Abstract
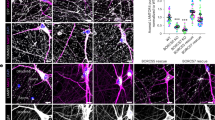
Dendrite branching has an important role in normal brain function. Here we report that overexpression of cypin, a protein that has guanine deaminase activity and is expressed in developing processes in rat hippocampal neurons, results in increased dendrite branching in primary culture. Mutant cypin proteins that lack guanine deaminase activity act in a dominant-negative manner when expressed in primary neurons. Furthermore, we knocked down cypin protein levels using a new strategy: expressing a 5′ end-mutated U1 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) to inhibit maturation of cypin mRNA. Neurons that express this mutant snRNA show little or no detectable cypin protein and fewer dendrites than normal. In addition, we found that cypin binds directly to tubulin heterodimers and promotes microtubule polymerization. Thus, our results demonstrate a new pathway by which dendrite patterning is regulated, and we also introduce a new method for decreasing endogenous protein expression in neurons.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Threadgill, R., Bobb, K. & Ghosh, A. Regulation of dendritic growth and remodeling by Rho, Rac, and Cdc42. Neuron 19, 625–634 (1997).
Ruchhoeft, M.L., Ohnuma, S., McNeill, L., Holt, C.E. & Harris, W.A. The neuronal architecture of Xenopus retinal ganglion cells is sculpted by rho-family GTPases in vivo. J. Neurosci. 19, 8454–8463 (1999).
Li, Z., Van Aelst, L. & Cline, H.T. Rho GTPases regulate distinct aspects of dendritic arbor growth in Xenopus central neurons in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 217–225 (2000).
Lee, T., Winter, C., Marticke, S.S., Lee, A. & Luo, L. Essential roles of Drosophila RhoA in the regulation of neuroblast proliferation and dendritic but not axonal morphogenesis. Neuron 25, 307–316 (2000).
Wong, W.T., Faulkner-Jones, B.E., Sanes, J.R. & Wong, R.O. Rapid dendritic remodeling in the developing retina: dependence on neurotransmission and reciprocal regulation by Rac and Rho. J. Neurosci. 20, 5024–5036 (2000).
Nakayama, A.Y., Harms, M.B. & Luo, L. Small GTPases Rac and Rho in the maintenance of dendritic spines and branches in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 20, 5329–5338 (2000).
Hernandez-Deviez, D.J., Casanova, J.E. & Wilson, J.M. Regulation of dendritic development by the ARF exchange factor ARNO. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 623–624 (2002).
Schmidt, C.J, Zubiaur, M., Valenzuela, D., Neer, E.J. & Drager, U.C. G(O), a guanine nucleotide binding protein, is expressed during neurite extension in the embryonic mouse. J. Neurosci. Res. 38, 182–187 (1994).
Volonte, C., Rukenstein, A., Loeb, D.M. & Greene, L.A. Differential inhibition of nerve growth factor responses by purine analogues: correlation with inhibition of a nerve growth factor-activated protein kinase. J. Cell. Biol. 109, 2395–2403 (1989).
Petrausch, B. et al. A purine-sensitive pathway regulates multiple genes involved in axon regeneration in goldfish retinal ganglion cells. J. Neurosci. 20, 8031–8041 (2000).
Firestein, B.L. et al., Cypin: a cytosolic regulator of PSD-95 postsynaptic targeting. Neuron 24, 659–672 (1999).
El-Husseini, A.E., Schnell, E., Chetkovich, D.M., Nicoll, R.A. & Bredt, D.S. PSD-95 involvement in maturation of excitatory synapses. Science 290, 1364–1368 (2000).
Yuan, G., Bin, J.C., McKay, D.J. & Snyder, F.F. Cloning and characterization of human guanine deaminase. Purification and partial amino acid sequence of the mouse protein. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 8175–8180 (1999).
Paletzki, R.F. Cloning and characterization of guanine deaminase from mouse and rat brain. Neuroscience 109, 15–26 (2002).
Karlin, S. & Zhu, Z.Y. Classification of mononuclear zinc metal sites in protein structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 14231–14236 (1997).
Li, W., Herman, R.K. & Shaw, J.E. Analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans axonal guidance and outgrowth gene unc-33. Genetics 132, 675–689 (1992).
Gu, Y. & Ihara, Y. Evidence that collapsin response mediator protein-2 is involved in the dynamics of microtubules. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 17917–17920 (2000).
Fukata, Y. et al. CRMP-2 binds to tubulin heterodimers to promote microtubule assembly. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 583–591 (2002).
Inagaki, N. et al. CRMP-2 induces axons in cultured hippocampal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 781–782 (2001).
Will, C.L. & Luhrmann, R. Protein functions in pre-mRNA splicing. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 320–328 (1997).
Fortes, P. et al. Inhibiting expression of specific genes in mammalian cells with 5′ end-mutated U1 small nuclear RNAs targeted to terminal exons of pre-mRNA. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 8264–8269 (2003).
Bito, H. et al. A critical role for a Rho-associated kinase, p160ROCK, in determining axon outgrowth in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuron 26, 431–441 (2000).
Ellezam, B.L. et al. Inactivation of intracellular Rho to stimulate axon growth and regeneration. Prog. Brain Res. 137, 371–380 (2002).
Vaillant, A.R. et al. Signaling mechanisms underlying reversible, activity-dependent dendrite formation. Neuron 34, 985–998 (2002).
McAllister, A.K., Katz, L.C. & Lo, D.C. Neurotrophin regulation of cortical dendritic growth requires activity. Neuron 17, 1057–1064 (1996).
Huang, E.J. & Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 677–736 (2001).
Zhang, L. & Poo, M.M. Electrical activity and development of neural circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 4 (Suppl.), 1207–1214 (2001).
Yu, X. & Malenka, R.C. β-catenin is critical for dendritic morphogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 1169–1177 (2003).
Felipo, V., Minana, M.D. & Grisolia, S. Hyperammonemia induces polymerization of brain tubulin. Neurochem. Res. 15, 945–948 (1990).
Minana, M.D., Felipo, V. & Grisolia, S. Assembly and disassembly of brain tubulin is affected by high ammonia levels. Neurochem. Res. 14, 235–238 (1989).
Wang, L.H. & Strittmatter, S.M. Brain CRMP forms heterotetramers similar to liver dihydropyrimidinase. J. Neurochem. 69, 2261–2226 (1997).
Bridge, A.J., Pebernard, S., Ducraux, A., Nicoulaz, A.L. & Iggo, R. Induction of an interferon response by RNAi vectors in mammalian cells. Nat. Genet. 34, 263–264 (2003).
Claiborne, B.J. Use of computers for quantitative, three–dimensional analysis of dendritic trees. in Computers and Computations in the Neurosciences Vol. 10 (ed. Conn, P.M.) 315–330 (Academic Press, California, 1992).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Rongo and L. Covey for insightful discussion and critical reading of our manuscript. We would also like to thank C. Barbieri for performing some preliminary experiments and A. Ghosh for constructs encoding dominant negative small GTPases. B.L.F. would like to thank M. Miller for his support. This work was supported in part by Busch Biomedical Grants (to B.L.F. and S.I.G.), New Jersey Commission on Spinal Cord Research Grant 03–004 and National Science Foundation grant IBN–0234206(to B.L.F.) and a Discovery Grant from Johnson and Johnson and National Institutes of Health grant GM57286 (to S.I.G.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akum, B., Chen, M., Gunderson, S. et al. Cypin regulates dendrite patterning in hippocampal neurons by promoting microtubule assembly. Nat Neurosci 7, 145–152 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1179
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1179
This article is cited by
-
Maternal brain reactive antibodies profile in autism spectrum disorder: an update
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
-
Maternal autoantibody profiles as biomarkers for ASD and ASD with co-occurring intellectual disability
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
Risk assessment analysis for maternal autoantibody-related autism (MAR-ASD): a subtype of autism
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Defective Mitochondrial Dynamics Underlie Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Intellectual disability: dendritic anomalies and emerging genetic perspectives
Acta Neuropathologica (2021)