Abstract
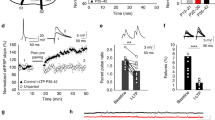
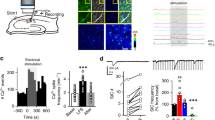
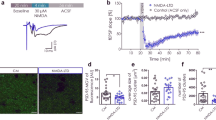
In the developing brain, many glutamate synapses have been found to transmit only NMDA receptor–mediated signaling, that is, they are AMPA-silent. This result has been taken to suggest that glutamate synapses are initially AMPA-silent when they are formed, and that AMPA signaling is acquired through activity-dependent synaptic plasticity. The present study on CA3–CA1 synapses in the hippocampus of the neonatal rat suggests that AMPA-silent synapses are created through a form of activity-dependent silencing of AMPA signaling. We found that AMPA signaling, but not NMDA signaling, could be very rapidly silenced by presynaptic electrical stimulation at frequencies commonly used to probe synaptic function (0.05–1 Hz). Although this AMPA silencing required a rise in postsynaptic Ca2+, it did not require activation of NMDA receptors, metabotropic glutamate receptors or voltage-gated calcium channels. The AMPA silencing, possibly explained by a removal of postsynaptic AMPA receptors, could subsequently be reversed by paired presynaptic and postsynaptic activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman, H.V., Bresler, T., Garner, C.C. & Ziv, N.E. Assembly of new individual excitatory synapses: time course and temporal order of synaptic molecule recruitment. Neuron 27, 57–69 (2000).
Diabira, D., Hennou, S., Chevassus-Au-Louis, N., Ben-Ari, Y. & Gozlan, H. Late embryonic expression of AMPA receptor function in the CA1 region of the intact hippocampus in vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 11, 4015–4023 (1999).
Kutsuwada, T. et al. Impairment of suckling response, trigeminal neuronal pattern formation, and hippocampal LTD in NMDA receptor epsilon 2 subunit mutant mice. Neuron 16, 333–344 (1996).
Varoqueaux, F. et al. Total arrest of spontaneous and evoked synaptic transmission but normal synaptogenesis in the absence of Munc13-mediated vesicle priming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 9037–9042 (2002).
Verhage, M. et al. Synaptic assembly of the brain in the absence of neurotransmitter secretion. Science 287, 864–869 (2000).
Groc, L., Gustafsson, B. & Hanse, E. In vivo evidence for an activity-independent maturation of AMPA/NMDA signaling in the developing hippocampus. Neuroscience 121, 65–72 (2003).
Groc, L., Gustafsson, B. & Hanse, E. Spontaneous unitary synaptic activity in CA1 pyramidal neurons during early postnatal development: constant contribution of AMPA and NMDA receptors. J. Neurosci. 22, 5552–5562 (2002).
Durand, G.M., Kovalchuk, Y. & Konnerth, A. Long-term potentiation and functional synapse induction in developing hippocampus. Nature 381, 71–75 (1996).
Isaac, J.T., Nicoll, R.A. & Malenka, R.C. Evidence for silent synapses: implications for the expression of LTP. Neuron 15, 427–434 (1995).
Hanse, E. & Gustafsson, B. Quantal variability at glutamatergic synapses in area CA1 of the rat neonatal hippocampus. J. Physiol. 531, 467–480 (2001).
Liao, D., Hessler, N.A. & Malinow, R. Activation of postsynaptically silent synapses during pairing-induced LTP in CA1 region of hippocampal slice. Nature 375, 400–404 (1995).
Hsia, A.Y., Malenka, R.C. & Nicoll, R.A. Development of excitatory circuitry in the hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 79, 2013–2024 (1998).
Liao, D. & Malinow, R. Deficiency in induction but not expression of LTP in hippocampal slices from young rats. Learn. Mem. 3, 138–149 (1996).
Atwood, H.L. & Wojtowicz, J.M. Silent synapses in neural plasticity: current evidence. Learn. Mem. 6, 542–571 (1999).
Malenka, R.C. & Nicoll, R.A. Silent synapses speak up. Neuron 19, 473–476 (1997).
Cohen-Cory, S. The developing synapse: construction and modulation of synaptic structures and circuits. Science 298, 770–776 (2002).
Zhu, J.J. & Malinow, R. Acute versus chronic NMDA receptor blockade and synaptic AMPA receptor delivery. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 513–514 (2002).
Luthi, A., Schwyzer, L., Mateos, J.M., Gahwiler, B.H. & McKinney, R.A. NMDA receptor activation limits the number of synaptic connections during hippocampal development. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 1102–1107 (2001).
Bayer, S.A. Development of the hippocampal region in the rat. II. Morphogenesis during embryonic and early postnatal life. J. Comp. Neurol. 190, 115–134 (1980).
Steward, O. & Falk, P.M. Selective localization of polyribosomes beneath developing synapses: a quantitative analysis of the relationships between polyribosomes and developing synapses in the hippocampus and dentate gyrus. J. Comp. Neurol. 314, 545–557 (1991).
Fiala, J.C., Feinberg, M., Popov, V. & Harris, K.M. Synaptogenesis via dendritic filopodia in developing hippocampal area CA1. J. Neurosci. 18, 8900–8911 (1998).
Kullmann, D.M. Excitatory synapses. Neither too loud nor too quiet. Nature 399, 111–112 (1999).
Choi, S., Klingauf, J. & Tsien, R.W. Postfusional regulation of cleft glutamate concentration during LTP at 'silent synapses'. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 330–336 (2000).
Renger, J.J., Egles, C. & Liu, G. A developmental switch in neurotransmitter flux enhances synaptic efficacy by affecting AMPA receptor activation. Neuron 29, 469–484 (2001).
Aravanis, A.M., Pyle, J.L. & Tsien, R.W. Single synaptic vesicles fusing transiently and successively without loss of identity. Nature 423, 643–647 (2003).
Gandhi, S.P. & Stevens, C.F. Three modes of synaptic vesicular recycling revealed by single-vesicle imaging. Nature 423, 607–613 (2003).
Malinow, R. & Malenka, R.C. AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 25, 103–126 (2002).
Lu, H.C. et al. Adenylyl cyclase I regulates AMPA receptor trafficking during mouse cortical 'barrel' map development. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 939–947 (2003).
Kullmann, D.M. Amplitude fluctuations of dual-component EPSCs in hippocampal pyramidal cells: implications for long-term potentiation. Neuron 12, 1111–1120 (1994).
Montgomery, J.M. & Madison, D.V. State-dependent heterogeneity in synaptic depression between pyramidal cell pairs. Neuron 33, 765–777 (2002).
Petralia, R.S. et al. Selective acquisition of AMPA receptors over postnatal development suggests a molecular basis for silent synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 31–36 (1999).
Nusser, Z. et al. Cell type and pathway dependence of synaptic AMPA receptor number and variability in the hippocampus. Neuron 21, 545–559 (1998).
Wu, G., Malinow, R. & Cline, H.T. Maturation of a central glutamatergic synapse. Science 274, 972–976 (1996).
Rumpel, S., Hatt, H. & Gottmann, K. Silent synapses in the developing rat visual cortex: evidence for postsynaptic expression of synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 18, 8863–8874 (1998).
Gomperts, S.N., Rao, A., Craig, A.M., Malenka, R.C. & Nicoll, R.A. Postsynaptically silent synapses in single neuron cultures. Neuron 21, 1443–1451 (1998).
Li, P. & Zhuo, M. Silent glutamatergic synapses and nociception in mammalian spinal cord. Nature 393, 695–698 (1998).
Isaac, J.T., Crair, M.C., Nicoll, R.A. & Malenka, R.C. Silent synapses during development of thalamocortical inputs. Neuron 18, 269–280 (1997).
Montgomery, J.M., Pavlidis, P. & Madison, D.V. Pair recordings reveal all-silent synaptic connections and the postsynaptic expression of long-term potentiation. Neuron 29, 691–701 (2001).
Cossart, R. et al. Quantal release of glutamate generates pure kainate and mixed AMPA/kainate EPSCs in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 35, 147–159 (2002).
Yin, H.Z., Sensi, S.L., Carriedo, S.G. & Weiss, J.H. Dendritic localization of Ca2+-permeable AMPA/kainate channels in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 409, 250–260 (1999).
Kumar, S.S., Bacci, A., Kharazia, V. & Huguenard, J.R. A developmental switch of AMPA receptor subunits in neocortical pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 22, 3005–3015 (2002).
Poncer, J.C. & Malinow, R. Postsynaptic conversion of silent synapses during LTP affects synaptic gain and transmission dynamics. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 989–996 (2001).
Tardin, C., Cognet, L., Bats, C., Lounis, B. & Choquet, D. Direct imaging of lateral movements of AMPA receptors inside synapses. Embo J. 22, 4656–4665 (2003).
Choquet, D. & Triller, A. The role of receptor diffusion in the organization of the postsynaptic membrane. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 251–265 (2003).
Zhou, Q., Xiao, M. & Nicoll, R.A. Contribution of cytoskeleton to the internalization of AMPA receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 1261–1266 (2001).
Blanpied, T.A., Scott, D.B. & Ehlers, M.D. Dynamics and regulation of clathrin coats at specialized endocytic zones of dendrites and spines. Neuron 36, 435–449 (2002).
Bredt, D.S. & Nicoll, R.A. AMPA receptor trafficking at excitatory synapses. Neuron 40, 361–379 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Swedish Medical Research Council (projects 01580, 12600 and 14842), Göteborgs Läkaresällskap, Åke Wibergs Stiftelse, Svenska Läkaresällskapet and Hjärnfonden. We thank J. Strandberg for participating in initial experiments and L. Groc for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, MY., Wasling, P., Hanse, E. et al. Creation of AMPA-silent synapses in the neonatal hippocampus. Nat Neurosci 7, 236–243 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1196
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1196
This article is cited by
-
A critical period for learning and plastic changes at hippocampal CA1 synapses
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Segregation of glutamatergic and cholinergic transmission at the mixed motoneuron Renshaw cell synapse
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Cocaine-Induced Synaptic Alterations in Thalamus to Nucleus Accumbens Projection
Neuropsychopharmacology (2016)
-
AMPA-silent synapses in brain development and pathology
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2013)
-
Development of synaptic connectivity onto interneurons in stratum radiatum in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus
BMC Neuroscience (2012)