenance of hippocampal function. Several neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are accompanied by memory deficits that could be related to alterations in AHN. Here, we took advantage of a conditional mouse model to study the involvement of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) overexpression (OE) in AHN. By injecting GFP- and PSD95-GFP-expressing retroviruses, we have determined that hippocampal GSK-3β-OE causes dramatic alterations in both dendritic tree morphology and post-synaptic densities in newborn neurons. Alterations in previously damaged neurons were reverted by switching off the transgenic system and also by using a physiological approach (environmental enrichment) to increase hippocampal plasticity. Furthermore, comparative morphometric analysis of granule neurons from patients with AD and from GSK-3β overexpressing mice revealed shared morphological alterations. Taken together, these data indicate that GSK-3β is crucial for hippocampal function, thereby supporting this kinase as a relevant target for the treatment of AD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garthe A, Behr J, Kempermann G . Adult-generated hippocampal neurons allow the flexible use of spatially precise learning strategies. PLoS ONE 2009; 4: e5464.
Wiskott L, Rasch MJ, Kempermann G . A functional hypothesis for adult hippocampal neurogenesis: avoidance of catastrophic interference in the dentate gyrus. Hippocampus 2006; 16: 329–343.
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH . Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 1999; 2: 266–270.
Shiurba RA, Ishiguro K, Takahashi M, Sato K, Spooner ET, Mercken M et al. Immunocytochemistry of tau phosphoserine 413 and tau protein kinase I in Alzheimer pathology. Brain Res 1996; 737: 119–132.
Leroy K, Boutajangout A, Authelet M, Woodgett JR, Anderton BH, Brion JP . The active form of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is associated with granulovacuolar degeneration in neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 2002; 103: 91–99.
Jope RS, Johnson GV . The glamour and gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem Sci 2004; 29: 95–102.
Salcedo-Tello P, Ortiz-Matamoros A, Arias C . GSK3 function in the brain during development, neuronal plasticity, and neurodegeneration. Int J Alzheimer's Dis 2011; 2011: 189728.
Salcedo-Tello P, Ortiz-Matamoros A, Arias C . GSK3 function in the brain during development, neuronal plasticity, and neurodegeneration. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011; 2011: 189728.
Peineau S, Taghibiglou C, Bradley C, Wong TP, Liu L, Lu J et al. LTP inhibits LTD in the hippocampus via regulation of GSK3beta. Neuron 2007; 53: 703–717.
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH . Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci 2000; 1: 191–198.
Choi SH, Veeraraghavalu K, Lazarov O, Marler S, Ransohoff RM, Ramirez JM et al. Non-cell-autonomous effects of presenilin 1 variants on enrichment-mediated hippocampal progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Neuron 2008; 59: 568–580.
Petrosini L, De Bartolo P, Foti F, Gelfo F, Cutuli D, Leggio MG et al. On whether the environmental enrichment may provide cognitive and brain reserves. Brain Res Rev 2009; 61: 221–239.
Ohm TG . The dentate gyrus in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Brain Res 2007; 163: 723–740.
Paxinos G . The human nervous system. In: Paxinos G, ed. The Human Nervous system. Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, USA, 2004 pp 871–914.
Lucas JJ, Hernandez F, Gomez-Ramos P, Moran MA, Hen R, Avila J . Decreased nuclear beta-catenin, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration in GSK-3beta conditional transgenic mice. EMBO J 2001; 20: 27–39.
Zhao C, Teng EM, Summers RG, Ming GL, Gage FH . Distinct morphological stages of dentate granule neuron maturation in the adult mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 3–11.
Kelsch W, Lin CW, Lois C . Sequential development of synapses in dendritic domains during adult neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105 (43): 16803–16808.
Llorens-Martin M, Tejeda GS, Trejo JL . Differential regulation of the variations induced by environmental richness in adult neurogenesis as a function of time: a dual birthdating analysis. PLoS ONE 2010; 5: e12188.
Sholl DA . The organization of the visual cortex in the cat. J Anat 1955; 89: 33–46.
Martinez-Martin P, Avila J . Alzheimer Center Reina Sofia Foundation: fighting the disease and providing overall solutions. J Alzheimers Dis 2010; 21: 337–348.
International Society for Biological and Environmental Repositories Biopreservation and Biobanking 2012. Collection, storage, retrieval, and distribution of biological materials for research. Cell Preserv Technol 2008; 6, doi:10.1089/cpt.2008.9997.
Fuster-Matanzo A, Llorens-Martin M, de Barreda EG, Avila J, Hernandez F . Different susceptibility to neurodegeneration of dorsal and ventral hippocampal dentate gyrus: a study with transgenic mice overexpressing GSK3beta. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e27262.
Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH . Experience-induced neurogenesis in the senescent dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 1998; 18: 3206–3212.
Seress L, Pokorny J . Structure of the granular layer of the rat dentate gyrus. A light microscopic and Golgi study. J Anat 1981; 133 (Pt 2): 181–195.
Kharatishvili I, Nissinen JP, McIntosh TK, Pitkanen A . A model of posttraumatic epilepsy induced by lateral fluid-percussion brain injury in rats. Neuroscience 2006; 140: 685–697.
Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR, Barnes CL . Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science (New York, NY) 1984; 225: 1168–1170.
de Ruiter JP, Uylings HB . Morphometric and dendritic analysis of fascia dentata granule cells in human aging and senile dementia. Brain Res 1987; 402: 217–229.
Collingridge GL, Isaac JT, Wang YT . Receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev 2004; 5: 952–962.
Hooper C, Markevich V, Plattner F, Killick R, Schofield E, Engel T et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition is integral to long-term potentiation. Eur J Neurosci 2007; 25: 81–86.
Arendt T . Synaptic plasticity and cell cycle activation in neurons are alternative effector pathways: the 'Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde concept' of Alzheimer's disease or the yin and yang of neuroplasticity. Prog Neurobiol 2003; 71: 83–248.
Engel T, Hernandez F, Avila J, Lucas JJ . Full reversal of Alzheimer's disease-like phenotype in a mouse model with conditional overexpression of glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 5083–5090.
Hernandez F, Borrell J, Guaza C, Avila J, Lucas JJ . Spatial learning deficit in transgenic mice that conditionally over-express GSK-3beta in the brain but do not form tau filaments. J Neurochem 2002; 83: 1529–1533.
Scheff SW, Sparks DL, Price DA . Quantitative assessment of synaptic density in the outer molecular layer of the hippocampal dentate gyrus in Alzheimer's disease. Dementia: Basel, Switzerland, 1996; 7 (4): 226–232.
Flood DG, Buell SJ, Horwitz GJ, Coleman PD . Dendritic extent in human dentate gyrus granule cells in normal aging and senile dementia. Brain Res 1987; 402: 205–216.
Yamasaki N, Maekawa M, Kobayashi K, Kajii Y, Maeda J, Soma M et al. Alpha-CaMKII deficiency causes immature dentate gyrus, a novel candidate endophenotype of psychiatric disorders. Mol Brain 2008; 1: 6.
Ribak CE, Shapiro LA, Perez ZD, Spigelman I . Microglia-associated granule cell death in the normal adult dentate gyrus. Brain Struct Funct 2009; 214: 25–35.
Monje ML, Toda H, Palmer TD . Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science (New York, NY) 2003; 302: 1760–1765.
Belarbi K, Arellano C, Ferguson R, Jopson T, Rosi S . Chronic neuroinflammation impacts the recruitment of adult-born neurons into behaviorally relevant hippocampal networks. Brain Behav Immun 2012; 26: 18–23.
Krathwohl MD, Kaiser JL . Chemokines promote quiescence and survival of human neural progenitor cells. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2004; 22: 109–118.
Koo JW, Duman RS . IL-1beta is an essential mediator of the antineurogenic and anhedonic effects of stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105 (2): 751–756.
Barkho BZ, Song H, Aimone JB, Smrt RD, Kuwabara T, Nakashima K et al. Identification of astrocyte-expressed factors that modulate neural stem/progenitor cell differentiation. Stem Cells Dev 2006; 15: 407–421.
Beck RD, Wasserfall C, Ha GK, Cushman JD, Huang Z, Atkinson MA et al. Changes in hippocampal IL-15, related cytokines, and neurogenesis in IL-2 deficient mice. Brain Res 2005; 1041: 223–230.
Ehninger D, Wang LP, Klempin F, Romer B, Kettenmann H, Kempermann G . Enriched environment and physical activity reduce microglia and influence the fate of NG2 cells in the amygdala of adult mice. Cell Tissue Res 2011; 345: 69–86.
Nimchinsky EA, Sabatini BL, Svoboda K . Structure and function of dendritic spines. Annu Rev Physiol 2002; 64: 313–353.
Falkenberg T, Mohammed AK, Henriksson B, Persson H, Winblad B, Lindefors N . Increased expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in rat hippocampus is associated with improved spatial memory and enriched environment. Neurosci Lett 1992; 138: 153–156.
Kee N, Teixeira CM, Wang AH, Frankland PW . Preferential incorporation of adult-generated granule cells into spatial memory networks in the dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 2007; 10: 355–362.
Foster TC, Dumas TC . Mechanism for increased hippocampal synaptic strength following differential experience. J Neurophysiol 2001; 85: 1377–1383.
Sale A, Berardi N, Maffei L . Enrich the environment to empower the brain. Trends Neurosci 2009; 32: 233–239.
Kopec CD, Real E, Kessels HW, Malinow R . GluR1 links structural and functional plasticity at excitatory synapses. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 13706–13718.
Gagne J, Gelinas S, Martinoli MG, Foster TC, Ohayon M, Thompson RF et al. AMPA receptor properties in adult rat hippocampus following environmental enrichment. Brain Res 1998; 799: 16–25.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by grants from Spanish Ministry of Health (SAF 2006-02424, BFU-2008-03980 and BFU-2010-21507), the Comunidad de Madrid (SAL/0202/2006), the Fundación M. Botín, the Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red sobre Enfermedades Neurodegenerativas (CIBERNED, ISCIII), and an institutional grant from the Fundación R Areces. Human control samples were generously provided by the Biobanco del Hospital Universitario Reina Sofia (Córdoba, Spain), and we thank Dr R Sánchez Sánchez for providing samples. AD samples were generously provided by the Banco de Tejidos de la Fundación CIEN (Madrid, Spain). We thank Drs I Fernaud-Espinosa and A Kastanauskaite for the estimating the volume of PSD95-GFP+ clusters; Dr V Borrell for kindly providing GFP-expressing retroviruses; Prof F.H. Gage for generously providing the plasmids used for the production of GFP-expressing retroviruses and Prof C Lois for kindly providing the plasmids used for the production of PSD95-GFP viruses. The authors are not aware of any affiliations, memberships, funding, or financial holdings that might be perceived as affecting the objectivity of this manuscript. Authors would like to thank Elena Langa for her help with animal experiments and Nuria de la Torre for her help with writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Llorens-Martín, M., Fuster-Matanzo, A., Teixeira, C. et al. GSK-3β overexpression causes reversible alterations on postsynaptic densities and dendritic morphology of hippocampal granule neurons in vivo. Mol Psychiatry 18, 451–460 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Wnt signalling pathways as mediators of neuroprotective mechanisms: therapeutic implications in stroke
Molecular Biology Reports (2024)
-
Prolonged fixation and post-mortem delay impede the study of adult neurogenesis in mice
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Promoting Endogenous Neurogenesis as a Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
GSK-3β orchestrates the inhibitory innervation of adult-born dentate granule cells in vivo
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Progression of Alzheimer's disease parallels unusual structural plasticity of human dentate granule cells
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2022)