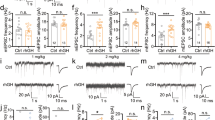
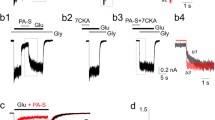
Abstract
Steroids exert long-term modulatory effects on numerous physiological functions by acting at intracellular/nuclear receptors influencing gene transcription. Steroids and neurosteroids can also rapidly modulate membrane excitability and synaptic transmission by interacting with ion channels, that is, ionotropic neurotransmitter receptors or voltage-dependent Ca2+ or K+ channels. More recently, the cloning of a plasma membrane-located G protein-coupled receptor for progestins, in various species has suggested that steroids/neurosteroids could also influence second-messenger pathways by directly interacting with specific membrane receptors. Here we review the experimental evidence implicating steroids/neurosteroids in the modulation of synaptic transmission and the evidence for a role of endogenously produced neurosteroids in such modulatory effects. We present some of our recent results concerning inhibitory synaptic transmission in lamina II of the spinal cord and show that endogenous 5α-reduced neurosteroids are produced locally in lamina II and modulate synaptic γ-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) receptor function during development, as well as during inflammatory pain. The production of 5α-reduced neurosteroids is controlled by the endogenous activation of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR), which initiates the first step of neurosteroidogenesis by stimulating the translocation, of cholesterol across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Tonic neurosteroidogenesis observed in immature animals was decreased during postnatal, development, resulting in an acceleration of GABAA receptor-mediated miniature inhibitory postsynaptic current (mIPSC) kinetics observed in the adult. Stimulation of the PBR resulted in a prolongation of GABA ergic mIPSCs at all ages and was observed during inflammatory pain. Neurosteroidogenesis might play an, important role in the control of nociception at least at the spinal cord level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdrachmanova G., Chodounska H., and Vyklicky L. Jr. (2001) Effects of steroids on NMDA receptors and excitatory synaptic transmission in neonatal motoneurons in rat spinal cord slices. Eur. J. Neurosci. 14, 495–502.
Baulieu E. E. (1997) Neurosteroids: of the nervous system, by the nervous system, for the nervous system. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 52, 1–32.
Baulieu E. E. (1998) Neurosteroids: a novel function of the brain. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 23, 963–987.
Belelli, D. and Herd M. B. (2003) The contraceptive agent Provera enhances GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibitory neurotransmission in the rat hippocampus: evidence for endogenous, neurosteroids. J. Neurosci. 23, 10013–10020.
Belelli D., Casula A., Ling A., and Lambert J. J. (2002) The influence of subunit composition on the interaction of neurosteroids with GABA(A) receptors. Neuropharmacology 43, 651–661.
Bergeron R., de Montigny C., and Debonnel G. (1996) Potentiation of neuronal NMDA response induced by dehydroepiandrosterone and its suppression by progesterone: effects mediated via sigma receptors. J. Neurosci. 16, 1193–1202.
Besson J. M. and Chaouch A. (1987) Peripheral and spinal mechanisms of nociception. Physiol. Rev. 67, 67–186.
Bixo M., Andersson A., Winblad, B., Purdy R. H., and Backstrom T. (1997) Progesterone, 5alpha-pregnane-3,20-dione and 3alpha-hydroxy-5alpha-pregnane-20-one in specific regions of the human female brain in different endocrine states. Brain Res. 764, 173–178.
Bohlhalter S., Weinmann O., Mohler H., and Fritschy J. M. (1996) Laminar compartmentalization of GABAA-receptor subtypes in the spinal cord: an immunohistochemical study. J. Neurosci. 16, 283–297.
Brussaard A. B. and Koksma J. J. (2003) Conditional regulation of neurosteroid sensitivity of GABAA receptors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1007, 29–36.
Caraiscos V. B., Elliott E. M., You-Ten K. E., Cheng V. Y., Belelli D., Newell J. G., et al. (2004) Tonic inhibition in mouse hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons is mediated by alpha5 subunit-containing gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 3662–3667.
Ceccon M., Rumbaugh G., and Vicini S. (2001) Distinct effect of pregnenolone sulfate on NMDA receptor subtypes. Neuropharmacology 40, 491–500.
Chizh B. A. and Illes P. (2001) P2X receptors and nociception. Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 553–568.
Coirini H., Gouezou M., Liere P., Delespierre B., Pianos A., Eychenne B., et al. (2002) 3 Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase expression in rat spinal cord. Neuroscience 113, 883–891.
Collo G., North R. A., Kawashima, E., Merlo-Pich E., Neidhart S., Surprenant A., and Buell G. (1996) Cloning of P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of anextended family of ATP-gated ion channels. J. Neurosci. 16, 2495–2507.
Compagnone N. A. and Mellon S. H. (2000) Neurosteroids: biosynthesis and function of these novel neuromodulators. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 21, 1–56.
Concas A., Follesa P., Barbaccia M. L., Purdy R. H., and Biggio G. (1999) Physiological modulation of GABA(A) receptor plasticity by progesterone metabolites. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 375, 225–235.
Costa E., Auta J., Guidotti A., Korneyev A., and Romeo E. (1994) The pharmacology of neurosteroidogenesis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 49, 385–389.
Covey D. F., Evers A. S., Mennerick S., Zorumski C. F., and Purdy R. H. (2001) Recent developments in structure-activity relationships for steroid modulators of GABA(A) receptors, Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev 37, 91–97.
DalBo S., Nardi G. M., Ferrara P., Ribeiro-do-Valle R. M., and Farges R. C. (2004) Antinociceptive effects of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Pharmacology 70, 188–194.
Dayanithi G. and Tapia-Arancibia L. (1996) Rise in intracellular calcium via a nongenomic effect of allopregnanolone in fetal rat hypothalamic neurons. J. Neurosci. 16, 130–136.
Debonnel G., Bergeron R., and de Montigny C. (1996) Potentiation by dehydroepiandrosterone of the neuronal response to N-methyl-D-aspartate in the CA3 region of the rat dorsal hippocampus: an effect mediated via sigma receptors. J. Endocrinol. 150 (Suppl.), S33-S42.
De Roo M., Rodeau J. L., and Schlichter R. (2003) Dehydroepiandrosterone potentiates native ionotropic ATP receptors containing the P2X2 subunit in rat sensory neurones. J. Physiol. 552 59–71.
Evrard H. C. and Balthazart J. (2002) Localization of oestrogen receptors in the sensory and motor areas of the spinal cord in Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica). J. Neuroendocrinol. 14, 894–903.
Evrard H. C., and Balthazart J. (2003) Aromatase, (estrogen synthase) activity in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord: functional implications. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1007, 263–271.
Evrard H. C. and Balthazart J. (2004) Rapid regulation of pain by estrogens synthesized in spinal dorsal horn neurons. J. Neurosci. 24, 7225–7229.
Evrard H., Baillien M., Foidart A., Absil P., Harada N., and Balthazart J. (2000) Localization and controls of aromatase in the quail spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 423, 552–564.
Evrard H. C., Willems E., Harada N., and Balthazart J. (2003) Specific innervation of aromatase neurons by substance P fibers in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord in quail. J. Comp. Neurol. 465, 309–318.
Feigenspan A., Wassle H., and Bormann J. (1993) Pharmacology of GABA receptor Cl-channels in rat retinal bipolar cells. Nature 361, 159–162.
ffrench-Mullen J. M. (1995) Cortisol inhibition of calcium currents in guinea pig hippocampal CA1 neurons via G-protein-coupled activation of protein kinase C. J. Neurosci. 15, 903–911.
ffrench-Mullen J. M., Danks P., and Spence K. T. (1994) Neurosteroids modulate calcium currents in hippocampal CA1 neurons via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein-coupled mechanism. J. Neurosci. 14, 1963–1977.
Foy M. R., Xu J., Xie X., Brinton R. D., Thompson R. F., and Berger T. W. (1999) 17 beta-estradiol enhances NMDA receptor-mediated EPSPs and long-term potentiation. J. Neurophysiol 81, 925–929.
Fugger H. N., Kumar A., Lubahn D. B., Korach K. S., and Foster T. C. (2001) Examination of estradiol effects on the rapid estradiol mediated in crease in hippocampal synaptic transmission in estrogen receptor alpha knockout mice. Neurosci. Lett. 309, 207–209.
Furukawa A., Miyatake A., Ohnishi T., and Ichikawa Y. (1998) Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) transcripts constitutively expressed in the adult rat central nervous system: colocalization, of StAR, cytochrome P-450SCC(CYPXIA1), and 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 71, 2231–2238.
Gu Q. and Moss R. L. (1996) 17 beta-Estradiol, potentiates kainate-induced currents via activation of the cAMP cascade. J. Neurosci. 16, 3620–3629.
Gu Q. and Moss, R. L. (1998) Novel mechanism for nongenomic action of 17 beta-oestradiol on kainate-induced currents in isolated rat CA1 hippocampal neurones. J. Physiol. 506(Pt. 3), 745–754.
Gu Q., Korach K. S., and Moss R. L. (1999) Rapid action of 17beta-estradiol on kainate-induced currents in hippocampal neurons lacking intracellular estrogen receptors. Endocrinology 140, 660–666.
Harney S. C., Frenguelli B. G., and Lambert J. J. (2003) Phosphorylation influences neurosteroid modulation of synaptic GABAA receptors in rat CA1 and dentate gyrus neurones. Neuropharmacology 45, 873–883.
Harrison N. L., Majewska M. D., Harrington J. W., and Barker J. L. (1987) Structure-activity relationships for steroid interaction with the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor complex. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 241, 346–353.
Hauet T., Liu J., Li H., Gazouli M., Culty M., and Papadopoulos V. (2002) PBR, StAR, and PKA: partners in cholesterol transport, in steroidogenic cells. Endocr. Res. 28, 395–401.
Horak M., Vlcek K., Petrovic M., Chodounska H., and Vyklicky L. Jr. (2004) Molecular mechanism of pregnenolone sulfate actionat NR1/NR2B receptors. J. Neurosci. 24, 10318–10325.
Huettner J. E. (2003) Kainate receptors and synaptic transmission. Prog. Neurobiol. 70, 387–407.
Hugel S. and Schlichter R. (2000) Presynaptic P2X receptors facilitate inhibitory GABA ergic transmission between cultured rat spinal cord dorsal horn neurons. J. Neurosci. 20, 2121–2130.
Jo Y. H. and Schlichter R. (1999) Synaptic corelease of ATP and GABA in cultured spinal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 241–245.
Kaneda M., Farrant M., and Cull-Candy S. G. (1995) Whole-cell and single-channel currents activated by GABA and glycine in granule cells of the rat cerebellum. J. Physiol. 485(Pt. 2), 419–435.
Kavaliers M. and Wiebe J. P. (1987) Analgesic effects of the progesterone, metabolite, 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one, and possible modes of action in mice. Brain Res. 415, 393–398.
Kavaliers M., Perrot-Sinal T. S., Desjardins D. C., Cross-Mellor S. K., and Wiebe J. P. (2000) Antinociceptive effects of the neuroactive steroid, 3alpha-hydroxy-5alpha-pregnan-20-one and progesterone in the land snail, Cepaea nemoralis. Neuroscience 95, 807–812.
Keller A. F., Breton J. D., Schlichter R., and Poisbeau P. (2004) Production of 5alpha-reduced neurosteroids is developmentally regulated and shapes GABA(A) miniature IPSCs in lamina II of the spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 24, 907–915.
Keller A. F., Coull J. A., Chery N., Poisbeau P., and De Koninck Y. (2001) Region-specific developmental specialization of GABA-glycine cosynapses in laminas I–II of the rat spinal dorsal horn. J. Neurosci. 21, 7871–7880.
Kelly M. J., Lagrange A. H., Wagner E. J., and Ronnekleiv O. K. (1999) Rapid effects of estrogen to modulate G protein-coupled receptors via activation of protein kinase A and protein kinase C pathways. Steroids 64, 64–75.
Kelly M. J., Loose M. D., and Ronnekleiv O. K. (1992) Estrogen suppresses mu-opioid- and GABAB-mediated hyperpolarization of hypothalamic arcuate neurons. J. Neurosci. 12, 2745–2750.
Kelly M. J., Qiu J., and Ronnekleiv O. K. (2003) Estrogen modulation of G-protein-coupled receptor activation of potassium channels in the central nervous system. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1007, 6–16.
Kibaly C., Patte-Mensah C., and Mensah-Nyagan A. G. (2005) Molecular and neurochemical evidence for the biosynthesis of dehydroepiandrosterone in the adult rat spinal cord. J. Neurochem. 93, 1220–1230.
King S. R., Manna P. R., Ishii T., Syapin P. J., Ginsberg S. D., Wilson K., et al. (2002) An essential component in steroid synthesis, the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, is expressed in discrete regions of the brain. J. Neurosci. 22, 10613–10620.
Koksma J. J., van Kesteren R. E., Rosahl T. W., Zwart R., Smit A. B., Luddens H., and Brussard A. B. (2003) Oxytocin regulates neurosteroid modulation of GABA(A) receptors in supraoptic nucleus around parturition. J. Neurosci. 23, 788–797.
Lambert J. J., Belelli D., Harney S. C., Peters J. A., and Frenguelli B. G. (2001) Modulation of native and recombinant GABA(A) receptors by endogenous and synthetic neuroactive steroids. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 37, 68–80.
Lambert J. J., Belelli D., Peden D. R., Vardy A. W., and Peters J. A. (2003) Neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors. Prog. Neurobiol. 71, 67–80.
Liu D. and Dillon J. S. (2004) Dehydroepiandrosterone stimulates nitric oxide release in vascular endothelial cells: evidence for a cell surface receptor. Steroids 69, 279–289.
Lovelace M., Watson T. G., and Stephenson G. L. (2003) Steroid 21-hydroxylase expression in cultured astrocytes. Brain Res. Bull. 61, 609–615.
Ma W., Saunders P. A., Somogyi R., Poulter M. O., and Barker J. L. (1993) Omogeny of GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in rat spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. J. Comp. Neurol. 338, 337–359.
Malayev A., Gibbs T. T., and Farb D. H. (2002) Inhibition of the NMDA response by pregnenolone sulphate reveals subtype selective modulation of NMDA receptors by sulphated steroids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 135, 901–909.
Maurice T., Urani A., Phan V. L., and Romieu P. (2001) The interaction between neuroactive steroids and the sigmal receptor function: behavioral consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 37, 116–132.
McEwen B. S. (1991) Non-genomic and genomic effects of steroids on neural activity. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 12, 141–147.
Melcangi R. C., Cavarretta I., Magnaghi V., Ballabio M., Martini L., and Motta M. (1998) Crosstalk between normal and tumoral brain cells. Effect on sex steroid metabolism. Endocrine 8, 65–71.
Melcangi R. C., Celotti F., and Martini L. (1994) Neurons influence the metabolism of testosterone in cultured astrocytes via humoral signals. Endocrine 2, 709–713.
Mensah-Nyagan A. G., Do-Rego J. L., Beaujean D., Luu-The V., Pelletier G., and Vaudry H. (1999) Neurosteroids expression of steroidogenic enzymes and regulation of steroid biosynthesis in the central nervous system. Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 63–81.
Mermelstein P. G., Becker J. B., and Surmeier D. J. (1996) Estradiol reduces calcium currents in rat neostriatal neurons via a membrane receptor. J. Neurosci. 16, 595–604.
Meyer J. H., Lee S., Wittenberg G. F., Randall R. D., and Gruol D. L. (1999) Neurosteroid regulation of inhibitory synaptic transmission in the rat hippocampus in vitro. Neuroscience 90, 1177–1183.
Mihalek R. M., Banerjee P. K., Korpi E. R., Quinlan J. J., Firestone L. L., Mi Z. P., et al. (1999) Attenuated sensitivity to neuroactive steroids in gamma-aminobutyrate type A receptor delta subunit knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 12905–12910.
Millan M. J. (1999) The induction of pain: an integrative review. Prog. Neurobiol. 57, 1–164.
Millan M. J. (2002) Descending control of pain. Prog. Neurobiol. 66, 355–474.
Moss R. L., Gu Q., and Wong M. (1997) Estrogen: nontranscriptional signaling pathway. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 52, 33–68.
Mtchedlishvili Z. and Kapur J. (2003) A presynaptic action of the neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate on GABA-ergic synaptic transmission. Mol. Pharmacol. 64, 857–864.
Nabekura J., Katsurabayashi S., Kakazu Y., Shibata S., Matsubara A., Jinno S., et al. (2004) Development switch from GABA to glycine release in single central synaptic terminals. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 17–23.
Ozawa S., Kamiya H., and Tsuzuki K. (1998) Glutamate receptors in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 54, 581–618.
Park-Chung M., Malayev A., Purdy R. H., Gibbs T. T., and Farb D. H. (1999) Sulfated and unsulfated steroids modultate gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor function through distinct sites. Brain Res. 830, 72–87.
Park-Chung M., Wu F. S., Purdy R. H., Malayev A. A., Gibbs T. T., and Farb D. H. (1997) Distinct sites for inverse modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by sulfated steroids. Mol. Pharmacol. 52, 1113–1123.
Patte-Mensah C., Penning T. M., and Mensah-Nyagan A. G. (2004) Anatomical and cellular localization of neuroactive 5 alpha/3 alpha-reduced steroid-synthesizing enzymes in the spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 477, 286–299.
Patte-Mensah C., Kappes V., Freund-Mercier M. J., Tsutsui K., and Mensah-Nyagan A. G. (2003) Cellular distribution and bioactivity of the key steroidogenic enzyme, cytochrome P450side chain cleavage, in sensory neural pathways. J. Neurochem. 86, 1233–1246.
Pinna G., Uzunova V., Matsumoto K., Puia G., Mienville J. M., Costa E., and Guidotti A. (2000) Brain allopregnanolone regulates the potency of the GABA(A) receptor agonist muscimol. Neuropharmacology 39, 440–448.
Poisbeau P., Feltz P., and Schlichter R. (1997) Modulation of GABAA receptor-mediated IPSCs by neuroactive steroids in a rat hypothalamo-hypophyseal coculture model. J. Physiol. 500 (Pt. 2), 475–485.
Puia G., Mienville J. M., Matsumoto K., Takahat H., Watanabe H., Costa E., and Guidotti A. (2003) On the putative physiological role of allopregnanoloneon GABA(A) receptor function. Neuropharmacology 44, 49–55.
Qiu J., Bosch M. A., Tobias S. C., Grandy D. K., Scanlan T. S., Ronnekleiv O. K., and Kelly M. J. (2003) Rapid signaling of estrogen in hypothalamic neurons involves a novel G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor that activates protein kinase C. J. Neurosci. 23, 9529–9540.
Reddy D. S. and Rogawski M. A. (2002) Stress-induced deoxycorticosterone-derived neurosteroids modulate GABA(A) receptor function and seizure susceptibility. J. Neurosci. 22, 3795–3805.
Reddy D. S., Castaneda D. C., O'Malley B. W., and Rogawski M. A. (2004) Anticonvulsant activity of progesterone and neurosteroids in progesterone receptor knockout mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 310, 230–239.
Reddy D. S., O'Malley B. W., and Rogawski M. A. (2005) Anxiolytic activity of progesterone in progesterone receptor knockout mice. Neuropharmacology 48, 14–24.
Reith C. A. and Sillar K. T. (1997) Pre and postsynaptic modulation of spinal GABAergic neurotransmission by the neurosteroid, 5 beta-pregnan-3 alpha-ol-20-one. Brain Res. 770, 202–212.
Robel P. and Baulieu E. E. (1994) Neurosteroids: biosynthesis and function. Trends Endocr. Metab 5, 1–8.
Rupprecht R. and Holsboer F. (1999a) Neuroactive steroids: mechanisms of action and neuropsychophar-macological perspectives. Trends Neurosci. 22, 410–416.
Rupprecht R. and Holsboer F. (1999b) Neuropsy-chopharmacological properties of neuroactive steroids. Steroids 64, 83–91.
Rupprecht R. Reul J. M., Trapp T., van Steensel B., Wetzel C., Damm K., et al. (1993) Progesterone receptor-mediated effects of neuroactive steroids. Neuron 11, 523–530.
Saleh T. M., Connell B. J., McQuaid T., and Cribb A. E. (2003) Estrogen-induced neurochemical and electro-physiological changes in the parabrachial nucleus of the male rat. Brain Res. 990, 58–65.
Sandkuhler J. (1996) The organization and function of endogenous antinociceptive systems. Prog. Neurobiol. 50, 49–81.
Sanna E., Talani G., Busonero F., Pisu M. G., Purdy R. H., Serra M., and Biggio G. (2004) Brain steroidogenesis mediates ethanol modulation of GABAA receptor activity in rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 24, 6521–6530.
Schlichter R., Rybalchenko V., Poisbeau P., Verleye M., and Gillardin J. (2000) Modulation of GABAergic synaptic transmission by the non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic etifoxine. Neuropharmacology 39, 1523–1535.
Semyanov A., Walker M. C., Kullmann D. M., and Silver R. A. (2004) Tonically active GABAA receptors: modulating gain and maintaining the tone. Trends Neurosci 27, 262–269.
Shen W., Mennerick S., Covey D. F., and Zorumski C. F. (2000) Pregnenolone sulfate modulates inhibitory synaptic transmission by enhancing GABA(A) receptor desensitization. J. Neurosci. 20, 3571–3579.
Shu H. J., Eisenman N., Jinadasa D., Covey D. F., Zorumski C. F., and Mennerick S. (2004) Slow actions of neuroactive steroids at GABAA receptors. J. Neurosci. 24, 6667–6675.
Sierra A. (2004) Neurosteroids: the StAR protein in the brain. J. Neuroendocrinol. 16, 787–793.
Spivak V., Lin A., Beebe P., Stoll L., and Gentile L. (2004) Identification of a neurosteroid binding site contained within the GluR2-S1S2 domain. Lipids 39, 811–819.
Steffensen S. C. (1995) Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate suppresses hippocampal recurrent inhibition and synchronizes neuronal activity to theta rhythm. Hippocampus 5, 320–328.
Stoffel-Wagner B. (2003) Neurosteroid biosynthesis in the human brain and its clinical implications. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1007, 64–78.
Wang W., Wu D. C., Chen Y. H., He W., and Yu L. C. (2002) Anti-nociceptive effects of diazepam binding inhibitor in the central nervous system of rats. Brain Res. 956, 393–397.
Womble M. D., Andrew J. A., and Crook J. J. (2002) 17beta-Estradiol reduces excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) amplitude in rat basolateral amygdala neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 331, 83–86.
Wong M. and Moss R. L. (1992) Long-term and short-term electrophysiological effects of estrogen on the synaptic properties of hippocampal CA1 neurons. J. Neurosci. 12, 3217–3225.
Wu F. S., Gibbs T. T., and Farb D. H. (1991) Pregnenolone sulfate: a positive allosteric modulator at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 40, 333–336.
Yaksh T. L., Hua X. Y., Kalcheva I., Nozaki-Taguchi N., and Marsala M. (1999) The spinal biology in humans and animals of pain states generated by persistent small afferent input. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96, 7680–7686.
Zhu Y., Bond J., and Thomas P. (2003a) Identification, classification, and partial characterization of genes in humans and other vertebrates homologous to a fish membrane progestin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 2237–2242.
Zhu Y., Rice C. D., Pang Y., Pace M., and Thomas P. (2003b) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a membrane progestin receptor and evidence it is an intermediary in meiotic maturation of fish oocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 2231–2236.
Zwain I. H. and Yen S. S. (1999a) Dehy droepiandrosterone: biosynthesis and metabolism in the brain. Endocrinology 140, 880–887.
Zwain I. H. and Yen S. S. (1999b) Neurosteroidogenesis in astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neurons of cerebral cortex of rat brain. Endocrinology 140, 3843–3852.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlichter, R., Keller, A.F., De Roo, M. et al. Fast nongenomic effects of steroids on synaptic transmission and role of endogenous neurosteroids in spinal pain pathways. J Mol Neurosci 28, 33–51 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:28:1:33
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:28:1:33