Abstract
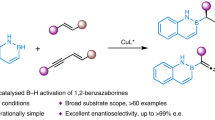
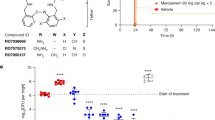
Patients taking fluoroquinolone antibiotics such as norfloxacin exhibit a low incidence of convulsions and anxiety. These side effects probably result from antagonism of the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the brain GABAA receptor complex (GRC). Modification of norfloxacin yields molecules such as compound 4 that potentiate GABA action with α2 subunit selectivity. Compound 4 is anxiolytic but does not cause sedation, and may represent a new class of ligands that have anxiolytic activity without sedative liability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chebib, M. & Johnston, G.A. J. Med. Chem. 43, 1427–1447 (2000).
Halliwell, R.F., Davey, P.G. & Lambert, J.J. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 31, 457–462 (1993).
Korpi, E.R., Grunder, G. & Luddens, H. Prog. Neurobiol. 67, 113–159 (2002).
De Sarro, A. et al. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43, 1729–1736 (1999).
McKernan, R.M. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 587–592 (2000).
Vogel, J.R., Beer, B. & Clody, D.E. Psychopharmacologia (Berlin) 21, 1–7 (1971).
Carboni, E., Wieland, S., Lan, N.C. & Gee, K.W. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 126, 173–178 (1996).
Crawley, J. & Goodwin, F.K. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 13, 167–170 (1980).
Wieland, S., Lan, N.C., Mirasedeghi, S. & Gee, K.W. Brain Res. 565, 263–268 (1991).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Institute of Mental Health grant MH60527 (K.W.G.) and the Wellcome Trust (R.F.H.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnstone, T., Hogenkamp, D., Coyne, L. et al. Modifying quinolone antibiotics yields new anxiolytics. Nat Med 10, 31–32 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm967
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm967
This article is cited by
-
New Pharmacological Agents to Aid Smoking Cessation and Tobacco Harm Reduction: What Has Been Investigated, and What Is in the Pipeline?
CNS Drugs (2016)
-
Modifications of Diflunisal and Meclofenamate Carboxyl Groups Affect Their Allosteric Effects on GABAA Receptor Ligand Binding
Neurochemical Research (2014)
-
Solvates of Two Ethyl 6-(2-(aryl)-4-oxothiazolidin-3-yl)-1-ethyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylates
Journal of Chemical Crystallography (2014)
-
Anxiogenic properties of an inverse agonist selective forα3 subunit-containing GABAAreceptors
British Journal of Pharmacology (2005)
-
Antibiotic yields anxiolytic
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2004)