Abstract
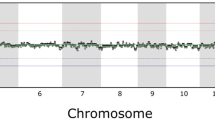
Cultured human embryonic stem (hES) cells have a known predisposition to aneuploidy of chromosomes 12, 17 and X. We studied 17 hES cell lines by array-based comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) and found that the cells accumulate other recurrent chromosomal abnormalities, including amplification at 20q11.21 and a derivative chromosome 18. These genomic changes have a variable impact at the transcriptional level.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Baker, D.E. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 207–215 (2007).
Josephson, R. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 7, 395–406 (2007).
Inzunza, J. et al. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 10, 461–466 (2004).
Maitra, A. et al. Nat. Genet. 37, 1099–1103 (2005).
Mateizel, I. et al. Hum. Reprod. 21, 503–511 (2006).
Wu, H. et al. Stem Cells 26, 1484–1489 (2008).
Scotto, L. et al. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 47, 755–765 (2008).
Guled, M. et al. Mod. Pathol. 21, 770–778 (2008).
Pfeiffer, P. et al. Mutagenesis 15, 289–302 (2000).
Lukusa, T. & Fryns, J.P. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1779, 3–16 (2008).
Herszfeld, D. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 351–357 (2006).
Camps, J. et al. Cancer Res. 68, 1284–1295 (2008).
Yin, Z. et al. Oncogene 20, 2273–2280 (2001).
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by grants from the Fund for Scientific Research Flanders (Fonds voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (FWO) Vlaanderen) and by the STEM-HD (STREP EU FP6 program). C.S. is a postdoctoral fellow at the FWO Vlaanderen. M.G. is a PhD student at the FWO Vlaanderen. A.M. is a PhD student at the Instituut voor de aanmoediging van innovatie door Wetenschap en Technologie in Vlaanderen (IWT-Vlaanderen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C. Spits designed the study, performed part of the aCGH analysis and G-bandings and wrote the manuscript. I.M. was responsible for the culture of the hES cell lines and significantly contributed to the design of the study. M.G. maintained some of the hES cells lines in culture for >200 passages and performed several of the G-bandings. A.M. performed part of the aCGH analysis. C. Staessen supervised the interpretation of the G-banding and FISH results. Y.V. carried out all FISH experiments. J.V.d.E. is head of the IVF lab at the CRM and provided embryos donated by the patients for research. I.L. is head of the cytogenetics and molecular lab at the CMG. K.S. is the supervisor of C. Spits, I.M. and A.M. and contributed to the design of the study. The manuscript was proofread by all authors.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Figures 1–10, Methods (PDF 6018 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spits, C., Mateizel, I., Geens, M. et al. Recurrent chromosomal abnormalities in human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 26, 1361–1363 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1510
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1510
This article is cited by
-
TPX2 prompts mitotic survival via the induction of BCL2L1 through YAP1 protein stabilization in human embryonic stem cells
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
TPX2 Amplification-Driven Aberrant Mitosis in Culture Adapted Human Embryonic Stem Cells with gain of 20q11.21
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2023)
-
Novel strategies for designing regenerative skin products for accelerated wound healing
3 Biotech (2022)
-
Immunological considerations and challenges for regenerative cellular therapies
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Acquired genetic changes in human pluripotent stem cells: origins and consequences
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2020)